0 引言
1 地质背景
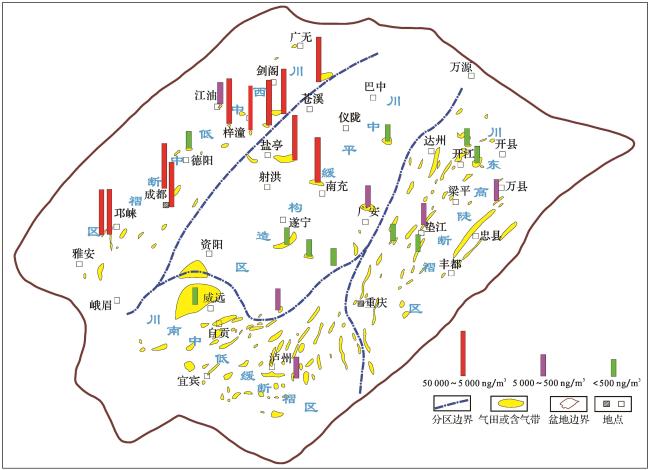
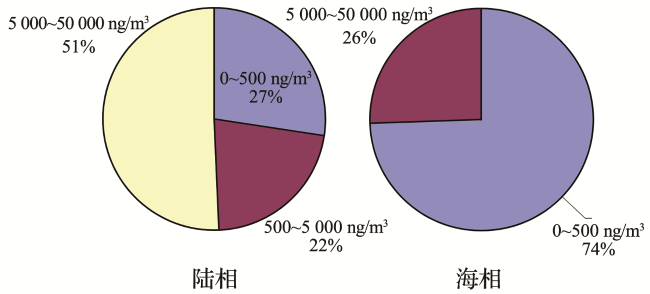
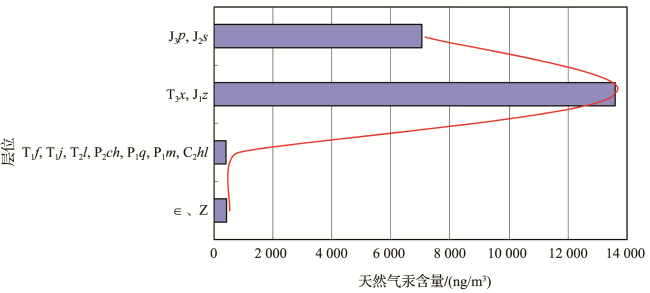
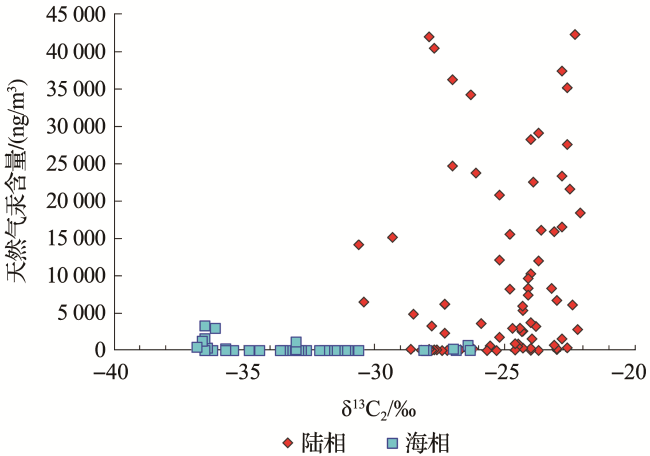
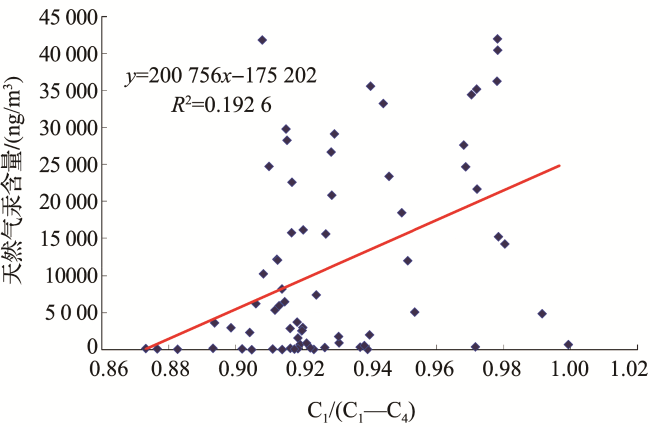
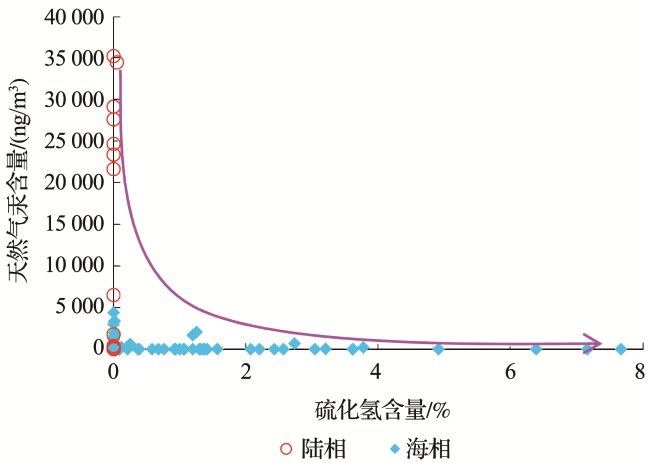
2 天然气中汞的分布特征
表2 四川盆地天然气汞含量检测数据Table 2 Detection data of mercury content in natural gas in Sichuan Basin |
| 地区 | 气田 /构造 | 层位 | 产层深度/m | 岩性 | 检测井数 | 汞含量/(ng/m3) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 最小值 | 最大值 | 平均值 | ||||||
| 川西 | 平落坝 | T3 x | 3 233~3 707 | 砂岩 | 4 | 381 | 27 600 | 18 600 |
| 邛西 | T3 x | 3 682~3 708 | 砂岩 | 2 | 34 400 | 35 200 | 34 800 | |
| 洛带 | J3 p,J2 s | 610~1 744 | 砂岩 | 14 | 78 | 28 200 | 7 260 | |
| 新都 | J3 p | 943~1 945 | 砂岩 | 6 | 342 | 22 600 | 10 100 | |
| 新场 | J3 p,J2 s | 2 100~2 600 | 砂岩 | 3 | 30 | 72 | 47 | |
| 中坝 | T3 x | 2 400~2 628 | 砂岩 | 10 | 889 | 6 900 | 3 080 | |
| 魏城 | T3 x | 3 832 | 砂岩 | 1 | 18 400 | 18 400 | 18 400 | |
| 老关庙 | T3 x | 3 672~3 738 | 砂岩 | 2 | 23 400 | 29 100 | 26 200 | |
| 文兴场 | T3 x,J1 z | 2 863~4 177 | 砂岩 | 3 | 2 000 | 33 200 | 20 600 | |
| 柘坝场 | T3 x,J1 z | 3 478~4 050 | 砂岩 | 2 | 11 900 | 35 600 | 23 700 | |
