0 引言
1 中国要突破当前单一的经济页岩气层组
1.1 中国经济页岩气层组及盆地均单一
图1 四川盆地及其毗邻南缘地区五峰组—龙马溪组和页岩气田分布特征Fig.1 Distribution map of the Wufeng-Longmaxi formations and shale gas fields in the Sichuan Basin and its adjacent southern areas |
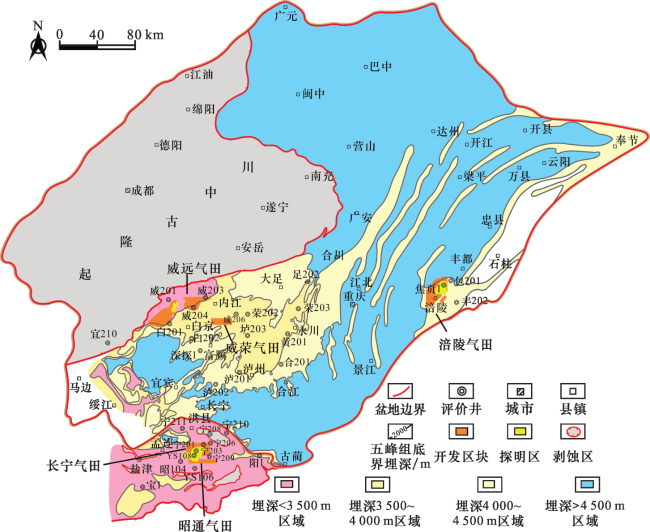
图2 中国主要富有机质黑色页岩分布特征Fig.2 Distribution map of the major organic rich black shale in China |
表1 中国主要盆地或地区重要页岩和经济页岩气层组有关参数Table 1 Relevant parameters of important shale and economic shale gas formations in major basins or regions of China |
| 沉积类型 | 盆地或地区 | 页岩地层 | 时代 | 面积/km2 | 厚度/m | TOC/% | 有机质类型 | 热成熟度(R O)/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 海相 | 华北地区 | 平凉组 | O2 p | 15 000 | 50~392.4 | 0.10~2.17 | I—II | 0.57~1.5 |
| 洪水庄组 | Pt3 jx | >20 000 | 40~100 | 0.95~12.83 | I | 1.10 | ||
| 下马岭组 | Pt3 jx | >20 000 | 50~170 | 0.85~24.30 | I | 0.60~1.65 | ||
| 四川盆地及南方地区 | 旧司组 | C1 j | 97 125 | 50~500 | 0.61~15.90 | I—II | 1.34~2.22 | |
| 应堂组—罗富组 | D2-3 y—D2-3 l | 236 355 | 50~1 113 | 0.53~12.10 | I—II | 0.99~2.03 | ||
| 五峰组—龙马溪组 | O3 w—S1 l | 389 840 | 23~847 | 0.41~25.73 | I—II | 1.60~4.91 | ||
| 筇竹寺组 | ∈1 q | 873 555 | 20~465 | 0.35~22.15 | I | 1.28~5.20 | ||
| 陡山沱组 | Z2 d | 290 325 | 10~233 | 0.58~12.00 | I | 2.00~4.50 | ||
| 塔里木盆地 | 印干组 | O3 y | 99 178 | 0~120 | 0.50~4.40 | I—II | 0.80~3.40 | |
| 萨尔干组 | O2-3 s | 101 125 | 0~160 | 0.61~4.65 | I—II | 1.20~4.60 | ||
| 玉尔吐斯组 | ∈1 y | 130 208 | 0~200 | 0.50~14.21 | I—II | 1.20~5.00 | ||
