

Application of carbon and hydrogen isotopes in the natural gas origin study
Received date: 2024-04-22
Revised date: 2024-05-08
Online published: 2024-07-25
Supported by
The Guizhou Provincial Science and Technology Projects(Grant No.[2022]ZD005)
the Science and Technology Projects of China National Petroleum Corporation Limited(2021DJ5302)
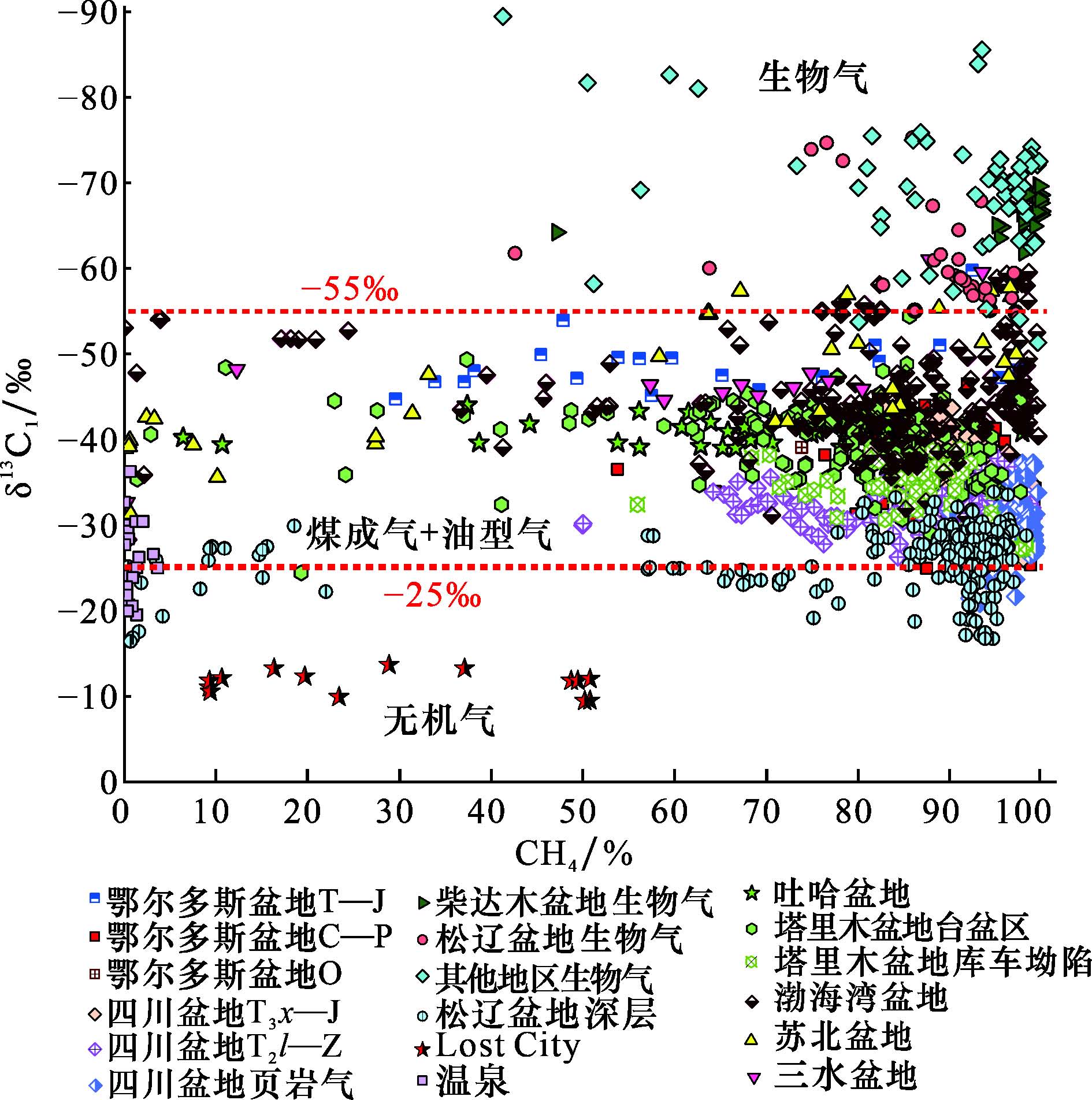
Different types of natural gas have different carbon and hydrogen isotopic compositions, so the carbon and hydrogen isotopic composition of natural gas is one of the important indicators of natural gas origin identification. With the continuous development of natural gas exploration technology and the continuous growth of exploration data, understanding of the origin and source of natural gas is also deepening, and how to update and verify the existing data to ensure the applicability of natural gas genetic identification figure has become crucial. This study comprehensively analyzes the stable carbon and hydrogen isotope characteristics of different genetic types of natural gases in Sichuan, Tarim, Ordos, Turpan-Hami, Songliao, Northern Jiangsu, Sanshui, Qaidam, and Bohai Bay basins in China, together with abiotic gases from the Lost City of the Middle Atlantic Ridge, and the genetic identification diagrams related to commonly used carbon and hydrogen isotopes are evaluated. The following four conclusions are obtained: (1) The carbon isotopic values of methane (δ13C1), ethane (δ13C2), propane (δ13C3) and butane (δ13C4) of natural gases from China are from -89.4‰ to -11.4‰ (average of -36.6 ‰),-66.0‰ to -17.5‰(average of -29.4‰),-49.5‰ to -13.2‰(average of -27.3‰), -38.5‰ to -16.0‰(average of -25.6‰),respectively. (2) The hydrogen isotopic values of methane (δD1), ethane (δD2) and propane (δD3) of natural gases from China range from -287‰ to -111‰ (average of -177‰), -249‰ to -94‰ (average of -158‰), and -237‰ to -75‰ (average of -146‰), respectively. (3) The carbon and hydrogen isotopic distribution patterns among methane and its homologues of natural gases in China are mainly in positive order (δ13C1<δ13C2<δ13C3<δ13C4, δD1<δD2<δD3). The fractionation amplitude between methane and ethane is greater than that between ethane and propane (Δ(δ13C2-δ13C1)> Δ(δ13C3-δ13C2), Δ(δD2-δD1)>Δ(δD3-δD2)) in most natural gas samples. (4) The δ13C1–δ13C2–δ13C3, the δ13C1–δD1, δ13C1–C1/C2+3, Δ(δ13C2-δ13C1)–Δ(δ13C3-δ13C2) and Δ(δD2-δD1)–Δ(δD3-δD2) charts, can be used to identify the gas origin in many different cases, and the combined application between different charts can enhance the identification effect.
Key words: Natural gas; Carbon isotope; Hydrogen isotope; Genetic identification; Diagram
Yunyan NI , Jinchuan ZHANG , Limiao YAO , Guoliang DONG , Yuan WANG , Li WANG , Jianping CHEN . Application of carbon and hydrogen isotopes in the natural gas origin study[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2024 , 35(11) : 1897 -1909 . DOI: 10.11764/j.issn.1672-1926.2024.05.007
本文在研究过程中,得到中国石油勘探开发研究院戴金星院士的帮助,在此深表感谢。
| 1 |
DAI J, XIA X, QIN S, et al. Origins of partially reversed alkane δ13C values for biogenic gases in China[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 2004, 35(4): 405-411.
|
| 2 |
戴金星, 倪云燕, 黄士鹏, 等. 次生型负碳同位素系列成因[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2016, 27(1): 1-7.
DAI J X, NI Y Y, HUANG S P, et al. Origins of secondary negative carbon isotopic series in natural gas[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2016, 27(1): 1-7.
|
| 3 |
MILKOV A V, ETIOPE G. Revised genetic diagrams for natural gases based on a global dataset of >20,000 samples[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 2018, 125: 109-120.
|
| 4 |
MILKOV A V. New approaches to distinguish shale-sourced and coal-sourced gases in petroleum systems[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 2021, 158: 104271.
|
| 5 |
戴金星.中国煤成大气田及气源[M].北京:科学出版社,2014.
DAI J X. Coal-forming Gas Fields and Gas Sources in China[M].Beijing: Science Press,2014.
|
| 6 |
SCHOELL M. The hydrogen and carbon isotopic composition of methane from natural gases of various origins[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1980, 44(5): 649-661.
|
| 7 |
戴金星. 天然气碳氢同位素特征和各类天然气鉴别[J]. 天然气地球科学, 1993,4(2-3): 1-40.
DAI J X. Characteristics of carbon and hydrogen isotopes of natural gases and their discriminations[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 1993,4(2-3): 1-40.
|
| 8 |
戴金星, 裴锡古, 戚厚发. 中国天然气地质学(卷一)[M].北京:石油工业出版社, 1992:298.
