0 引言
1 气体溶解度模型的理论基础
2 CH4溶解度模型
2.1 CH4溶解度模型概述
表1 纯水与NaCl溶液中CH4溶解度的典型模型Table 1 Typical models for calculating CH4 solubilities in water and aqueous NaCl solution |
2.2 DUAN等的CH4溶解度计算模型
2.2.1 摩尔分数y的计算
2.2.2 逸度因子 的计算
2.2.3 标准态化学势与活度因子的计算
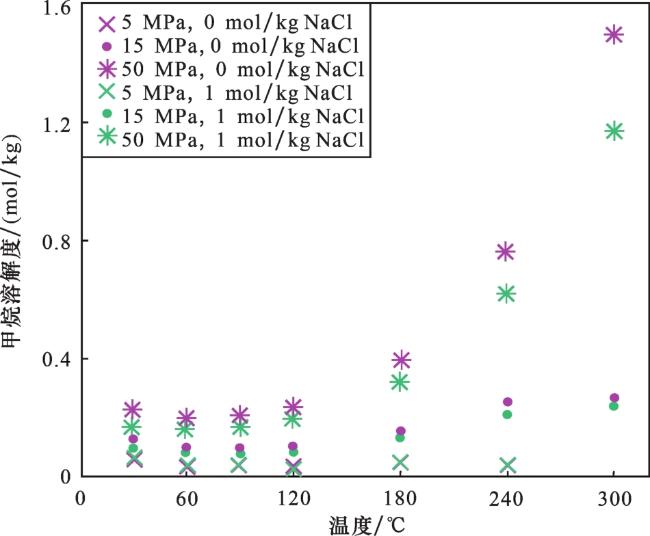
3 CO2溶解度模型
3.1 CO2溶解度模型概述
表2 纯水与NaCl溶液中CO2溶解度的典型模型Table 2 Typical models for calculating CO2 solubilities in water and aqueous NaCl solution |
3.2 MAO等的CO2溶解度计算模型
3.2.1 摩尔分数y与逸度因子 的计算
3.2.2 标准态化学势与活度因子的计算
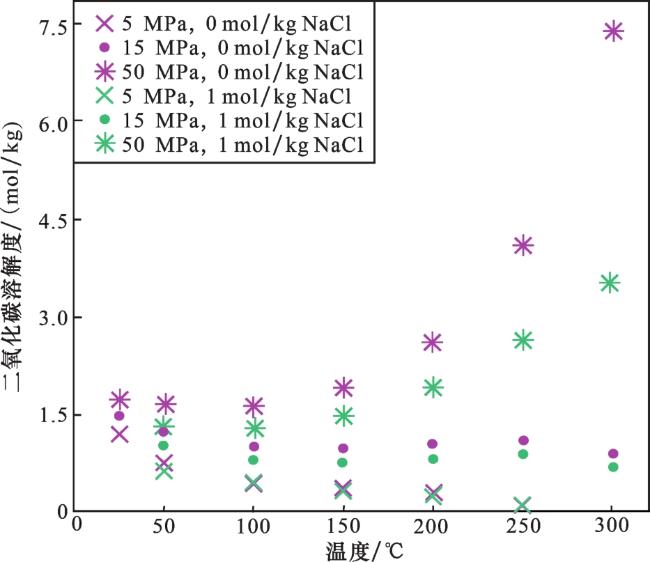
4 稀有气体溶解度模型
4.1 大气稀有气体的溶解度模型
表3 大气稀有气体溶解度与亨利常数计算公式(19)与公式(20)中各系数的取值Table 3 Coefficients of formulas (19) and (20) for calculating solubilities and Henry constants of atmospheric noble gases |
| 公式 | 系数 | He | Ne | Ar | Kr | Xe |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 19 | A 1 | -178.142 4 | -274.132 9 | -227.460 7 | -122.469 4 | -224.510 0 |
| A 2 | 217.599 1 | 352.620 1 | 305.434 7 | 153.565 4 | 292.823 4 | |
| A 3 | 140.750 6 | 226.967 6 | 180.527 8 | 70.196 9 | 157.612 7 | |
| A 4 | -23.019 54 | -37.133 93 | -27.994 50 | -8.525 24 | -22.668 95 | |
| B 1 | -0.038 129 | -0.063 860 | -0.066 942 | -0.049 522 | -0.084 915 | |
| B 2 | 0.019 190 | 0.035 326 | 0.037 201 | 0.024 434 | 0.047 996 | |
| B 3 | -0.002 689 8 | -0.005 325 8 | -0.005 636 4 | -0.003 396 8 | -0.007 359 5 | |
| C 1 | -2.55 | 12.8 | -5.30 | 4.19 | 6.69 | |
| 20 | A | -83.696 8 | -180.580 3 | -88.646 2 | -36.036 9 | -142.030 3 |
| B | 106.020 0 | 240.622 2 | 122.887 1 | 54.195 9 | 202.744 8 | |
| C | 51.762 4 | 137.872 1 | 48.639 6 | 1.529 9 | 88.909 6 | |
| D | -5.466 4 | -19.601 2 | -4.120 8 | 3.417 6 | -9.567 7 |
4.2 纯水中稀有气体的溶解度模型
表4 纯水中稀有气体溶解度与亨利常数计算公式(21,24,26-28)中各系数的取值Table 4 Coefficients of formulas (21,24,26-28) for calculating solubilities and Henry constants of noble gases in water |
| 公式 | 系数 | He | Ne | Ar | Kr | Xe |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 21 | A | -233.163 | -310.827 | -336.76 | -270.967 | -360.119 |
| B | 8 737.84 | 12 766.8 | 16 170.1 | 15 992.9 | 18 744.6 | |
| C | 32.265 2 | 43.618 5 | 46.211 7 | 33.289 2 | 49.033 2 | |
| D | -0.011 972 6 | -0.012 753 4 | -0.006 087 9 | 0.026 048 5 | -0.003 113 2 | |
| 24 | A 0 | - | -7.259 | -9.52 | -6.292 | -3.902 |
| A 1 | - | 6.95 | 8.83 | 5.612 | 2.439 | |
| A 2 | - | -1.382 6 | -1.895 9 | -0.888 1 | 0.386 3 | |
| A 3 | - | 0.053 8 | 0.069 8 | -0.045 8 | -0.221 1 | |
| 26 | a 0 | 4.827 122 | 4.612 54 | 3.718 433 | 3.095 855 | 1.984 034 |
| a 1 | 6.586 451 | 7.218 989 | 8.545 065 | 9.212 515 | 10.405 394 | |
| a 2 | -1.542 063 | -1.819 817 | -2.479 705 | -2.779 465 | -3.211 715 | |
| 27 | A 0 | 5.424 148 | 5.196 67 | 4.289 125 | 3.648 42 | 2.560 135 |
| A 1 | 15.355 998 | 16.677 833 | 19.225 988 | 20.615 112 | 23.220 466 | |
| A 2 | -16.804 423 | -18.403 594 | -21.603 721 | -23.292 806 | -26.324 042 | |
| 28 | a -2 | -2.067 744 | -1.992 174 | -2.577 657 | -2.680 26 | -2.646 469 |
| a -1 | 9.985 833 | 8.330 898 | 9.174 933 | 8.570 473 | 6.747 425 | |
| a 0 | -2.486 081 | 2.226 299 | 2.371 603 | 4.4776 67 | 9.855 588 | |
| a 1 | 5.234 082 | 1.703 614 | 0.957 659 | -0.988 997 | -5.632 491 |
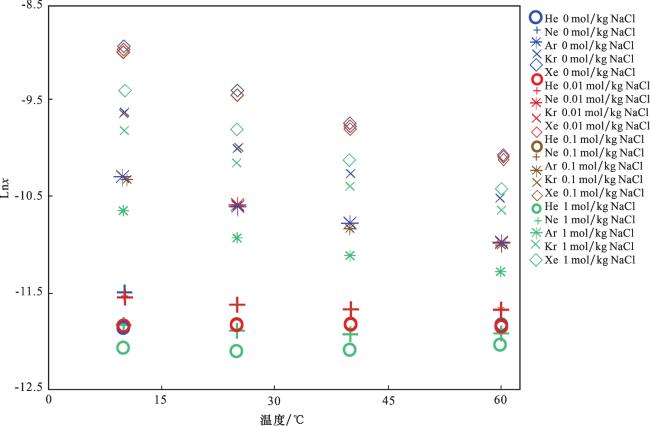
4.3 NaCl溶液中稀有气体的溶解度模型
表5 稀有气体的Setschenow系数与溶解度的计算公式(30)与(31)中各系数取值Table 5 Coefficients of formulas (30) and (31) for setschenow coefficients and solubilities of noble gases |
| 气体 | 公式(30) | 公式(31) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A 1 | A 2 | A 3 | C 1 | C 2 | C 3 | |
| He | -10.081 0 | 15.106 8 | 4.812 7 | -41.461 1 | 42.596 2 | 14.009 4 |
| Ne | -11.955 6 | 18.406 2 | 5.546 4 | -52.857 3 | 61.349 4 | 18.915 7 |
| Ar | -10.695 1 | 16.751 3 | 4.955 1 | -57.666 1 | 74.762 7 | 20.139 8 |
| Kr | -9.970 7 | 15.161 9 | 4.618 1 | -66.992 8 | 91.016 6 | 24.220 7 |
| Xe | -14.552 4 | 22.525 5 | 6.751 3 | -74.739 8 | 105.210 0 | 27.466 4 |


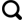
 甘公网安备 62010202000678号
甘公网安备 62010202000678号