| 羌塘盆地 | 布曲组 | J2 b | 79 830 | 25~400 | 0.30~9.83 | Ⅲ | 1.79~2.40 | |
| 夏里组 | J2 x | 114 200 | 78~713 | 0.13~26.12 | Ⅱ | 0.69~2.03 | ||
| 肖茶卡组 | T3 x | 141 960 | 100~747 | 0.11~13.45 | Ⅱ | 1.13~5.35 | ||
| 海陆过渡相 | 四川盆地 | 梁山组—龙潭组 | P1 l—P2 l | 18 900 | 20~170 | 0.50~12.55 | Ⅲ | 1.80~3.00 |
| 滇东—鄂西 | 龙潭组 | P2 l | 132 000 | 20~200 | 0.35~6.50 | Ⅲ | 2.00~3.00 | |
| 中—下扬子 | 龙潭组 | P2 l | 65 700 | 20~600 | 0.10~12.00 | Ⅲ | 1.30~3.00 | |
| 华南地区 | 龙潭组 | P2 l | 84 400 | 50~600 | 0.10~10.00 | Ⅲ | 2.00~4.00 | |
| 鄂尔多斯盆地 | 山西组 | P2 sh | 250 000 | 30~180 | 0.50~31.00 | Ⅲ | 0.60~3.00 | |
| 太原组 | P1 t | 250 000 | 30~180 | 0.50~36.79 | Ⅲ | 0.60~3.00 | ||
| 本溪组 | C2 b | 250 000 | 30~180 | 0.50~25.00 | Ⅲ | 0.60~3.00 | ||
| 渤海湾盆地 | 二叠系 | P | 200 000 | 20~160 | 0.50~3.00 | Ⅲ | 0.50~2.60 | |
| 石炭系 | C | 200 000 | 20~180 | 0.50~3.00 | Ⅲ | 0.50~2.80 | ||
| 准噶尔盆地 | 滴水泉组—巴山组 | C1 d—C2 b | 50 000 | 120~300 | 0.17~26.76 | Ⅲ | 1.6~2.626 | |
| 陆相 | 松辽盆地 | 青一段 | K1 q 1 | 184 673 | 50~500 | 0.40~4.50 | Ⅰ—Ⅱ | 0.50~1.50 |
| 青二段、青三段 | K1 q 2-3 | 164 538 | 25~360 | 0.20~1.80 | Ⅱ | 0.50~1.40 | ||
| 渤海湾盆地 | 沙一段 | E3 s 1 | 8 816 | 50~250 | 0.80~27.30 | Ⅱ2 | 0.70~1.80 | |
| 沙三段 | E3 s 3 | 8 874 | 10~600 | 0.50~13.80 | Ⅰ—Ⅱ1 | 0.40~2.00 | ||
| 沙四段 | E3 s 4 | 7 911 | 10~400 | 0.80~16.70 | Ⅱ1 | 0.60~3.00 | ||
| 四川盆地 | 须家河组 | T3 x 1 | 41 800 | 50~300 | 1.00~4.00 | Ⅲ+Ⅱ2 | 1.60~3.60 | |
| T3 x 3 | 45 000 | 20~100 | 1.50~8.00 | Ⅲ | 1.20~3.60 | |||
| T3 x 5 | 63 900 | 10~200 | 1.00~9.00 | Ⅲ | 1.20~3.30 | |||