DAI J X, PEI X G, QI H F. Natural Gas Geology in China (Vol. I)[M]. Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press, 1992:298.
|
| 9 |
戴金星,陈英. 中国生物气中烷烃组分的碳同位素特征及其鉴别标志[J]. 中国科学(B辑), 1993, 23(3): 303-310.
DAI J X, CHEN Y. Carbon isotope characteristics and identification indexes of alkane components in Chinese biogas[J]. Science in China (Series B), 1993, 23(3): 303-310.
|
| 10 |
戴金星, 倪云燕, 龚德瑜, 等. 中国大气田烷烃气碳同位素组成的若干特征[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2024, 51(2): 223-233.
DAI J X, NI Y Y, GONG D Y, et al. Characteristics of carbon isotopic composition of alkane gas in large gas fields in China[J].Petroleum Exploration and Development,2024,51(2): 223-233.
|
| 11 |
沈平,徐永昌. 中国陆相成因天然气同位素组成特征[J]. 地球化学,1991,20(2):144-152.
SHEN P, XU Y C. The isotopic composition of natural gases from continental sediments in China[J].Geochimica,1991,20(2):144-152.
|
| 12 |
STAHL W J,Carbon isotopes in petroleum geochemistry[M]// JAGER E,HUNZIKER J C. Lectures in Isotope Geology. New York:Springer,1979:274-283.
|
| 13 |
WHITICAR M J. Carbon and hydrogen isotope systematics of bacterial formation and oxidation of methane[J]. Chemical Geology, 1999, 161(1-3): 291-314.
|
| 14 |
JENDEN P D, KAPLAN I R. Comparison of microbial gases from the Middle American Trench and Scripps Submarine Canyon: Implications for the origin of natural gas[J]. Applied Geochemistry, 1986, 1(6): 631-646.
|
| 15 |
戴金星, 戴春森, 宋岩, 等. 中国一些地区温泉中天然气的地球化学特征及碳、氦同位素组成[J]. 中国科学(B辑), 1994, 24(4): 426-433.
DAI J X, DAI C S, SONG Y, et al. Geochemical characters, carbon and helium isotopic compositions of natural gas from hot springs of some areas in China[J]. Science in China (Series B), 1994, 24(4): 426-433.
|
| 16 |
戴金星,宋岩. 鉴别煤成气的指标[M]// 《煤成气地质研究》编委会.煤成气地质研究.北京:石油工业出版社,1987:156-170.
DAI J X, SONG Y. Coal-derived gas discrimination criteria[M]// Editorial Board of the Geological Research of Coal-derived Gas. Geological Research of Coal-derived Gas.Beijing:Petroleum Industry Press,1987:156-170.
|
| 17 |
王世谦. 四川盆地侏罗系—震旦系天然气的地球化学特征[J]. 天然气工业, 1994, 14(6): 1-5.
WANG S Q. Geochemical characteristics of natural gases from the Jurassic-Sinian formations in the Sichuan Basin[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 1994, 14(6): 1-5.
|
| 18 |
刚文哲, 高岗, 郝石生, 等. 论乙烷碳同位素在天然气成因类型研究中的应用[J]. 石油实验地质, 1997, 19(2): 164-167.
GANG W Z, GAO G, HAO S S, et al. Carbon isotope of ethane applied in the analyses of genetic types of natural gas[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment,1997,19(2):164-167.
|
| 19 |
肖芝华, 谢增业, 李志生, 等. 川中—川南地区须家河组天然气同位素组成特征[J]. 地球化学, 2008, 37(3): 245-250.
XIAO Z H, XIE Z Y, LI Z S, et al. Isotopic characteristics of natural gas of Xujiahe Formation in southern and middle of Sichuan basin[J]. Geochimica, 2008, 37(3): 245-250.
|
| 20 |
张士亚, 郜建军, 蒋泰然.利用甲、乙烷碳同位素判别天然气类型的一种新方法[M]//地质矿产部石油地质研究所.石油与天然气地质文集(第一集):中国煤成气研究.北京:地质出版社,1988.
