0 引言
1 实验方法
1.1 仪器设备及流程
1.2 实验材料
表1 岩心基础参数和实验条件Table 1 Core parameters and experimental conditions |
| 孔隙度 /% | 渗透率/ (10-3 μm2) | S w/% | 直径×长度 /(cm×cm) | 初始孔隙压力 /MPa | 实验配产 /(L/min) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 12.7 | 1.63 | 69.9 | 2.5×52.0 | 20 | 0.50 |
| 40.1 | 20 | ||||
| 30.3 | 20 | ||||
| 10.6 | 0.58 | 71.0 | 2.5×51.5 | 20 | 0.05 |
| 56.6 | 20 | ||||
| 46.3 | 20 | ||||
| 32.1 | 20 | ||||
| 6.9 | 0.175 | 70.0 | 2.5×24.8 | 20 | 0.05 |
| 52.3 | 20 | ||||
| 41.8 | 20 | ||||
| 30.4 | 20 | ||||
| 5.9 | 0.063 | 71.1 | 2.5×52.2 | 20 | 0.05 |
| 53.6 | 20 | ||||
| 31.6 | 20 |
1.3 实验步骤
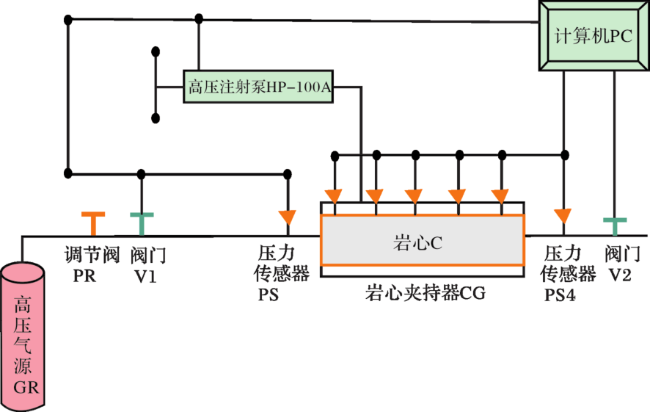
2 实验结果
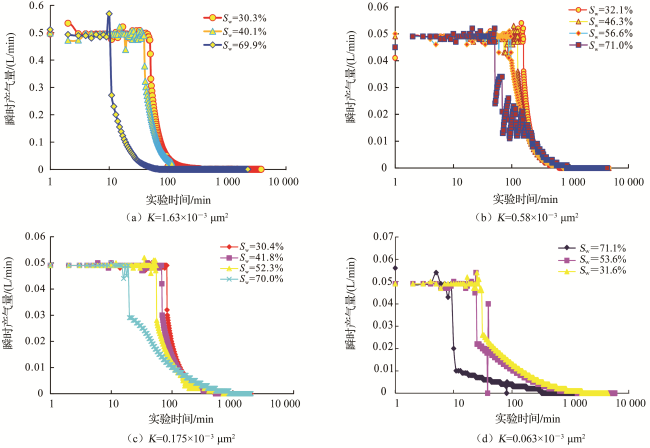
3 动用范围与压力分布预测
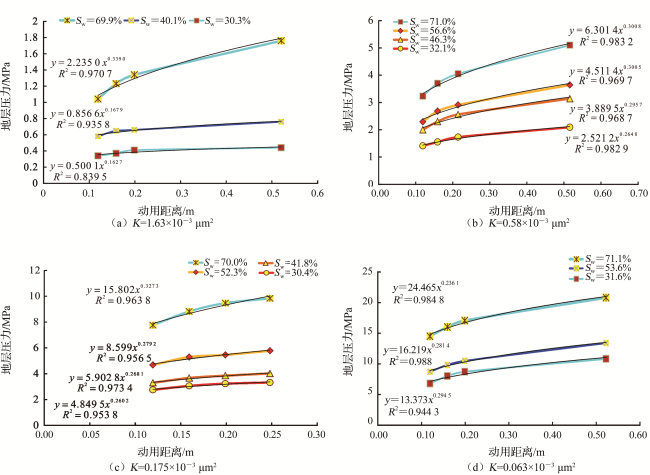
3.1 幂函数拟合关系
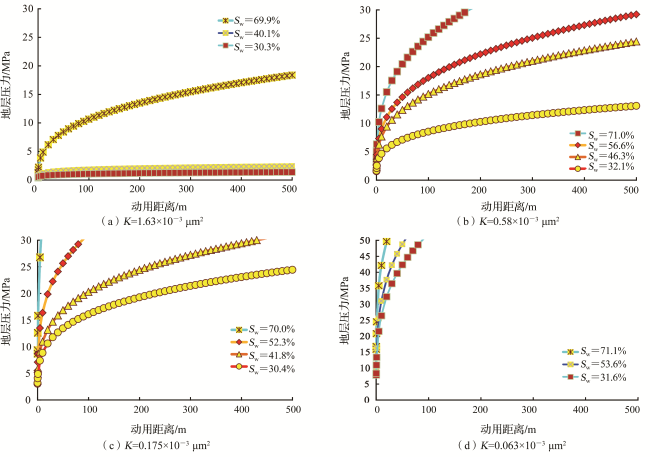
3.2 动用距离与压力分布
4 井网加密优化分析
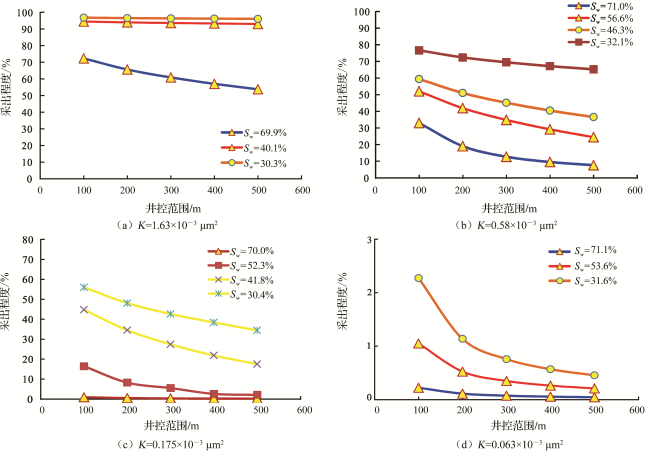
4.1 不同井控范围的采出程度评价
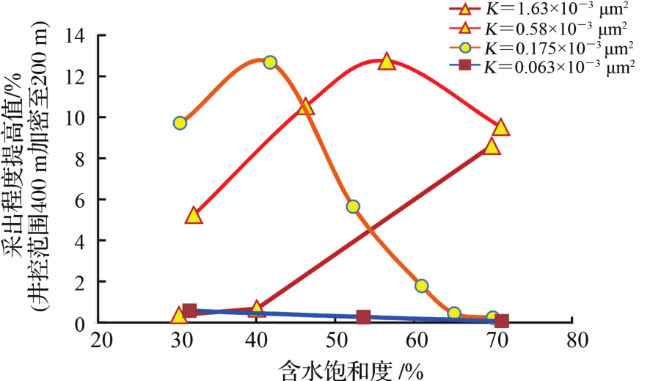
4.2 井网加密优化适用条件
图7 井控范围400 m加密至200 m采出程度提高幅度Fig.7 Well control range from 400 m to 200 m, the degree of recovery is improved |