| 自流井组 | J1-2 zh | 90 000 | 40~180 | 0.80~2.00 | Ⅰ—Ⅱ1 | 0.60~1.60 | ||
| 鄂尔多斯盆地 | 长7段 | T3 ch 7 | 37 000 | 10~45 | 0.30~36.22 | Ⅰ—Ⅱ1 | 0.60~1.16 | |
| 长9段 | T3 ch 9 | 14 000 | 10~15 | 0.36~11.30 | Ⅰ—Ⅱ1 | 0.90~1.30 | ||
| 吐哈盆地 | 西山窑组 | J2 x | 18 870 | 100~600 | 0.50~20.00 | Ⅲ | 0.40~1.6 | |
| 八道湾组+三工河组 | J1 b-s | 20 050 | 100~600 | 0.50~20.00 | Ⅲ | 0.50~1.80 | ||
| 塔里木盆地 | 克孜勒努尔组 | J2 k | 130 480 | 50~700 | 1.90~15.86 | Ⅲ | 0.60~1.60 | |
| 阳霞组 | J1 y | 83 400 | 40~120 | 2.50~20.00 | Ⅲ | 0.40~1.60 | ||
| 塔里奇克组 | T3 t | 125 500 | 100~600 | 15.50~23.70 | Ⅲ | / | ||
| 黄山街组 | T3 h | 133 450 | 200~550 | 1.00~30.00 | Ⅲ | 0.60~2.80 | ||
| 准噶尔盆地 | 西山窑组 | J2 x | 90 500 | 25~250 | 0.50~20.00 | Ⅲ | 0.50~2.30 | |
| 三工河组 | J1 s | 93 430 | 25~240 | 0.50~31.00 | Ⅲ | 0.50~2.40 | ||
| 八道湾组 | J1 b | 97 100 | 50~350 | 0.60~35.00 | Ⅲ | 0.50~2.50 | ||
| 乌尔禾组 | P2-3 w | 63 400 | 50~450 | 0.70~12.08 | Ⅰ—Ⅱ1 | 0.80~1.00 | ||
| 夏子街组 | P2 x | 57 200 | 50~150 | 0.41~10.80 | Ⅰ—Ⅱ1 | 0.56~1.31 | ||
| 风城组 | P1 f | 31 800 | 50~300 | 0.47~21.00 | Ⅰ—Ⅱ1 | 0.54~1.41 |
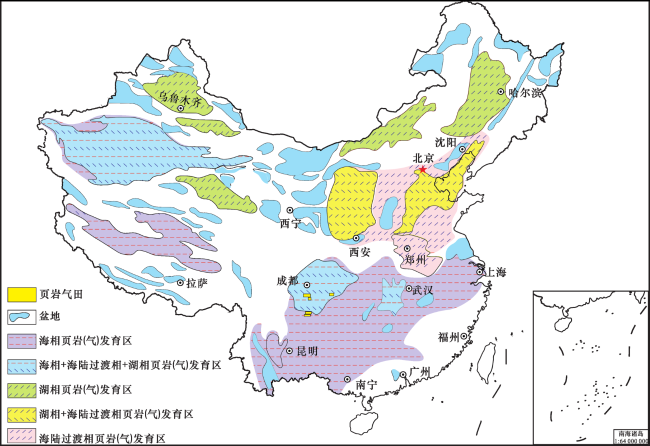
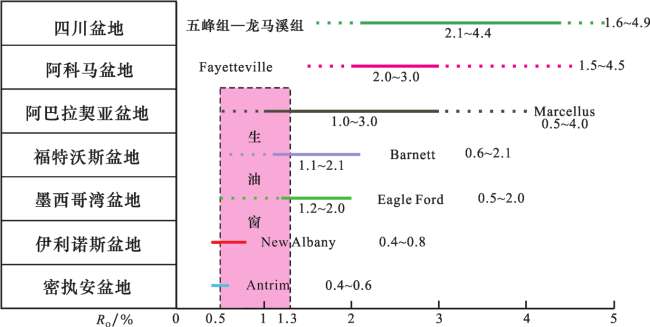
1.2 美国多经济页岩气层组及盆地保障了其世界产气之冠地位
表2 美国中、东部主要盆地经济页岩气层组相关参数Table 2 Relevant parameters of economic shale gas formations in major basins in the middle and eastern United States |
| 盆地 | 经济页岩 气层组 | 时代 | 面积/(104 km2) | 深度/m | 净厚度/m | TOC/% | 有机质类型 | R O/% | 2018年产气量/(108 m3/a)[1,8,9] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 阿巴拉契亚 | Ohio | D3 | 4.14 | 600~1 500 | 9~30 | 0~4.7 | I—II | 0.4~1.3 | 34(1999年) |