ZHANG S Y,GAO J J,JIANG T R.Genetic characterization of natural gases using carbon isotopic composition of methane and ethane[M]//Resources Ministry of Geology and Mineral. Collected Works of Petroleum and Natural Gas: Research of Coal-derived Gas in China.Beijing:Geological Publishing House,1988.
|
| 21 |
陈践发, 李春园, 沈平, 等. 煤型气烃类组分的稳定碳、氢同位素组成研究[J]. 沉积学报, 1995, 13(2): 59-69.
CHEN J F, LI C Y, SHEN P, et al. Carbon and hydrogen isotopic characteristics of hydrocarbons in coal type gas from China[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica,1995,13(2):59-69.
|
| 22 |
DAI J, NI Y, ZOU C. Stable carbon and hydrogen isotopes of natural gases sourced from the Xujiahe Formation in the Sichuan Basin,China[J].Organic Geochemistry,2012,43:103-111.
|
| 23 |
WANG X, LIU W, SHI B, et al. Hydrogen isotope characteristics of thermogenic methane in Chinese sedimentary basins[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 2015, 83-84: 178-189.
|
| 24 |
倪云燕, 廖凤蓉, 龚德瑜, 等. 吐哈盆地台北凹陷天然气碳氢同位素组成特征[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2019, 46(3): 531-542.
NI Y Y, LIAO F R, GONG D Y, et al. Stable carbon and hydrogen isotopic characteristics of natural gas from Taibei Sag, Turpan-Hami Basin,NW China[J].Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2019, 46(3): 531-542.
|
| 25 |
NI Y, ZHANG D, LIAO F, et al. Stable hydrogen and carbon isotopic ratios of coal-derived gases from the Turpan-Hami Basin, NW China[J]. International Journal of Coal Geology, 2015, 152(Part A): 144-155.
|
| 26 |
刘丹, 吴伟, 房忱琛, 等. 渤海湾盆地古近系低熟煤成气地球化学特征[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2016, 27(5): 873-882.
LIU D, WU W, FANG C C, et al. Geochemistry of low-mature gas derived from Paleogene coal-measure source rock of Baihai Bay Basin[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience,2016,27(5):873-882.
|
| 27 |
胡安平, 戴金星, 杨春, 等. 渤海湾盆地CO2气田(藏)地球化学特征及分布[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2009, 36(2): 181-189.
HU A P,DAI J X,YANG C,et al.Geochemical characteristics and distribution of CO2 gas fields in Bohai Bay Basin[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development,2009,36(2):181-189.
|
| 28 |
戴金星, 邹才能, 张水昌, 等. 无机成因和有机成因烷烃气的鉴别[J]. 中国科学(地球科学):2008,38(11):1329-1341.
DAI J X, ZOU C N, ZHANG S C, et al. Discrimination of abiogenic and biogenic alkane gases[J]. Science China (Earth Sciences), 2008, 38(11): 1329-1341.
|
| 29 |
NI Y, DAI J, ZOU C, et al. Geochemical characteristics of biogenic gases in China[J]. International Journal of Coal Geology, 2013, 113: 76-87.
|
| 30 |
沈平, 王晓峰, 徐茵, 等. 我国生物气藏碳、氢同位素特征、形成途径及意义[J]. 沉积学报, 2010, 28(1): 183-187.
SHEN P, WANG X F, XU Y, et al. Carbon and hydrogen isotopic compositions:Generation pathway of bacterial gas in China[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica,2010,28(1):183-187.
|
| 31 |
罗毅, 朱扬明, 薛秀丽, 等. 百色盆地第三系浅层气成因类型与形成机制[J]. 广西科学, 2003, 10(4): 286-291.
LUO Y, ZHU Y M, XUE X L, et al. Genetic type and formation mechanism of shallow gas in Baise Basin[J]. Guangxi Science, 2003, 10(4): 286-291.
|
| 32 |
YUEN G, BLAIR N, DES MARAIS D J, et al. Carbon isotope composition of low molecular weight hydrocarbons and monocarboxylic acids from Murchison meteorite[J]. Nature, 1984, 307(5948): 252-254.
|
| 33 |
DAI J, NI Y, GONG D, et al. Geochemical characteristics of gases from the largest tight sand gas field (Sulige) and shale gas field (Fuling) in China[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2017, 79(Supplement C): 426-438.
|
| 34 |
DAI J, ZOU C, LIAO S, et al. Geochemistry of the extremely high thermal maturity Longmaxi shale gas, southern Sichuan Basin[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 2014, 74: 3-12.