| 九龙山 | T3 x,J1 z | 3 103~3 563 | 砂岩 | 6 | 4 880 | 42 000 | 25 500 | |
| 川中 | 龙岗 | T1 f, P2 ch | 5 955~6 735 | 碳酸盐岩 | 7 | <10 | 686 | 224 |
| 八角场 | T3 x,J1 z | 2 544~3 352 | 砂岩 | 5 | 2 870 | 41 800 | 19 100 | |
| 西充 | T3 x | 2 118~3 151 | 砂岩 | 3 | 2 330 | 24 700 | 11 100 | |
| 广安 | T3 x | 1 719~2 449 | 砂岩 | 3 | <10 | 1 780 | 629 | |
| 磨溪 | T2 l | 2 657~2 694 | 碳酸盐岩 | 3 | <10 | <10 | <10 | |
| 潼南 | T3 x | 2 206~2 241 | 砂岩 | 3 | 28 | 156 | 95 | |
| 合川 | T3 x | 2 079~2 191 | 砂岩 | 3 | 18 | 191 | 100 | |
| 河包场 | T3 x, P2 ch,P1 m | 1 660~3 382 | 砂岩、碳酸盐岩 | 8 | <10 | 6 490 | 2 026 | |
| 川南 | 威远 | ∈、Z | 1 911~3 000 | 碳酸盐岩 | 4 | <10 | 1 680 | 420 |
| 庙高寺 | P1 q,P1 m,T1 j | 2 151~3 035 | 碳酸盐岩 | 4 | <10 | 4 390 | 1 420 | |
| 川东 | 黄龙场 | P2 ch,T1 f | 3 174~4 102 | 碳酸盐岩 | 5 | <10 | <10 | <10 |
| 五百梯 | P2 ch,C2 hl | 4 232~5 045 | 碳酸盐岩 | 8 | <10 | <10 | <10 | |
| 高峰场 | P2 ch,C2 hl | 3 802~3 888 | 碳酸盐岩 | 3 | 12 | 3 380 | 1 817 | |
| 沙坪场 | C2 hl | 4 061~5 180 | 碳酸盐岩 | 2 | 447 | 1 980 | 1 210 | |
| 板东 | P2 ch | 3 520 | 碳酸盐岩 | 1 | <10 | <10 | <10 | |
| 卧龙河 | T1 j,P1 q,P1 m,P2 ch,C2 hl | 1 288~4 744 | 碳酸盐岩 | 5 | <10 | 229 | 50 | |


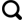
 甘公网安备 62010202000678号
甘公网安备 62010202000678号