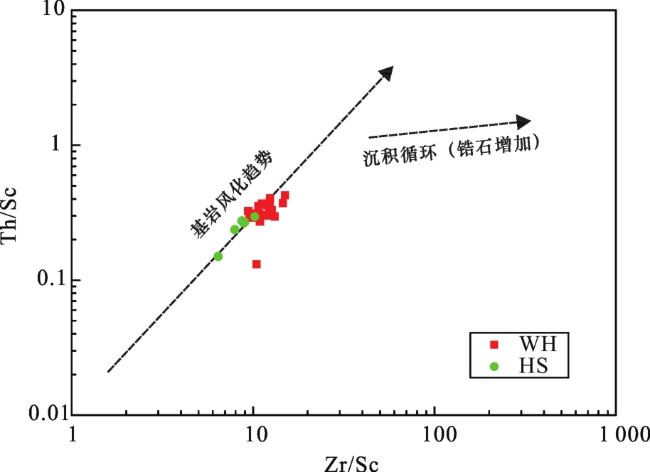
(1)成分变异指数ICV显示乌尔禾地区和哈拉阿拉特西南地区的沉积物经历了简单的沉积旋回,无再旋回作用发生。化学蚀变指数CIA和A—CN—K三角图解表明整个哈拉阿拉特地区沉积物从物源区搬运至沉积盆地过程中经历的低等风化强度的风化作用。
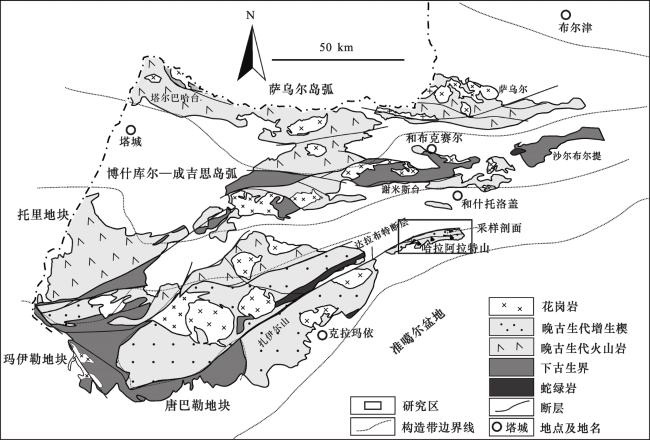
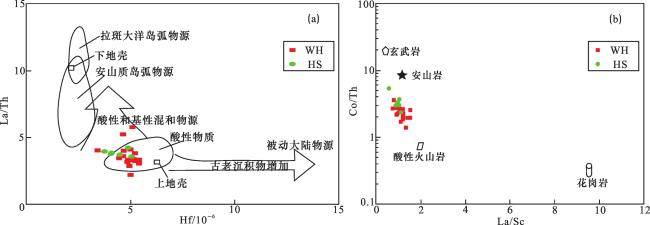
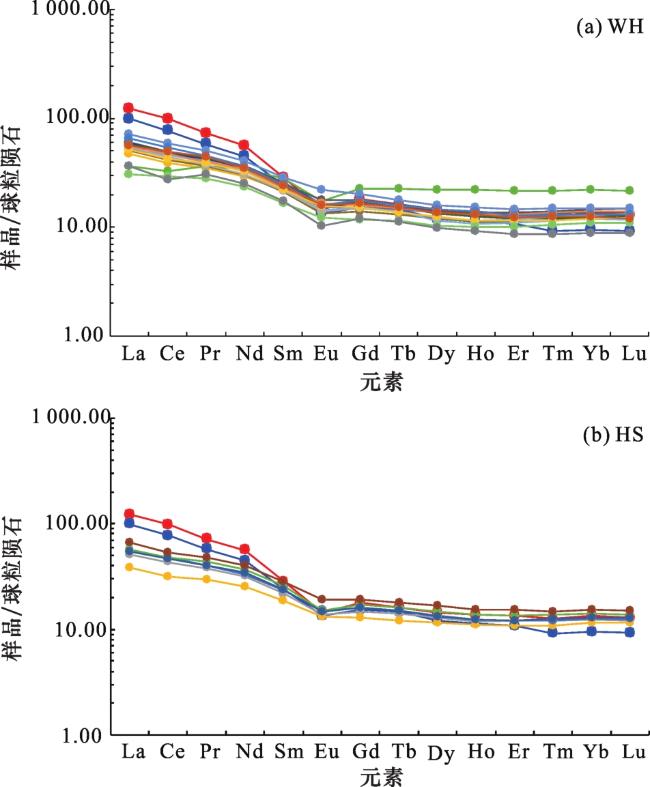
(2)微量元素比值Eu/Eu*、La/Sc、La/Co、Th/Sc、Th/Co及Cr/Th,源区母岩类型判别图版La/Th—Hf图解和La/Sc—Co/Th图解,稀土元素球粒陨石标准化配分模式及Eu元素异常特征等表明哈拉阿拉特地区沉积物母岩以中—酸性岩为主,可能有少量中—基性岩混入,显示出中—酸性母岩的特征。
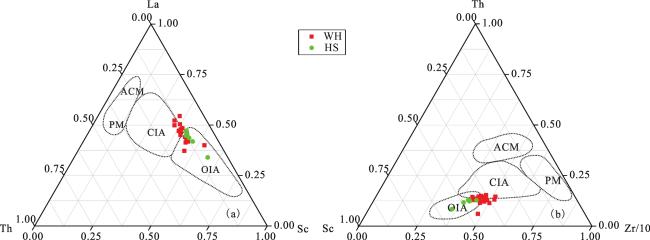
(3)La—Th—Sc与Th—Sc—Zr/10图解表明沉积构造背景属于大洋岛弧和大陆岛弧环境。
[1] MCLENNAN S, HEMMING S, MCDANIEL D, et al. Geochemical approaches to sedimentation, provenance, and tectonics[J]. Geological Society of America Special Papers, 1993, 284: 21-40.
[2] BHATIA M R. Plate tectonics and geochemical composition of sandstones[J]. The Journal of Geology, 1983, 6: 611-627.
[3] FLOYD P A, LEVERIDGE B E. Tectonic environments of the Devonian Gramscatho Basin, south Cornwall: Framework mode and geochemical evidence from turbidite sandstones[J]. Journal of the Geological Society, 1987, 144: 531-542.
[4] CULLERS R L. The controls on the major and trace element variation of shales, siltstones, and sandstones of Pennsylvanian-Permian age from uplifted continental blocks in Colorado to platform sediment in Kansas, USA[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta,1994, 58 (22): 4955-4972.
[5] NESBITT H W, YOUNG G M. Prediction of some weathering trends of plutonic and volcanic rocks based on thermodynamic and kinetic considerations[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta,1984, 48: 1523-1534.
[6] FEDO C M, YOUNG G M, NESBITT H W, et al. Potassic and sodic metasomatism in the southern province of the Canadian shield: Evidence from the paleoproterozoic serpent formation,Huronian Supergroup,Canada[J].Precambrian Research, 1997, 84: 17-36.
[7] FEDO C M, NESBITT H W, YOUNG G M. Unraveling the effects of potassium metasomatism in sedimentary rocks and paleosols, with implications for paleoweathering conditions and provenance[J]. Geology,1995, 23: 921-924.
[8] HOSSAIN H M Z, ROSER B P, KIMURA J I.Petrography and whole-rock geochemistry of the Tertiary Sylhet succession, northeastern Bengal Basin, Bangladesh: Provenance and source area weathering[J].Sedimentary Geology,2010,228(3): 171-183.
[9] SPALLETI L A, LIMARINO C O, PINOL F C. Petrology and geochemistry of Carboniferous siliciclastics from the argentine frontal cordillera: A test of methods for interpreting provenance and tectonic setting[J]. Journal of South American Earth Sciences, 2012, 36: 32-54.
[10] ARMSTRONG-ALTRIN J S, MACHAIN-CASTILLO M L, ROSALES-HOZ L, et al. Provenance and depositional history of continental slope sediments in the southwestern Gulf of Mexico unraveled by geochemical analysis[J].Continental Shelf Research,2015, 95: 15-26.