|
| 35 |
FENG Z, HAO F, DONG D, et al. Geochemical anomalies in the Lower Silurian shale gas from the Sichuan Basin, China: Insights from a Rayleigh-type fractionation model[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 2020, 142: 103981.
|
| 36 |
XIONG Y, ZHANG L, CHEN Y, et al. The origin and evolution of thermogenic gases in organic-rich marine shales[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2016, 143: 8-13.
|
| 37 |
HAO F,ZOU H. Cause of shale gas geochemical anomalies and mechanisms for gas enrichment and depletion in high-maturity shales[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology,2013,44:1-12.
|
| 38 |
NI Y, DONG D, YAO L, et al. Geochemical characteristics and origin of shale gases from Sichuan Basin, China[J]. Frontiers in Earth Science, 2022, 10: 884445.
|
| 39 |
戴金星. 中国大气田及气源[M].北京:石油工业出版社,2024.
DAI J X. Giant Gas Fields and Gas Sources in China[M]. Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press, 2024.
|
| 40 |
DAI J, ZOU C, DONG D, et al. Geochemical characteristics of marine and terrestrial shale gas in China[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2016, 76: 444-463.
|
| 41 |
NI Y, LIAO F, GAO J, et al. Hydrogen isotopes of hydrocarbon gases from different organic facies of the Zhongba Gas Field,Sichuan Basin,China[J].Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2019, 179: 776-786.
|
| 42 |
王晓锋, 刘文汇, 徐永昌, 等. 不同成因天然气的氢同位素组成特征研究进展[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2006, 17(2): 163-169.
WANG X F, LIU W H, XU Y C, et al. The hydrogen isotopic composition of natural gases generated from different pathway[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2006, 17(2): 163-169.
|
| 43 |
PROSKUROWSKI G, LILLEY M D, SEEWALD J S, et al. Abiogenic hydrocarbon production at Lost City hydrothermal field[J]. Science, 2008, 319(5863): 604-607.
|
| 44 |
SHERWOOD LOLLAR B, WESTGATE T D, WARD J A, et al. Abiogenic formation of alkanes in the Earth's crust as a minor source for global hydrocarbon reservoirs[J]. Nature, 2002, 416(6880): 522-524.
|
| 45 |
BERNARD B B, BROOKS J M, SACKETT W M. Natural gas seepage in the Gulf of Mexico[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1976, 31(1): 48-54.
|
| 46 |
BERNARD B, BROOKS J, SACKETT W. A geochemical model for characterization of hydrocarbon gas sources in marine sediments[C].Offshore Technology Conference,Houston,USA, 1977, 2934.
|
| 47 |
FABER E,GERLING P,DUMKE I. Gaseous hydrocarbons of unknown origin found while drilling[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 1988, 13: 875-879.
|
| 48 |
张居和, 李景坤, 霍秋立. 松辽盆地三站气田天然气地球化学特征与烃源岩产气贡献[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2006, 17(6): 837-841.
ZHANG J H, LI J K, HUO Q L. Gas geochemistry feature and ration contribution of hydrocarbon source rocks in Sanzhan Gas Field of Songliao Basin[J].Natural Gas Geoscience,2006, 17(6): 837-841.
|
| 49 |
BIGELEISEN J. Chemistry of isotopes[J]. Science, 1965, 147(3657): 463-471.
|
| 50 |
CRISS R E.Principles of Stable Isotope Distribution[M].New York: Oxford University Press, 1999:254.
|
| 51 |
TANG Y,JENDEN P D, Theoretical modeling of carbon and hydrogen isotope fractionation in natural gas[M]//Organic Geo-chemistry,Developments and Applications to Energy,Climate and Human History.ed.Grimalt J.O.Dorronsoro C.,1995,Euro-pean Association of Organic Geochemists,1067-1069,A.I.G.O.A.
|
| 52 |
NI Y, MA Q, ELLIS G S, et al. Fundamental studies on kinetic isotope effect (KIE) of hydrogen isotope fractionation in natural gas systems[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2011, 75(10): 2696-2707.
|
| 53 |
WHITICAR M J, FABER E, SCHOELL M. Biogenic methane formation in marine and freshwater environments: CO2 reduction vs. acetate fermentation-Isotope evidence[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1986, 50(5): 693-709.
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |