0 引言
1 甲烷吸附分子模拟
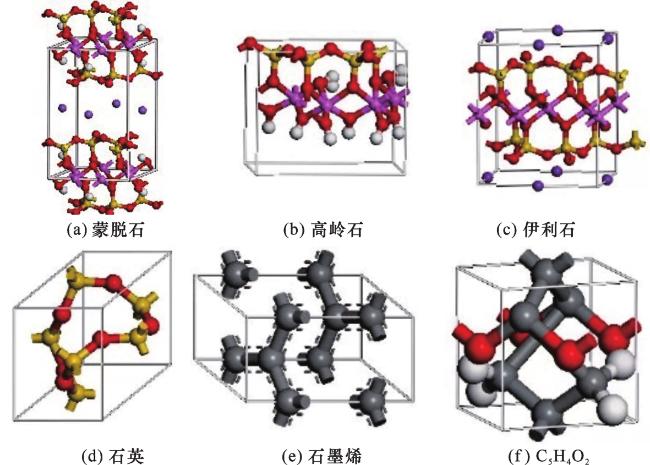
1.1 页岩纳米孔模型
表1 6种主要页岩成分的晶胞参数Table 1 Cell parameters of six shale components |
| 页岩成分 | a/nm | b/nm | c/nm | α/(°) | β/(°) | γ/(°) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 蒙脱石 | 0.523 | 0.906 | 1.25 | 90 | 90 | 99 |
| 高岭石 | 0.515 | 0.893 | 0.738 | 91.9 | 105 | 89.8 |
| 伊利石 | 0.520 | 0.895 | 1.018 | 90 | 90 | 99 |
| 石英 | 0.491 | 0.491 | 0.540 | 90 | 90 | 120 |
| 石墨烯 | 0.246 | 0.246 | 0.680 | 90 | 90 | 120 |
| C5H4O2 | 0.357 | 0.357 | 0.540 | 90 | 90 | 90 |
|
1.2 分子力场
2 甲烷在纳米孔中的吸附特性
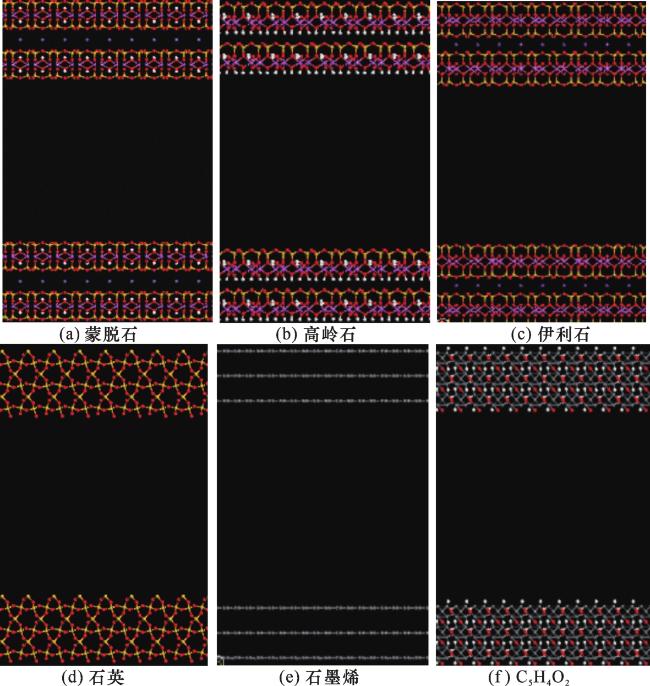
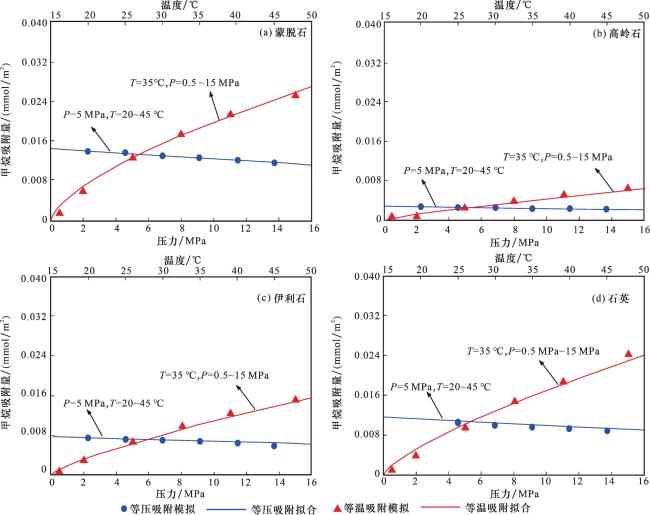
2.1 甲烷在有机质中的吸附规律
表3 有机质纳米孔的甲烷吸附常数Table 3 Methane absorption constants of organic matter nanopore |
| 纳米孔 | n 0/(mmol/m2) | α | β |
|---|---|---|---|
| 石墨烯 | 0.002 73 | 0.559 | 0.985 |
| C5H4O2 | 0.002 44 | 0.566 | 0.970 |
2.2 甲烷在黏土矿物和石英中的吸附规律
图4 黏土矿物与石英纳米孔中的甲烷吸附量与压力和温度的变化关系Fig.4 Variation of methane adsorption on temperature and pressure in clay mineral and quartz nanopores |
