0 引言
1 地质概况
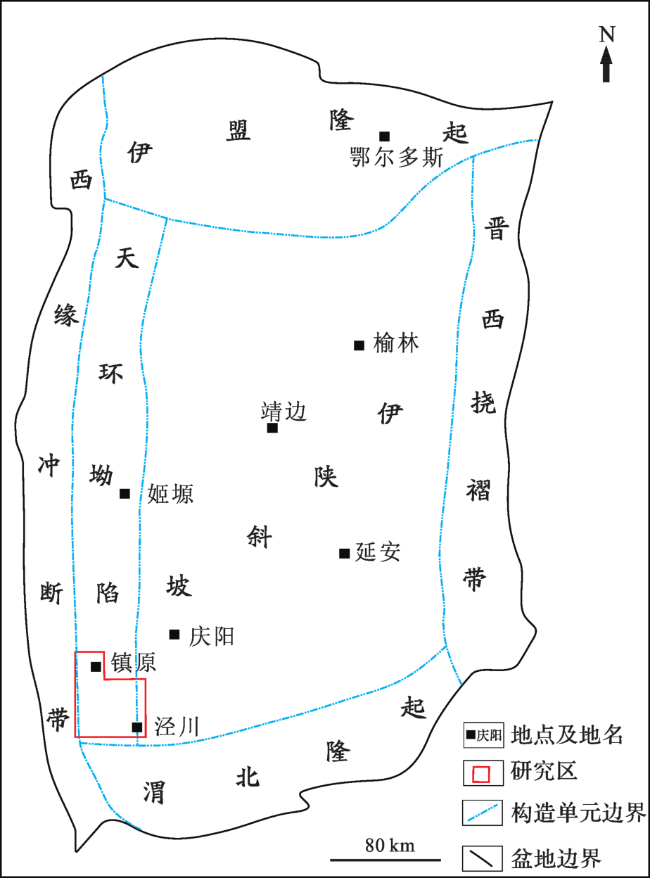
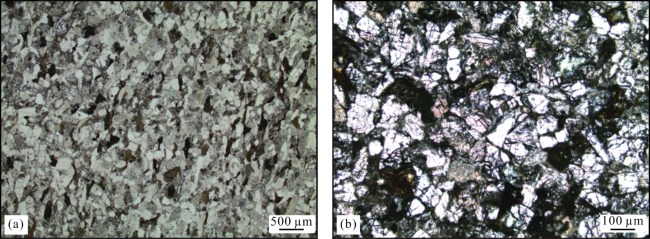
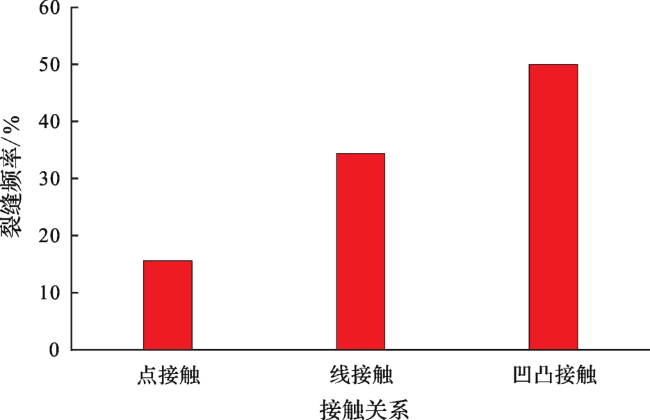
2 微观裂缝成因类型
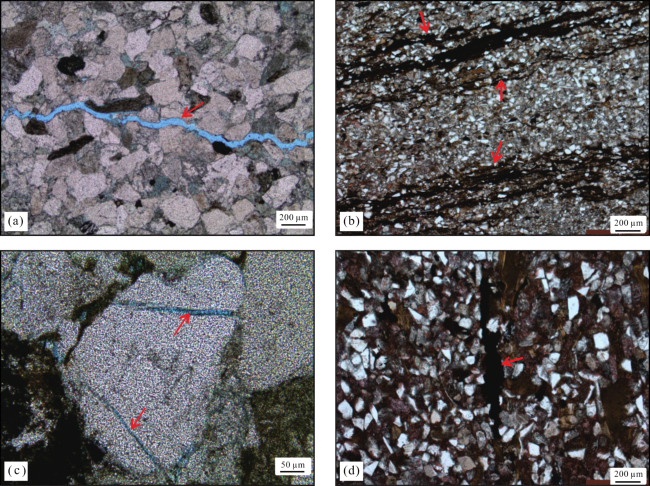
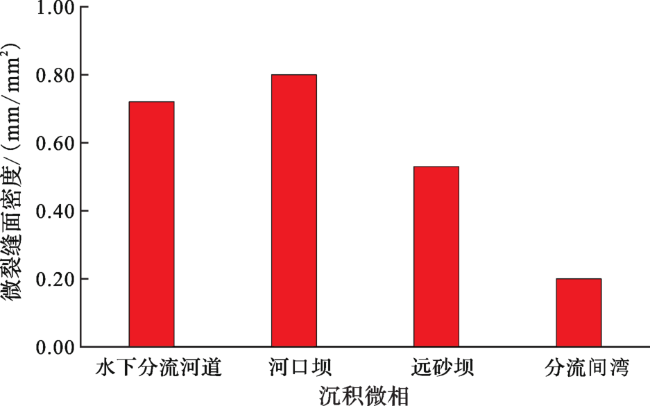
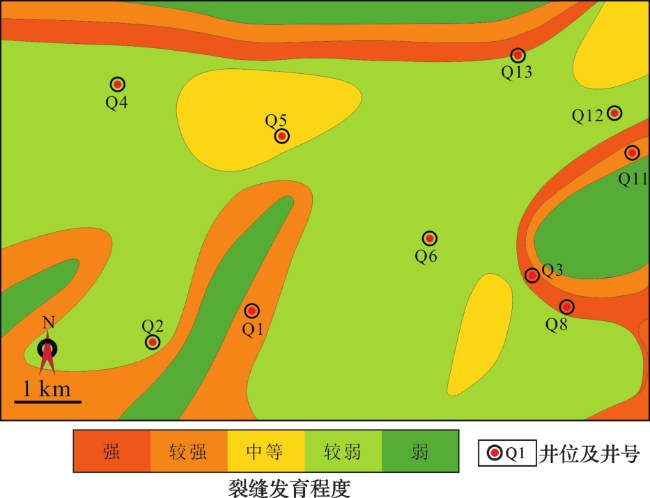
3 微观裂缝分布特征
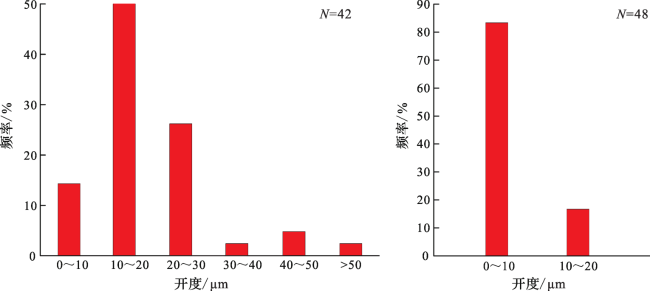
图3 微观裂缝面密度分布频率(a)穿粒缝面密度分布频率图 (b)粒内缝和粒缘缝面密度分布频率图 Fig.3 The distribution frequency diagram of microfracture areal intensities |
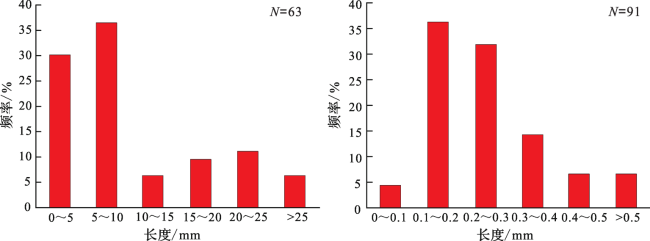
图4 微观裂缝长度分布频率(a)穿粒缝长度分布频率图 (b)粒内缝和粒缘缝长度分布频率图 Fig.4 The distribution frequency diagram of microfracture lengths |


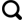
 甘公网安备 62010202000678号
甘公网安备 62010202000678号