研究大量现场实际生产经历可以发现,50%左右的油气可采地质储量都是在产量递减过程中产出,递减期内产出油气数量大,持续时间长,递减规律复杂
[1]。因此,研究产量递减规律对油气田生产动态预测、油气生产规划工作具有重要意义
[2]。基于此,国内外研究者
[3]提出了大量产量递减模型,其中的Arps模型递减应用最为广泛,但是利用该模型分析常规油气井产量递减时,很多情况下出现递减指数可能出现
n<-1或
n>1的情况,造成累计产量无限大的不合理性
[4]。主要原因在于Arps递减模型适合于达到拟稳定状态的流动,而致密低渗透油气井生产很难达到拟稳定状态。因此,在此模型基础上,国内外学者
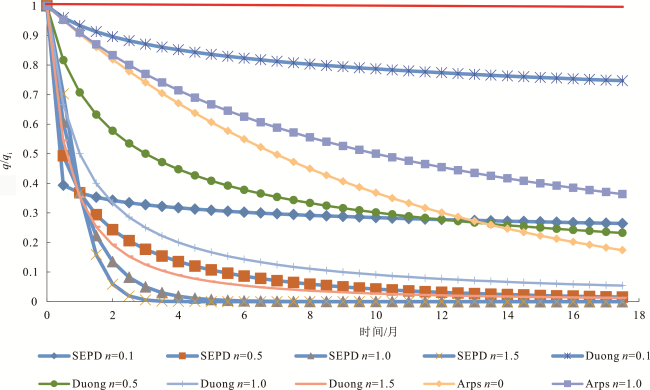
[5,6]提出了通过对Arps模型中的递减指数加以修正的方法,还有学者提出了一些新模型,如SEPD模型
[7,8]、Duong模型
[9,10]和组合模型
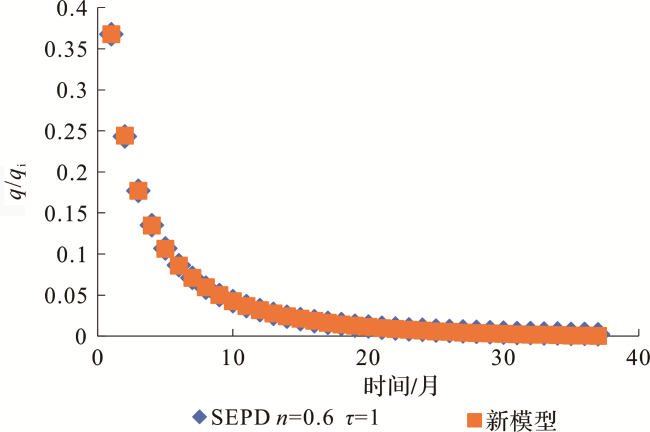
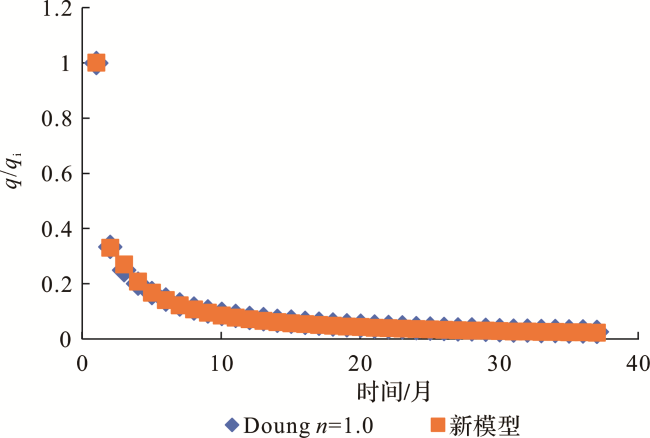
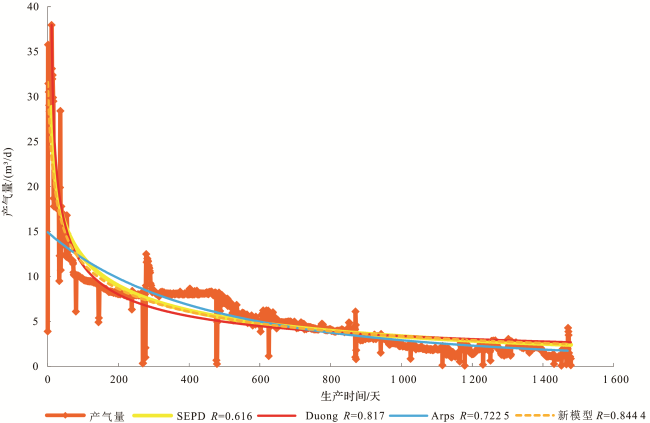
[11,12,13]。SEPD模型与Arps模型中指数递减类似,区别在于:Arps指数递减的递减率为常数,而SEPD模型递减率是变化的
[14];Duong模型基本原理是当流体处于裂缝线性流时,流量与时间存在一定关系,当气井产量递减处于缓慢递减的稳定阶段时,该方法预测结果较为准确,但是受生产前期液体反排或工作制度影响,会导致生产数据离散波动,造成多解问题。与此同时,这些模型在实际应用时,具体选择哪种模型进行产量递减分析往往难以确定
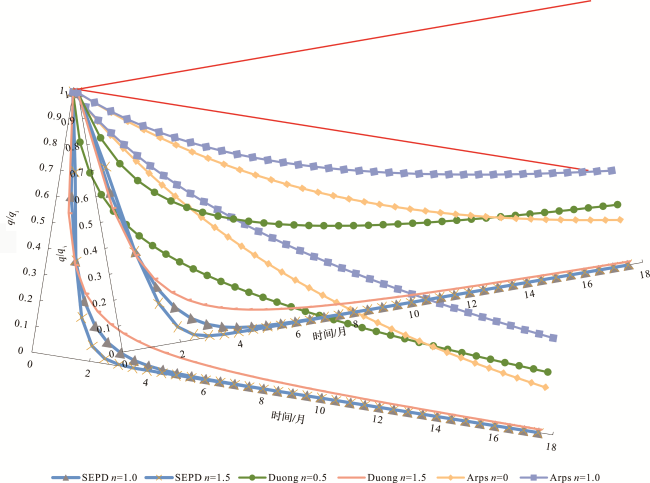
[15]。针对以上问题,本文提出一种新的产量递减模型。


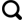
 甘公网安备 62010202000678号
甘公网安备 62010202000678号