0 引言
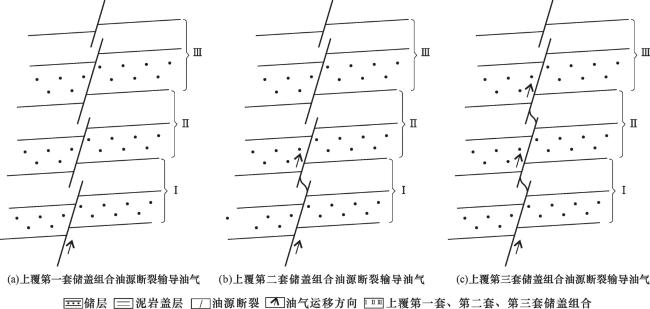
1 上覆不同储盖组合油源断裂输导油气时期
图1 上覆不同储盖组合油源断裂输导油气机理示意Fig.1 Mechanism of oil source fault transporting oil and gas to overlying different reservoir-cap assemblages |
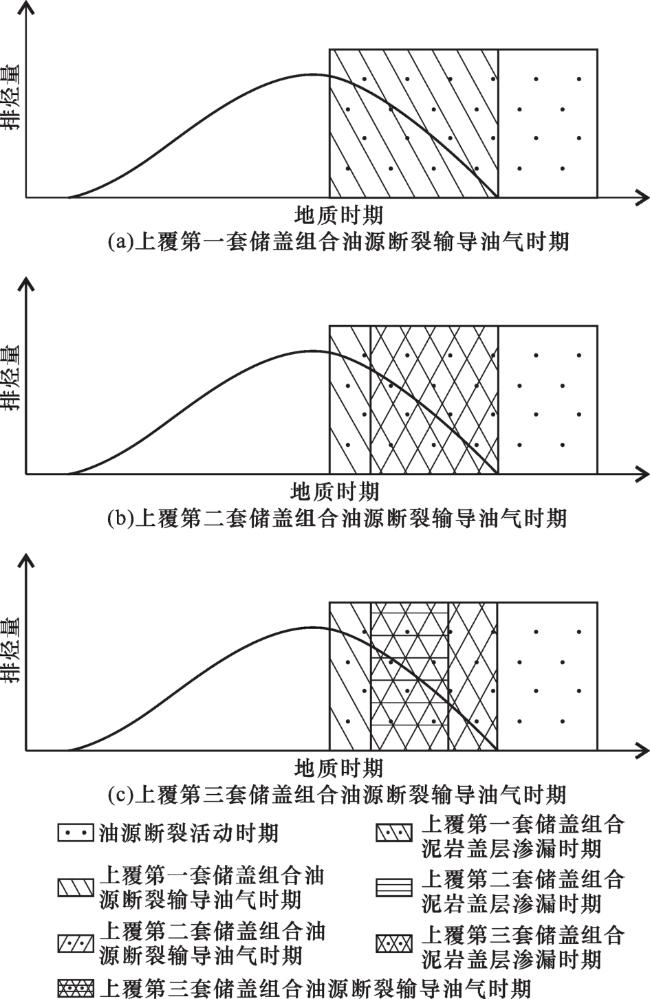
2 上覆不同储盖组合油源断裂输导油气时期的厘定方法
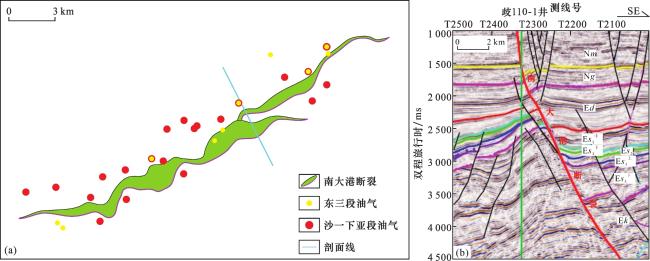
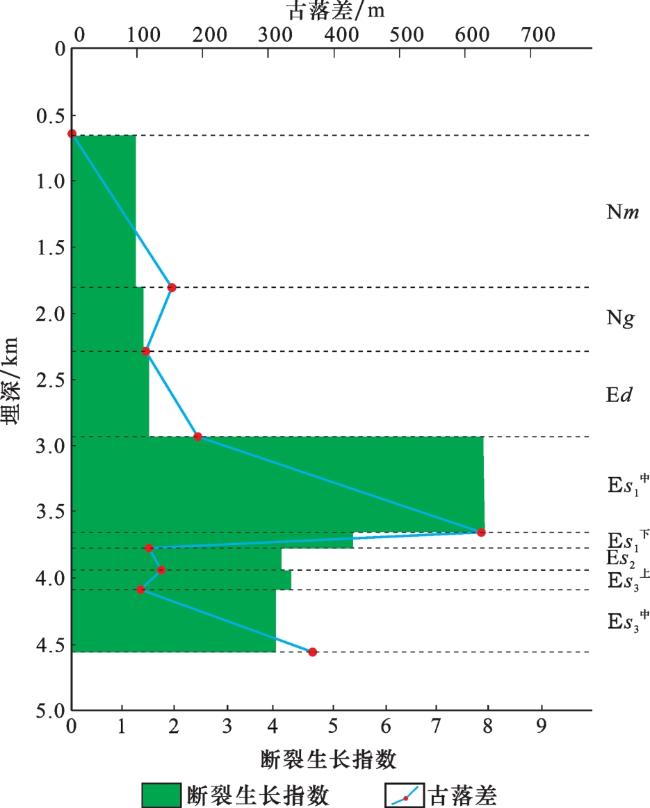
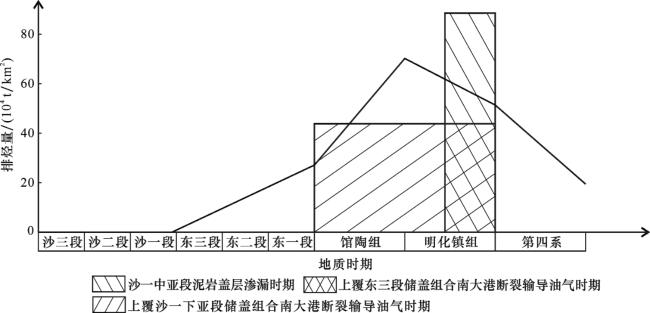
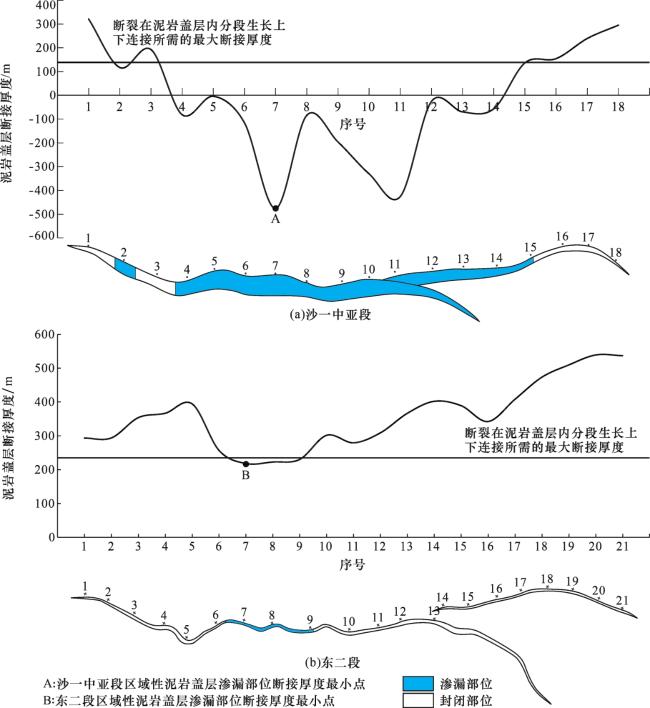
3 实例应用
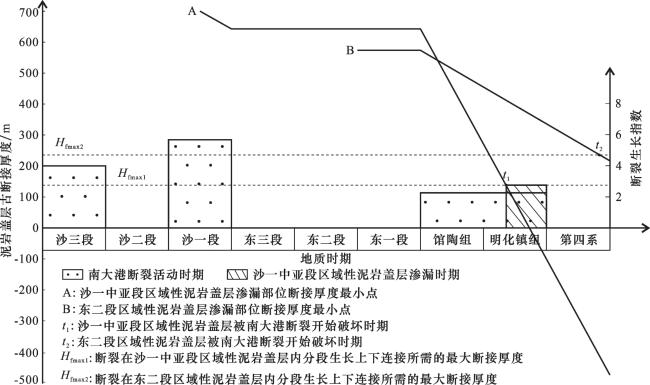
图7 南大港断裂处沙一中亚段和东二段区域性泥岩盖层渗漏部位厘定Fig.7 Determination of leakage position of regional mudstone caprock of the middle sub-member of Es 1 and Ed 2 at Nandagang Fault |


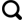
 甘公网安备 62010202000678号
甘公网安备 62010202000678号