表4 黏土矿物及石英纳米孔的甲烷吸附常数Table 4 Methane absorption constants of clay mineral and quartz nanopores |
| 纳米孔 | n 0 /(mmol/m2) | α | β |
|---|---|---|---|
| 蒙脱石 | 0.001 260 | 0.650 | 0.950 |
| 伊利石 | 0.000 415 | 0.762 | 0.929 |
| 高岭石 | 0.000 135 | 0.803 | 0.913 |
| 石 英 | 0.000 722 | 0.735 | 0.945 |
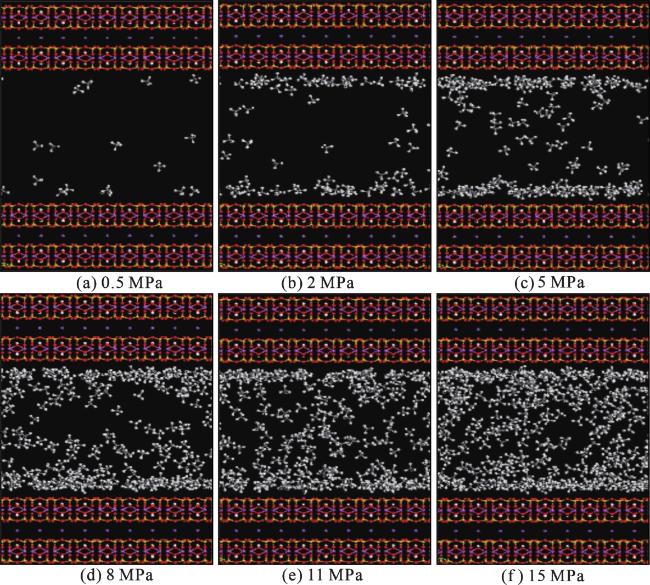
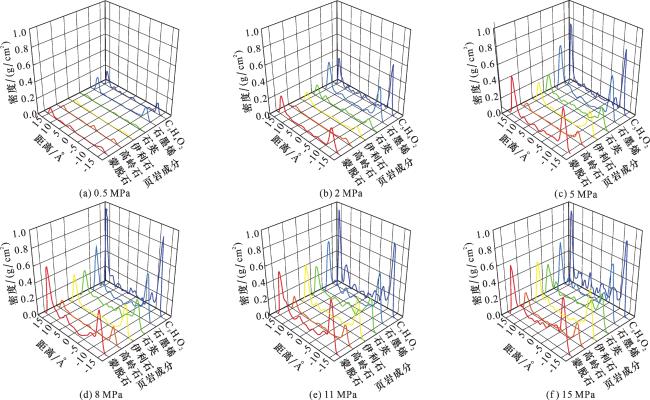
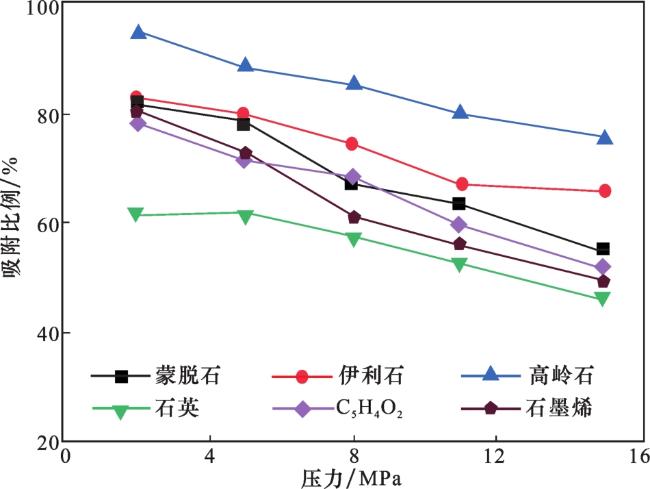
3 甲烷分子在纳米孔中的分布特征和吸附比例
表5 甲烷气相密度和吸附态界限Table 5 Gas-phase density and adsorption state boundaries of methane |
| 压力 | 纳米孔 | 蒙脱石 | 高岭石 | 伊利石 | 石英 | 石墨烯 | C5H4O2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 MPa | 气相密度/(g/cm3) | 0.099 | 0.018 | 0.060 | 0.0078 | 0.120 | 0.123 |
| 吸附态界限/nm | 0.502 | 0.490 | 0.534 | 0.511 | 0.514 | 0.496 | |
| 8 MPa | 气相密度/(g/cm3) | 0.142 | 0.028 | 0.086 | 0.112 | 0.162 | 0.159 |
| 吸附态界限/nm | 0.521 | 0.509 | 0.544 | 0.527 | 0.484 | 0.503 |


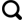
 甘公网安备 62010202000678号
甘公网安备 62010202000678号