[11] ARMSTRONG-ALTRIN J S,NAGARAJAN R,BALA-RAM V, et al. Petrography and geochemistry of sands from the Chachalacas and Veracruz beach areas, western Gulf of Mexico, Mexico: Constraints on provenance and tectonic setting[J]. Journal of South American Earth Sciences, 2015, 64: 199-216.
[12] PERRI F, CARACCIOLO L, CAVALCANTE F,et al. Sedimentary and thermal evolution of the Eocene-Oligocene mudrocks from the southwestern Thrace Basin (NE Greece)[J]. Basin Research,2016, 28: 319-339.
[13] XIAO W J, WINDLEY B F, BADARCH G, et al. Palaeozoic accretionary and convergent tectonics of the southern Altaids: Implications for the growth of central Asia[J]. Journal of the Geological Society, 2004, 161: 339-342.
[14] CHOULET F, FAURE M, CLUZEL D, et al. From oblique accretion to transpression in the evolution of the Altaid collage: New insights from west Junggar, northwestern China[J]. Gondwana Research, 2012, 21: 530-547.
[15] GENG H Y, SUN M, YUAN C, et al. Geochemical, Sr-Nd and zircon U-Pb-Hf isotopic of Late Carboniferous magmatism in the west Junggar, Xinjiang: Implications for ridge subduction?[J]. Chemical Geology,2009, 266: 364-389.
[16] XIAO W J, HAN C M, YUAN C, et al. Middle Cambrian to permian subduction-related accretionary orogenesis of northern Xinjiang, NW China: Implications for the tectonic evolution of central Asia[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences,2008, 32: 102-117.
[17] ZHANG J E, XIAO W J, HAN C M, et al. A Devonian to carboniferous intra-oceanic subduction system in western Junggar, NW China[J]. Lithos,2011, 125: 592-606.
[18] ZHANG J E, XIAO W J, HAN C M, et al. Kinematics and age constraints of deformation in a Late Carboniferous accretionary complex in western Junggar, NW China[J]. Gondwana Research, 2011,19:958-974.
[19] GENG H Y, SUN M, YUAN C, et al. Geochemical and geochronological study of Early Carboniferous volcanic rocks from the west Junggar: Petrogenesis and tectonic implications[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences,2011, 42: 854-866.
[20] TANG G J, WANG Q, WYMAN D A,et al. Ridge subduction and crustal growth in the Central Asian orogenic belt: Evidence from Late Carboniferous adakites and high-Mg diorites in the western Junggar region, northern Xinjiang (west China)[J]. Chemical Geology, 2010, 277: 281-300.
[21] ZHENG J P, SUN M, ZHAO G C, et al. Elemental and Sr-Nd-Pb isotopic geochemistry of Late Paleozoic volcanic rocks beneath the Junggar Basin, NW China: Implications for the formation and evolution of the basin basement[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences,2007, 29: 778-794.
[22] 李甘雨, 李永军, 王冉,等. 西准噶尔哈拉阿拉特山一带晚石炭世赞岐岩的发现及其地质意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2017, 33(1):16-30.
LI G Y,LI Y J,WANG R,et al.The discovery and significance of Late Carboniferous sanukitoids in Hala’alate Mountain, west Junggar[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica,2017, 33(1):16-30.
[23] 李甘雨.新疆西准噶尔哈拉阿拉特组火山岩地球化学特征研究[D].西安:长安大学,2014:1-65.
LI G Y. The Study of Geochemistry Characteristics of the Hala’alate Formation Volcanic Rocks in Western Junggar,Xinjiang[D]. Xi’an: Chang’an University,2014: 1-65.
[24] 向坤鹏, 李永军, 李钊, 等. 新疆西准噶尔哈拉阿拉特山火山岩LA—ICP—MS锆石U—Pb年龄,地球化学特征及意义[J]. 地质学报, 2015, 89(5): 843-855.
XIANG K P, LI Y J, LI Z, et al. LA-ICP-MS Zircon age and geochemistry of the Aladeyikesai Formation volcanic rocks in the Hala’alate Mountain of west Junggar, Xinjiang, and there tectonic significance[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2015, 89(5):843-855.
[25] CHOULET F, CLUZEL D, FAURE M, et al. New constraints on the pre-Permian continental crust growth of Central Asia (west Junggar, China) by U-Pb and Hf isotopic data from detrital zircon[J]. Terra Nova,2012,24:189-198.
[26] WEI W, PANG X Y, WANG Y, et al. Sediments facies, provenance evolution and their implication of the Lower Devonian to Lower Carboniferous in Shaerbuerti mountain in north Xinjiang[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2009, 25 (3): 689-698.
[27] 廖婉琳, 肖龙, 张雷,等. 新疆西准噶尔早石炭世沉积地层的物源及构造环境[J]. 地球科学, 2015,40(3): 485-503.
LIAO W L, XIAO L, ZHANG L, et al. Provenance and tectonic setting of Early Carboniferous sedimentary strata in western Junggar, Xinjiang[J]. Earth Science: Journal of China University of Geoscience, 2015, 40(3): 485-503.
[28] FENG Y M, COLEMAN R G, TILTON G R, et al. Tectonic evolution of the west Junggar Region, Xinjiang, China[J]. Tectonics,1989, 8: 729-752.
[29] 向坤鹏. 新疆西准噶尔包古图—哈拉阿拉特山一带石炭纪沉积盆地分析及构造意义[D].西安:长安大学,2015:1-268.
XIANG K P. Carboniferous Sedimentary Basin Analysis and Tectonic Significance in the Baogutu-Halaalate Mountain, Western Junggar, Xinjiang[D].Xi’an: Chang’an University, 2015: 1-268.
[30] 陶辉飞,邱振,吉鸿杰,等. 西准噶尔晚石炭世哈拉阿拉特山组烃源岩发育沉积环境与有机质富集因素分析[J]. 地球科学, 2017, 52(1): 79-92.
TAO H F, QIU Z, JI H J, et al. Sedimentary environment and organic carbon enrichment factors of the Late Carboniferous Hala’alat hydrocarbon source rocks in west Junggar[J]. Earth Science:Journal of China University of Geoscience, 2017, 52(1): 79-92.
[31] 马明,陈国俊,吕成福,等.珠江口盆地白云凹陷始新统—下渐新统沉积环境与泥岩物源[J].石油学报,2016,37(5):610-621.
MA M, CHEN G J, LV C F, et al. Eocene-Low Oligocene sedimentary environment and mudstone provenance in Baiyun Sag, Pearl River Mouth Basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2016, 37(5):610-621.
[32] TAYLOR S R, MCLENNAN S M. The Continental Crust: Its Composition and Evolution[M]. Oxford: Blackwell Scientific Publishers,1985.
[33] RUDNICK R, GAO S. Composition of the continental crust[J]. Treatise on Geochemistry, 2003, 3: 1-64.
[34] COX R, LOWE D R, CULLERS R L. The influence of sediment recycling and basement composition on evolution of mudrock chemistry in the southwestern United States[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1995, 59: 2919-2940.
[35] HU J J, LI Q, HUANG J,et al. Geochemical characteristics and depositional environment of the Middle Permian mudstones from central Qiangtang Basin, northern Tibet[J]. Geological Journal, 2015, 51, 560-571. DOI: 10.1002/gj.2653.
[36] MA M, CHEN G J, LI C, et al. Petrography and geochemistry of oligocene to Lower Miocene sandstones in the Baiyun Sag, pearl river mouth basin, South China Sea: Provenance, source area weathering, and tectonic setting[J]. Geological Journal, 2018, 54: 564-589.
[37] ABSAR N, SREENIVAS B. Petrology and geochemistry of greywackes of the ~1.6Ga Middle Aravalli Supergroup, northwest India: Evidence for active margin processes[J]. International Geology Review, 2015, 57: 134-158.
[38] NESBITT H W, YOUNG G M. Early Proterozoic climates and plate motions inferred from major element chemistry of lutites[J]. Nature,1982, 299: 715-717.
[39] BOCK B, MCLENNAN S M, HANSON G N. Geochemistry and provenance of the Middle Ordovician Austin Glen Member (Normanskill Formation) and the Taconian Orogeny in New England[J]. Sedimentology, 1998, 45: 635-655.
[40] GHOSH S, SARKAR S, GHOSH P. Petrography and major element geochemistry of the Permo-Triassic sandstones, central India: Implications for provenance in an intracratonic pull-apart basin[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2012, 43: 207-240.