| Marcellus | D2 | 2.5 | 914~4 511 | 15~61 | 3.0~12.0 | II、Ⅲ | 1.5~3.0 | 2 152 | |
| Utica | O3 | 1.3 | 2 500 | 30~50 | 2.5 | II | 2.2 | 651 | |
| 二叠 | Wolfcamp | P | 17.4 | 2 500~3 000 | 60~2 150 | 2.0~9.0 | I、II1 | 0.7~1.5 | 934 |
| 阿科马 | Fayetteville | C1 | 2.3 | 457~2 591 | 6~61 | 4.0~9.8 | I、II1 | 1.2~4.5 | 142 |
| Woodford | D3 | 1.2 | 1 220~4 270 | 37~67 | 1.0~14.0 | I、II1 | 1.1~3.0 | 368 | |
| 福特沃斯 | Barnett | C1 | 1.7 | 1 981~2 591 | 15~60 | 2.0~6.0 | II1 | 1.1~2.1 | 340 |
| 路易斯安那 | Haynesville | J | 2.3 | 3 048~4 511 | 61~91 | 0.7~6.2 | I、II1 | 2.2~3.2 | 736 |
| 西湾 | Eagle Ford | K2 | 0.3 | 1 220~4 270 | 61 | 4.3 | II | 0.5~2.0 | 566 |
| 阿纳达科 | Woodford | D3 | 0.18 | 3 500~4 420 | 60 | 4.0~7.0 | II | 1.1~3.5 | 375 |
| 密执安 | Antrim | D1 | 0.3 | 183~671 | 21~37 | 1.0~2.0 | I | 0.4~0.6 | 22 |
| 伊利诺斯 | New Albany | D3-C1 | 11.13 | 180~1 500 | 30~122 | 1.0~25.0 | II | 0.4~0.8 | 8.5(2011年) |
| 威利斯顿 | Bakken | D3-C1 | 1.69 | 1 370~2 290 | 20~50 | 10.0~20.0 | II | 0.7~1.3 | 243 |
表3 美国主要经济页岩气层组及其盆地近五年来页岩气年产量和储量[1,9]Table 3 Annual production and reserves of the major economic shale gas formations in the United States and their basins in the past five years[1,9] |
| 盆地 | 经济页岩气层组 | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 产量 | 储量 | 产量 | 储量 | 产量 | 储量 | 产量 | 储量 | 产量 | 储量 | ||
| /(1012 m3) | |||||||||||
| Appalachian | Marcellus | 0.138 8 | 2.392 8 | 0.164 2 | 2.058 6 | 0.178 4 | 2.381 4 | 0.195 4 | 3.505 6 | 0.215 2 | 3.825 6 |
| Fort Worth | Barnett | 0.051 7 | 0.688 8 | 0.045 3 | 0.482 0 | 0.039 6 | 0.475 7 | 0.034 0 | 0.543 7 | 0.034 0 | 0.487 0 |
| Western Gulf | Eagle Ford | 0.053 3 | 0.669 8 | 0.062 3 | 0.555 8 | 0.059 5 | 0.642 8 | 0.053 8 | 0.775 9 | 0.056 6 | 0.872 2 |
| Texas-Louisiana Salt | Haynesville/Bossier | 0.039 6 | 0.470 1 | 0.039 6 | 0.362 6 | 0.042 5 | 0.368 1 | 0.051 0 | 1.016 6 | 0.073 6 | 1.265 8 |
| Arkoma,Anadarko,S.OK | Woodford | 0.024 0 | 0.470 0 | 0.028 3 | 0.526 0 | 0.031 1 | 0.572 0 | 0.036 8 | 0.637 1 | 0.036 8 | 0.606 0 |
| Arkoma | Fayetteville | 0.029 3 | 0.330 7 | 0.026 1 | 0.202 2 | 0.019 8 | 0.178 4 | 0.017 0 | 0.201 0 | 0.014 2 | 0.169 9 |
| Appalachian | Utica/Pt.Pleasant | 0.012 5 | 0.180 8 | 0.028 3 | 0.352 0 | 0.040 0 | 0.438 9 | 0.048 1 | 0.750 4 | 0.065 1 | 0.676 8 |
| Permian Basin | Wolfcamp,Cline | 0.008 5 | 0.085 7 | 0.048 1 | 0.540 9 | 0.062 3 | 0.903 3 | 0.093 4 | 1.322 4 | ||
| Williston | Bakken/Three Forks | 0.019 8 | 0.288 8 | 0.025 5 | 0.339 8 | ||||||
| 小计 | 0.349 2 | 5.203 0 | 0.402 6 | 4.624 9 | 0.459 0 | 5.598 2 | 0.518 2 | 8.622 4 | 0.614 4 | 9.565 5 | |
| 其他页岩气 | 0.031 5 | 0.451 5 | 0.028 1 | 0.347 5 | 0.022 3 | 0.342 6 | 0.008 2 | 0.096 4 | 0.010 0 | 0.122 8 | |
| 美国所有页岩气 | 0.380 7 | 5.654 5 | 0.430 7 | 4.972 4 | 0.481 3 | 5.940 8 | 0.526 4 | 8.718 8 | 0.624 4 | 9.688 3 | |
