0 引言
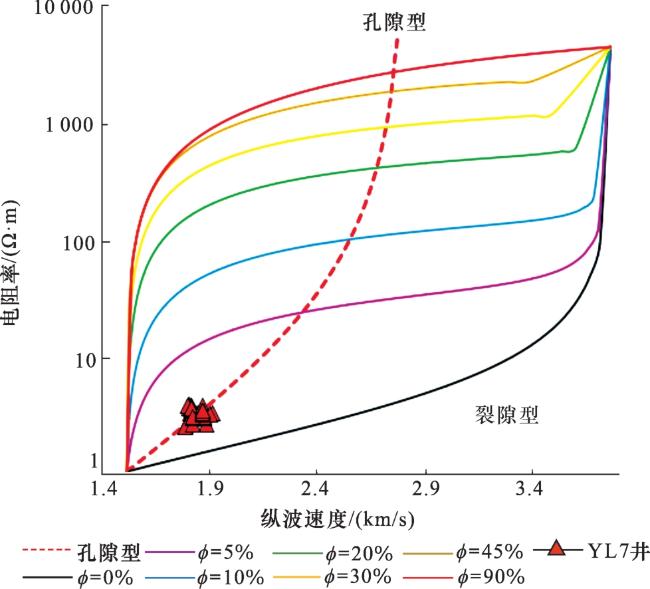
1 水合物赋存状态交会图版法
1.1 孔隙型水合物图版识别法
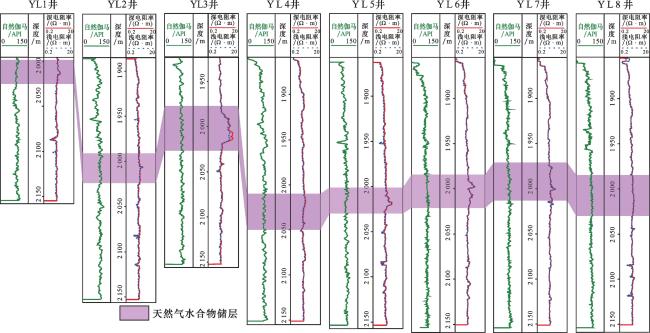
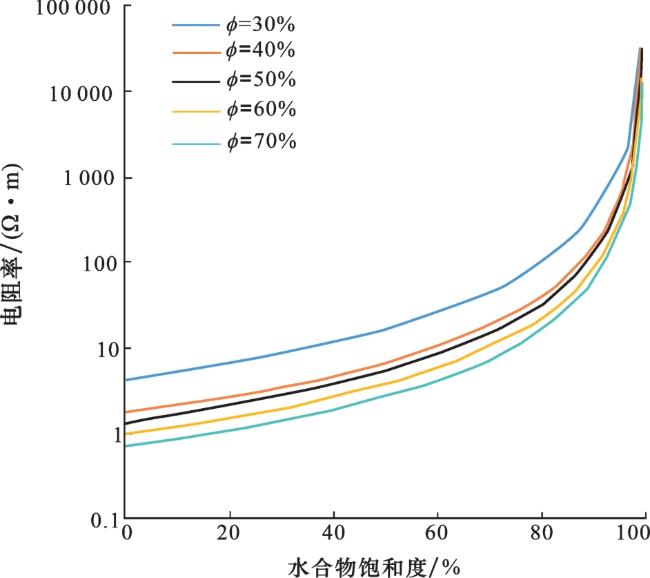
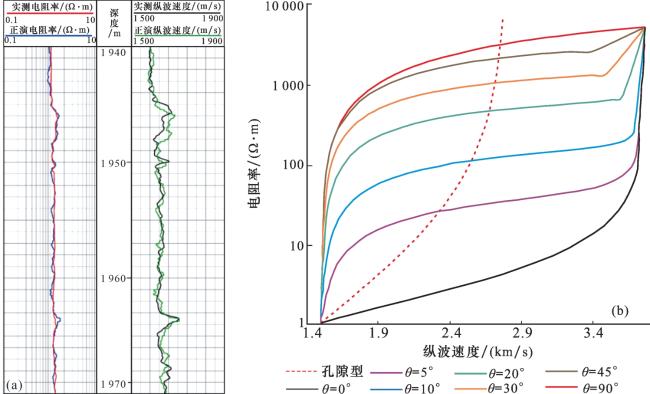
1.1.1 孔隙型水合物层电阻率正演
图2 QDN盆地YL靶区深水浅层取样的松散沉积物(a)块状泥砂样品;(b)糊状泥砂样品 Fig.2 Loose sediment samples collected from the shallow waters of the YL target area in the QDN Basin |
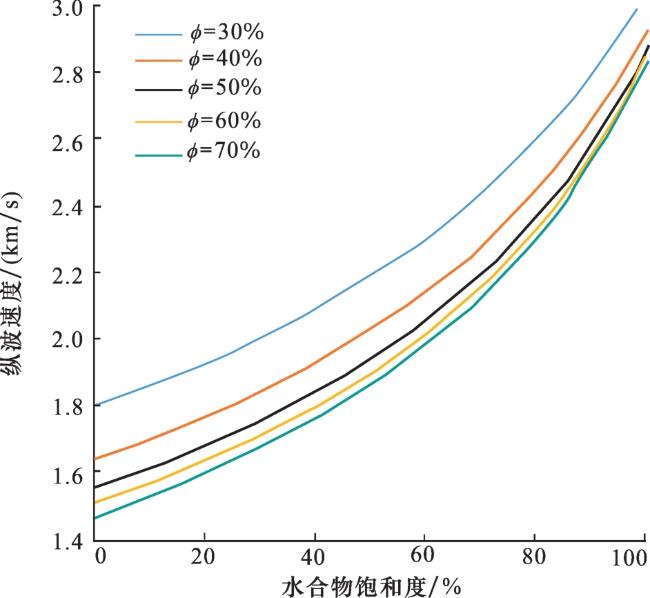
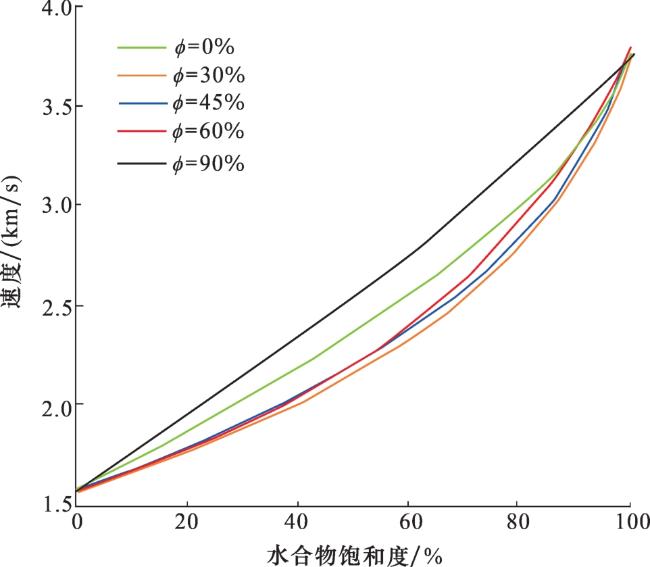
1.1.2 孔隙型水合物层声波正演
表1 不同矿物组分及水合物和海水的弹性模量、密度Table 1 Elastic moduli and densities of different mineral components, hydrates, and seawater |
| 矿物组分 | 平均含量 /% | 体积模量 /GPa | 剪切模量 /GPa | 密度 /(g/cm³) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 石英 | 53.69 | 38.0 | 44.1 | 2.66 |
| 钠长石 | 4.99 | 75.6 | 25.6 | 2.63 |
| 伊利石 | 11.42 | 60.2 | 25.4 | 2.70 |
| 绿泥石 | 10.90 | 83.9 | 46.8 | 2.60 |
| 方解石 | 10.31 | 74.8 | 32.0 | 2.71 |
| 白云石 | 6.31 | 76.4 | 49.7 | 4.16 |
| 角闪石 | 2.38 | 87.0 | 43.0 | 3.10 |
| 水合物 | / | 8.4 | 3.54 | 0.924 |
| 海水 | / | 2.3 | 0 | 1.05 |
|
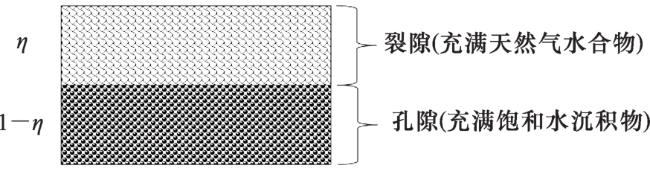
1.2 裂隙型水合物的图版识别法
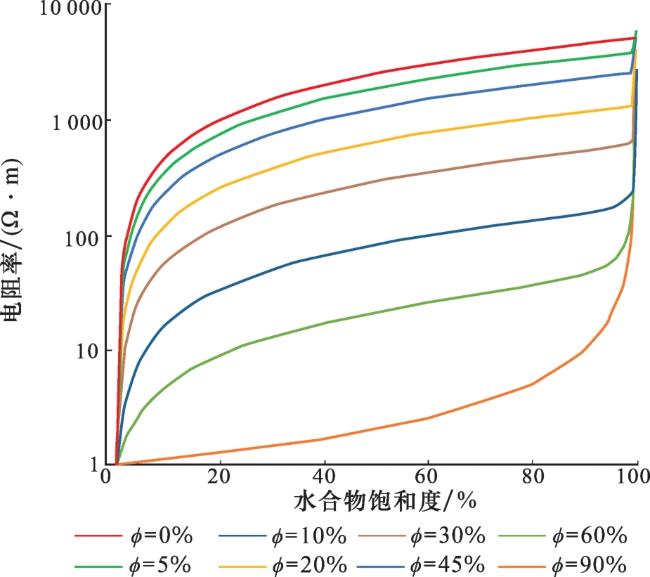
1.2.1 裂隙型水合物层电阻率模拟
1.2.2 裂隙水合物层声波模拟
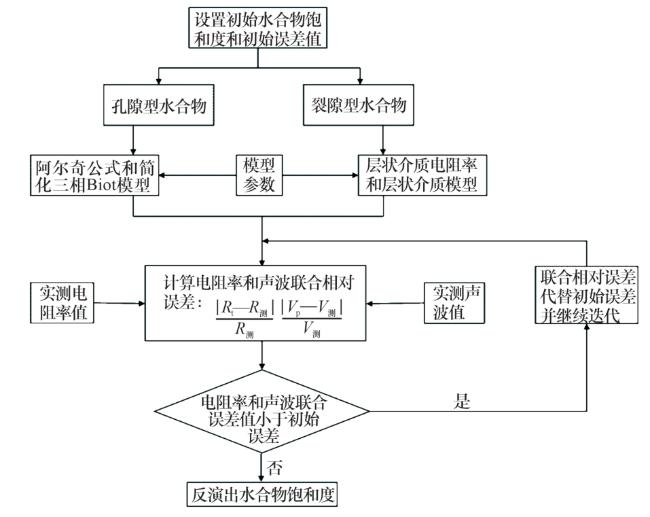
2 基于声电联合反演的饱和度计算
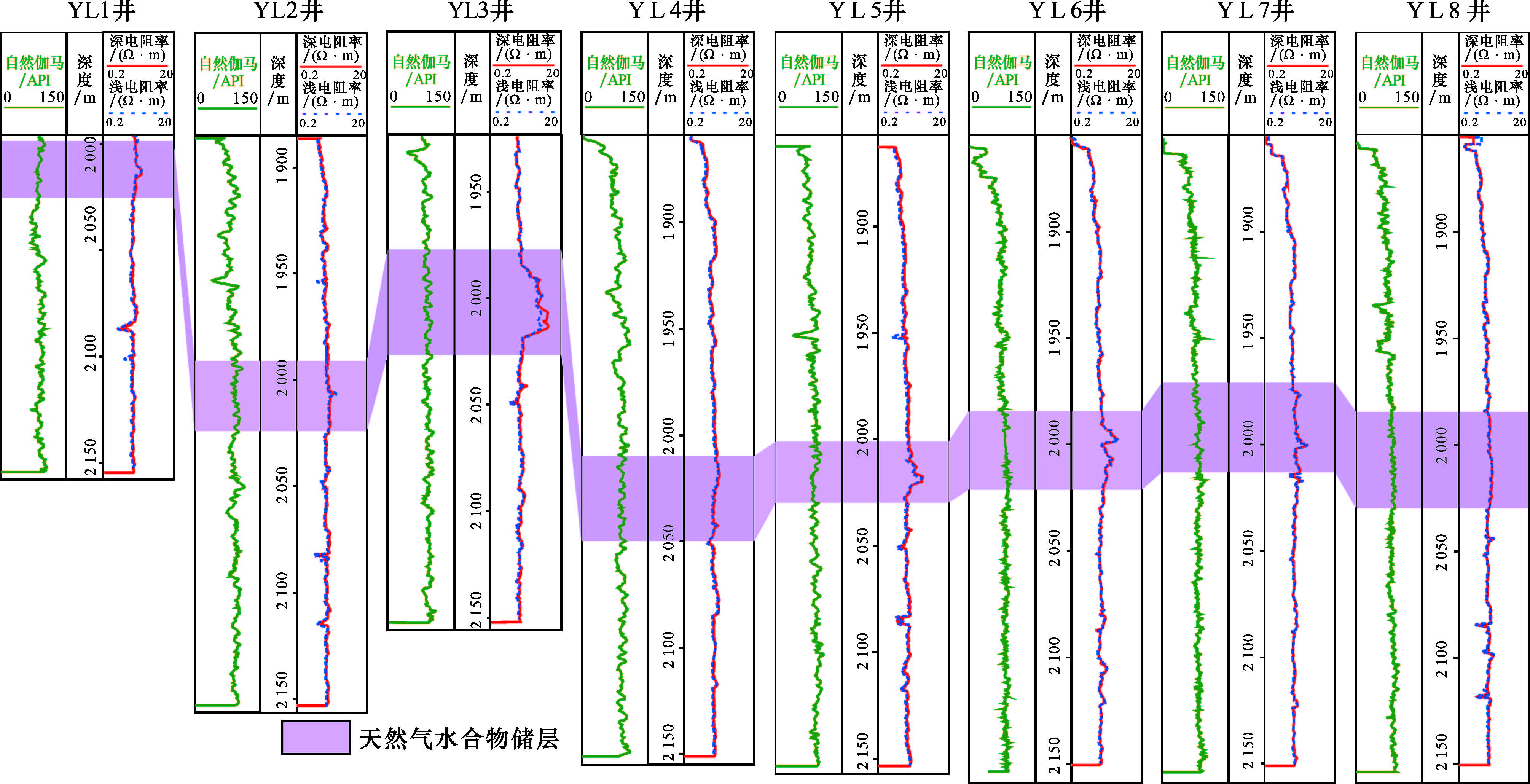
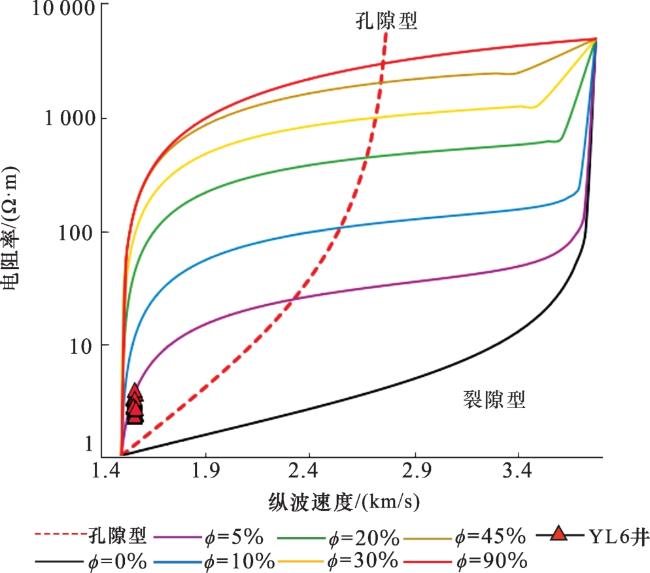
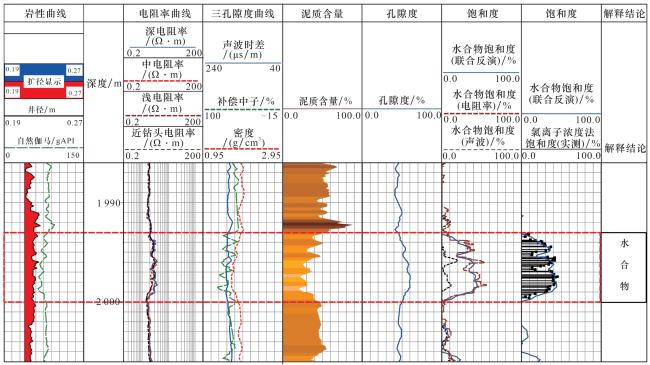
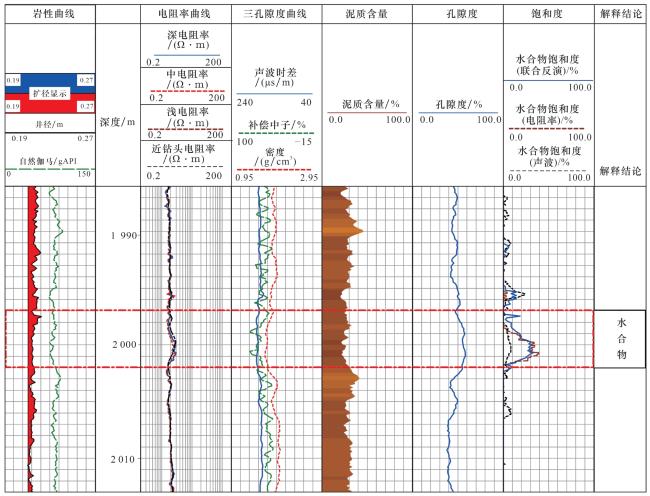
3 应用及效果分析
表2 不同方法计算QDN盆地天然气水合物层饱和度结果对比Table 2 Comparison of results of different methods for calculating the hydrate saturation of natural gas hydrate layers in the QDN Basin |
| 井号 | 计算方法 | 饱和度预测值范围/% | 误差分布范围/% | 平均误差/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| YL6 | 等效介质法 | 0~19.28 | 3.58~38.04 | 22.74 |
| 含泥质修正的电阻率法 | 6.12~56.3 | 1.38 ~21.89 | 12.85 | |
| 声电联合反演法 | 4.13~44.26 | 0.09 ~14.89 | 6.85 |


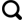

 甘公网安备 62010202000678号
甘公网安备 62010202000678号