[41] ARMSTRONG-ALTRINA J S, NAGARAJAN R, MADHAVARAJU J, et al. Geochemistry of the Jurassic and Upper Cretaceous shales from the Molango Region, Hidalgo, eastern Mexico: Implications for source-area weathering, provenance, and tectonic setting[J]. Comptes Rendus Géoscience, 2013, 345(4): 185-202.
[42] CULLERS R L. The geochemistry of shales, siltstones and sandstones of Pennsylvanian-Permian age, Colorado, U.S.A.: Implications for provenance and metamorphic studies[J]. Lithos, 2000, 51: 181-203.
[43] WANG C L, ZHANG L C, DAI Y P,et al. Geochronological and geochemical constraints on the origin of clastic meta-sedimentary rocks associated with the Yuanjiacun BIF from the Lüliang Complex,North China[J].Lithos,2015,212: 231-246.
[44] AMSTRONG-ALTRIN J S, LEE Y I, VERMA S P,et al. Geochemistry of sandstones from the Upper Miocene Kudankulam Formation, southern India: Implications for provenance, weathering, and tectonic setting[J]. Journal of Sedimentary Research,2004, 74: 285-297.
[45] CASTILLO P, LACASSIE J P, AUGUSTSSON C,et al. Petrography and geochemistry of the Carboniferous-Triassic Trinity Peninsula Group, west Antarctica: Implications for provenance and tectonic setting[J].Geological Magazine,2015, 152(4): 575-588.
[46] ETEMAD-SAEED N,HOSSEINI-BARZI M,ARMST-RONG-ALTRIN J S. Petrography and geochemistry of clastic sedimentary rocks as evidences for provenance of the Lower Cambrian Lalun Formation,Posht-e-badam block, central Iran[J]. Journal of African Earth Sciences, 2011, 61: 142-159.
[47] PERRI F, CRITELLI S, MONGELLI G,et al. Sedimentary evolution of the Mesozoic continental redbeds using geochemical and mineralogical tools: The case of Upper Triassic to Lowermost Jurassic M.te di Gioiosa mudstones (Sicily, southern Italy)[J]. International Journal of Earth Sciences, 2011, 100: 1569-1587.
[48] PUREVJAV N, ROSER B. Geochemistry of Silurian-Carboniferous sedimentary rocks of the Ulaanbaatar terrane, Hangay-hentey belt, central Mongolia: Provenance, paleoweathering, tectonic setting, and relationship with the neighbouring tsetserleg terrane[J].Chemie der Erde-Geochemistry-Interdisciplinary Journal for Chemical Problems of the Geosciences and Geoecology, 2013, 73(4): 481-493.
[49] ZHANG L, QIN X G, LIU J Q,et al. Geochemistry of sediments from the Huaibei plain (east China): Implications for provenance, weathering, and invasion of the Yellow River into the Huaihe River[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Science,2016, 121: 72-83.
[50] BHATIA M R, CROOK K A. Trace element characteristics of graywackes and tectonic setting discrimination of sedimentary basins[J].Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 1986, 92: 181-193.
[51] AMENDOLA U, PERRI F, CRITELLI S, et al. Composition and provenance of the Macigno Formation (Late Oligocene-Early Miocene) in the Trasimeno lake area (northern Apennines)[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology,2016,69:146-167.
[52] PERRI F, CRITELLI S, DOMINICI R,et al. Sourceland controls and dispersal pathways of Holocene muds from boreholes of the Ionian Basin, Calabria, southern Italy[J]. Sedimentary Geology,2015, 152: 957-972.
[53] PERRI F, DOMINICI R, CRITELLI S. Stratigraphy, composition and provenance of argillaceous marls from the Calcare di Base Formation, Rossano Basin (northeastern Calabria)[J]. Geological Magazine,2015, 152: 193-209.
[54] BHATIA M R. Rare earth element geochemistry of Australian Paleozoic graywackes and mudrocks: Provenance and tectonic control[J]. Sedimentary Geology,1985, 45: 97-113.


 甘公网安备 62010202000678号
甘公网安备 62010202000678号