1.3 中美经济页岩气层组对比及启示
1.3.1 经济页岩气层组仅分布在部分盆地中
1.3.2 储量大产量高的经济页岩气层组分布在构造稳定或相对稳定的大盆地
1.3.3 超大型经济页岩气层组是勘探研究的主攻大目标
2 经济页岩气层组的R O区间值
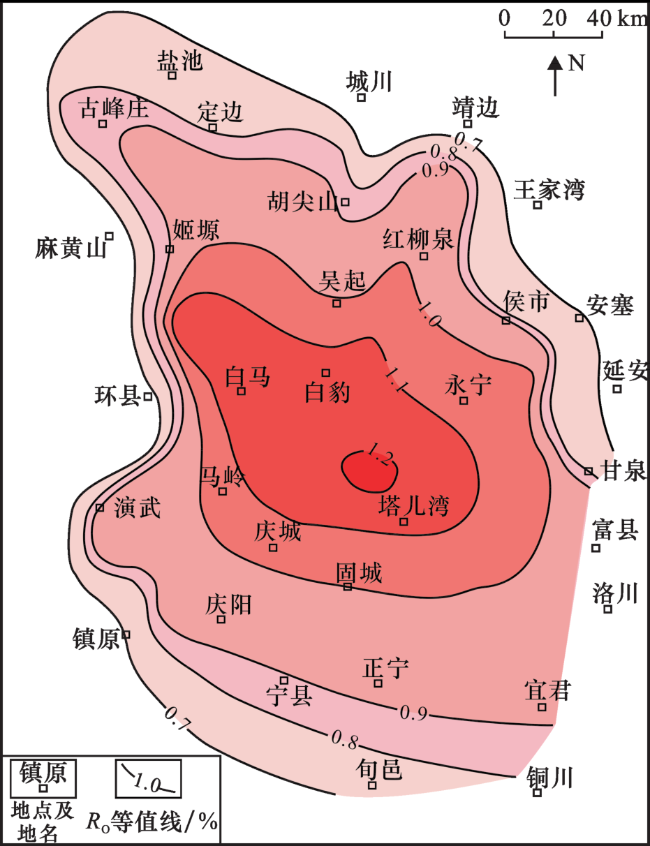
2.1 页岩气田R O及其经济页岩气层组R O的关系
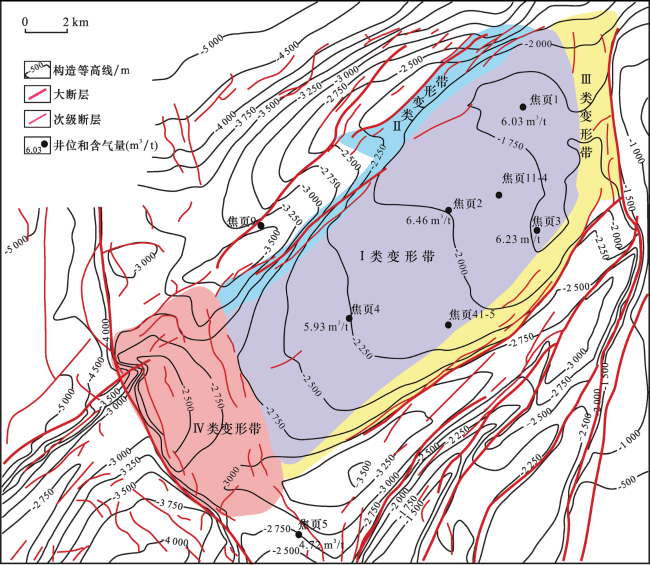
表4 五峰组—龙马溪组页岩气田相关井R O值Table 4 R O values of the related wells in the shale gas field of Wufeng-Longmaxi formations |
| 气田 | 地质储量/(108 m3) | 井号 | 井深/m | R O/% | 气田 | 地质储量/(108 m3) | 井号 | 井深/m | R O/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 长宁—昭通 | 1 361.8 | 宁211 | 2 313~2 341 | 3.2 | 威远 | 威202 | 2 591 | 2.4 | |
| 宁201 | 2 463.1~2 500 | 3.15~3.62 | 威204 | 3 519.3~3 536 | 2.4~2.5 | ||||
| 宁203 | 2 130~2 400 | 3.15~3.24 | 自201 | 3 659.3~3 671 | 2.1~2.2 | ||||
| 昭101 | 1 700~1 760 | 4.08~4.44 | 自202 | 3 628.3~3 648.2 | 2.3~2.4 | ||||
| 昭104 | 2 035~2 037 | 3.4 | 涪陵 | 6 008.14 | 焦页1 | 2 408~2 416 | 2.9 | ||
| 昭104 | 2 117.5 | 3.3 | 焦页8—2 | 2 622 | 3.1 | ||||
| YSL1-1H | 2 002~2 028 | 3.2 | 焦页4 | 2 609.35 | 3.85 | ||||
| YS109 | 2 180~2 210 | 2.18~3.8 | 焦页1 | 2 395~2 535.3 | 2.57~3.78 | ||||
| 威远 | 1 838.95 | 威201 | 1 520~1 523 | 2.1 | 焦页1 | 2 370~2 416 | 2.20~3.06 |
2.2 腐泥型页岩生油窗高阶段内的页岩气
2.3 中美页岩气R O对比及其启示
2.3.1 中美页岩气田R O及中国有利勘探区
2.3.2 中国生油窗高阶期勘探页岩气探讨
2.4 勘探研究煤系经济页岩气层组
3 世界首个页岩气大气田开发启示
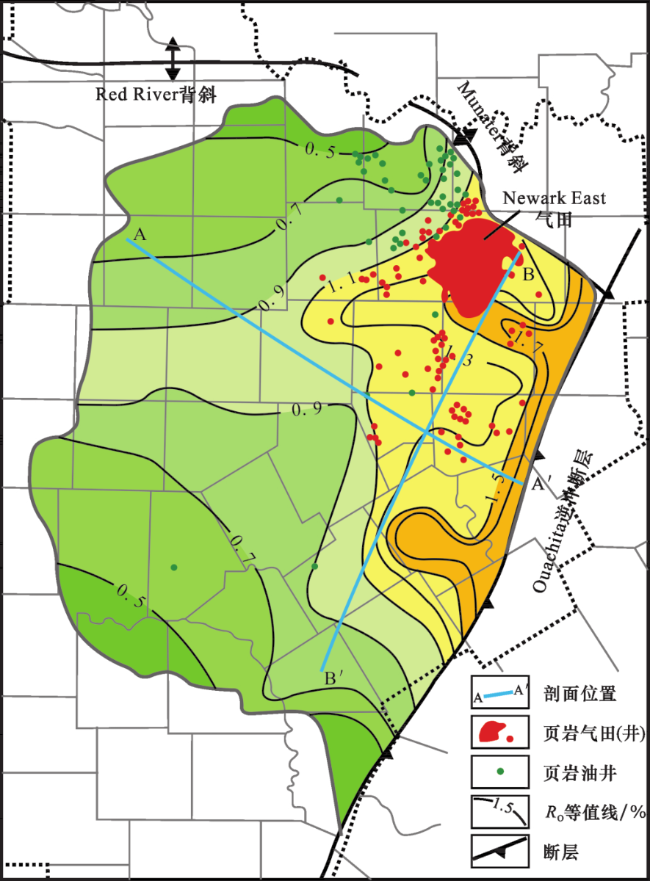
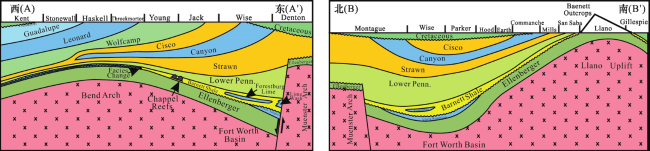
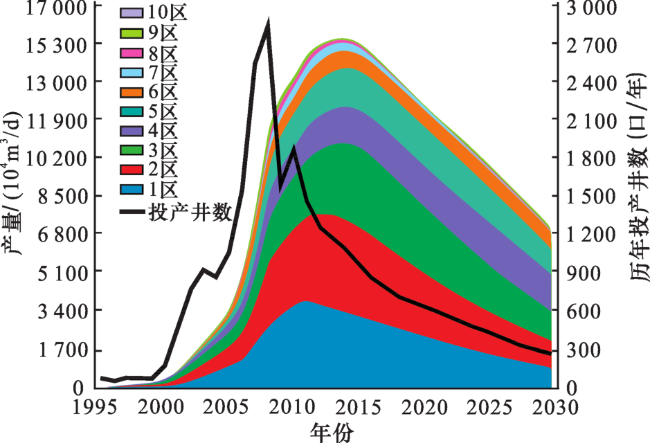
3.1 Barnett页岩气田勘探开发历程
3.2 Barnett页岩气田产量变化与趋势
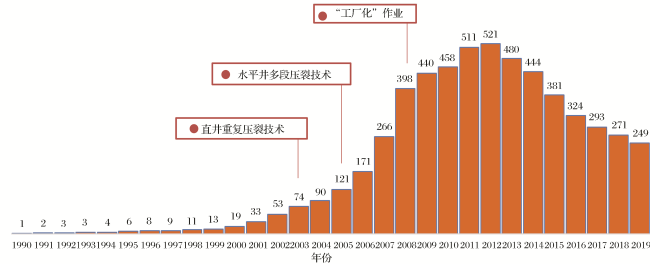