表2 各类储层井网加密优化适用条件及判识Table 2 Applicable conditions and identification of well pattern infilling optimization in various reservoirs |
| 序号 | φ/% | K/(10-3 μm2) | S w/% | 采出程度/% | 适用条件判识 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 200 m | 400 m | 井控范围400 m加密至200 m提高幅度 | 提高5% | 提高10% | ||||
| 1 | 12.745 | 1.63 | 69.9 | 65.6 | 57.0 | 8.6 | √ | × |
| 2 | 12.745 | 1.63 | 40.1 | 93.9 | 93.2 | 0.7 | × | × |
| 3 | 12.745 | 1.63 | 30.3 | 96.5 | 96.1 | 0.4 | × | × |
| 4 | 10.6 | 0.58 | 71.0 | 19.0 | 9.5 | 9.5 | √ | × |
| 5 | 10.6 | 0.58 | 56.6 | 41.9 | 29.2 | 12.7 | √ | √ |
| 6 | 10.6 | 0.58 | 46.3 | 51.0 | 40.4 | 10.5 | √ | √ |
| 7 | 10.6 | 0.58 | 32.1 | 72.4 | 67.2 | 5.2 | √ | × |
| 8 | 6.9 | 0.175 | 70.0 | 0.4 | 0.2 | 0.2 | × | × |
| 9 | 6.9 | 0.175 | 52.3 | 8.2 | 2.6 | 5.6 | √ | × |
| 10 | 6.9 | 0.175 | 41.8 | 34.5 | 21.8 | 12.7 | √ | √ |
| 11 | 6.9 | 0.175 | 30.4 | 48.1 | 38.3 | 9.7 | √ | × |
| 12 | 5.9 | 0.063 | 71.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | × | × |
| 13 | 5.9 | 0.063 | 53.6 | 0.5 | 0.3 | 0.3 | × | × |
| 14 | 5.9 | 0.063 | 31.6 | 1.1 | 0.6 | 0.6 | × | × |


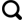
 甘公网安备 62010202000678号
甘公网安备 62010202000678号