表5 Barnett页岩1990—2019年页岩气产量与钻井数统计[36,39,40]Table 5 Statistics of the shale gas production and drilling wells of Barnett shale in 1990-2019[36,39,40] |
| 时间/年 | 1980 | 1981 | 1982 | 1983 | 1984 | 1985 | 1986 | 1987 | 1988 | 1989 | 1990 | 1991 | 1992 | 1993 | 1994 | 1995 | 1996 | 1997 | 1998 | 1999 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 当年钻井数/口 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 6 | 11 | 8 | 4 | 7 | 9 | 20 | 18 | 14 | 27 | 42 | 76 | 56 | 74 | 72 | 77 |
| 累计钻井数/口 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 8 | 19 | 27 | 31 | 38 | 47 | 67 | 85 | 99 | 126 | 168 | 244 | 300 | 374 | 446 | 523 |
| 产量/(108 m3) | 1 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 6 | 8 | 9 | 11 | 13 | ||||||||||
| 时间/年 | 2000 | 2001 | 2002 | 2003 | 2004 | 2005 | 2006 | 2007 | 2008 | 2009 | 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 |
| 当年钻井数/口 | 109 | 517 | 789 | 938 | 877 | 1 085 | 1 606 | 2 560 | 2 921 | 1 637 | 1 804 | 1 025 | 1 531 | 1 506 | 1 002 | 850 | 602 | 513 | 461 | 453 |
| 累计钻井数/口 | 632 | 1 149 | 1 938 | 2 876 | 3 753 | 4 838 | 6 444 | 9 004 | 11 925 | 13 562 | 15 366 | 16 391 | 17 922 | 19 428 | 20 430 | 21 280 | 21 882 | 22 395 | 22 856 | 23 309 |
| 产量/(108 m3) | 19 | 33 | 53 | 74 | 90 | 121 | 171 | 266 | 398 | 440 | 458 | 511 | 521 | 480 | 444 | 381 | 324 | 293 | 271 | 249 |


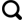
 甘公网安备 62010202000678号
甘公网安备 62010202000678号