0 引言
1 地质背景
2 实验分析及方法
表1 鄂尔多斯盆地临兴地区上古生界天然气组分和碳同位素Table 1 The natural gas composition and carbon isotope in Upper Paleozoic in Linxing area, Ordos Basin |
| 井号 | 层位 | 组分含量/% | 干燥 系数 | δ13C/‰(VPDB) | R O/%① | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CH4 | C2H6 | C3H8 | iC4H10 | nC4H10 | CO2 | N2 | C1 | C2 | C3 | ||||
| X-1 | P2 sq | 99.32 | 0.21 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.40 | 0.00 | 0.998 | / | / | / | / |
| X-2 | P2 sh | 93.06 | 0.98 | 0.21 | 0.04 | 0.05 | 0.04 | 5.54 | 0.986 | -37.7 | -25.5 | -23.5 | 0.58 |
| X-3 | P2 sh | 97.96 | 1.56 | 0.28 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0 | 0.11 | 0.981 | -36 | -26.1 | -23.5 | 0.77 |
| X-4 | P2 sh | 96.82 | 1.35 | 0.36 | 0.06 | 0.07 | 0.02 | 1.2 | 0.981 | -37.3 | -27.2 | -24.8 | 0.62 |
| X-5 | P2 sh | 97.14 | 1.17 | 0.2 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 1.32 | 0.985 | -37.5 | -27.1 | -24.0 | 0.6 |
| X-6 | P2 sh | 99.11 | 0.15 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.57 | 0 | 0.990 | / | / | / | 1.95 |
| X-7 | P2 sh | 91.16 | 4.69 | 1.33 | 0.19 | 0.26 | 0.02 | 1.94 | 0.934 | -34.8 | -27.5 | -25.3 | 0.94 |
| X-8 | P2 sh | 93.93 | 2.73 | 0.76 | 0.13 | 0.19 | 0.04 | 1.76 | 0.961 | -36.4 | -26.6 | -24.7 | 0.72 |
| X-9 | P2 sh | 93.82 | 1.15 | 0.32 | 0.06 | 0.09 | 0.01 | 3.78 | 0.983 | -36.5 | -28.9 | -26.0 | 0.71 |
| X-10 | P2 sh | 98.92 | 0.84 | 0.13 | 0 | 0 | 0.11 | 0 | 0.990 | -32.9 | -23.9 | -21.6 | 1.28 |
| X-11 | P2 sh | 98 | 1.44 | 0.28 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.06 | 0.11 | 0.982 | -37.2 | -26.1 | -24.1 | 0.63 |
| X-12 | P2 sh | 94.56 | 3.6 | 0.9 | 0.14 | 0.15 | 0.08 | 0.49 | 0.952 | -34.6 | -25.9 | -24.5 | 0.97 |
| X-13 | P1 s | 90.74 | 5.2 | 1.68 | 0.23 | 0.32 | 0.05 | 1.45 | 0.924 | -33.2 | -28.1 | -26.2 | 1.21 |
| X-14 | P1 t | 96.04 | 0.75 | 0.08 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 2.1 | 0.97 | 0.991 | -39.8 | -24.1 | -20.3 | 0.41 |
| X-15 | P1 t | 92.68 | 6.31 | 0.28 | 0.13 | 0.12 | 0.15 | 0.45 | 0.931 | -41.3 | -22.3 | / | 0.32 |
| X-16 | P1 t | 93.33 | 0.12 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.02 | 6.47 | 0.990 | -40.4 | -26.5 | -19.1 | 0.38 |
| X-17 | P1 t | 96.53 | 1.14 | 0.17 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 1.8 | 0.25 | 0.986 | -41.1 | -24.8 | -22.8 | 0.33 |
| X-18 | P1 t | 95.93 | 1.48 | 0.23 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 1.58 | 0.62 | 0.982 | -39.6 | -24.6 | -22.7 | 0.43 |
| X-19 | P1 t | 95.92 | 0.27 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2.2 | 1.6 | 0.990 | -40.3 | / | / | 0.38 |
| X-20 | P1 t | 93.37 | 0.17 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0 | 5.50 | 0.96 | 0.990 | -46.5 | / | / | / |
|
表2 鄂尔多斯盆地临兴地区上古生界天然气轻烃参数Table 2 The light hydrocarbon parameters of natural gas in Upper Paleozoic in Linxing area, Ordos Basin |
| 井号 | 层位 | nC7/% | MCH/% | ∑DMCP/% | C5-7正构烷烃/% | C5-7异构烷烃/% | C5-7环烷烷烃/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X-2 | P2 sh | 12.4 | 65.8 | 21.9 | 18.5 | 55.4 | 26.1 |
| X-4 | P2 sh | 24.5 | 58.2 | 17.3 | 30.9 | 56.5 | 12.6 |
| X-5-1 | P2 sh | 14.9 | 66.7 | 18.5 | 15.3 | 47.0 | 37.7 |
| X-5-2 | P2 sh | 14.5 | 65.7 | 19.8 | 25.6 | 52.0 | 22.4 |
| X-8 | P2 sh | 26.8 | 53.5 | 19.7 | 30.6 | 46.5 | 22.9 |
| X-9 | P2 sh | 26.6 | 52.7 | 20.8 | 14.4 | 26.8 | 58.8 |
| X-7 | P2 sh | 29.1 | 57.0 | 13.9 | 35.9 | 43.9 | 20.2 |
| X-13 | P1 s | 22.6 | 60.6 | 16.8 | 33.0 | 52.3 | 14.7 |
| X-14-1 | P1 t | 14.4 | 63.7 | 21.9 | 13.2 | 34.2 | 52.5 |
| X-14-2 | P1 t | 12.1 | 69.6 | 18.3 | 20.2 | 44.8 | 35.0 |
| X-17 | P1 t | 15.2 | 67.8 | 17.0 | 18.2 | 39.7 | 42.1 |
表3 鄂尔多斯盆地临兴地区上古生界烃源岩地球化学参数Table 3 The geochemical parameters of source rocks in Upper Paleozoic in Linxing area, Ordos Basin |
| 类别 | 有机碳/% | (S 1+S 2)/(mg/g) | R O/% | T max/℃ | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P1 s | 煤 | ||||
| 暗色泥岩 | |||||
| P1 t | 煤 | ||||
| 暗色泥岩 | |||||
| C2 b | 煤 | ||||
| 暗色泥岩 | |||||
|
3 天然气地球化学特征
3.1 组分特征
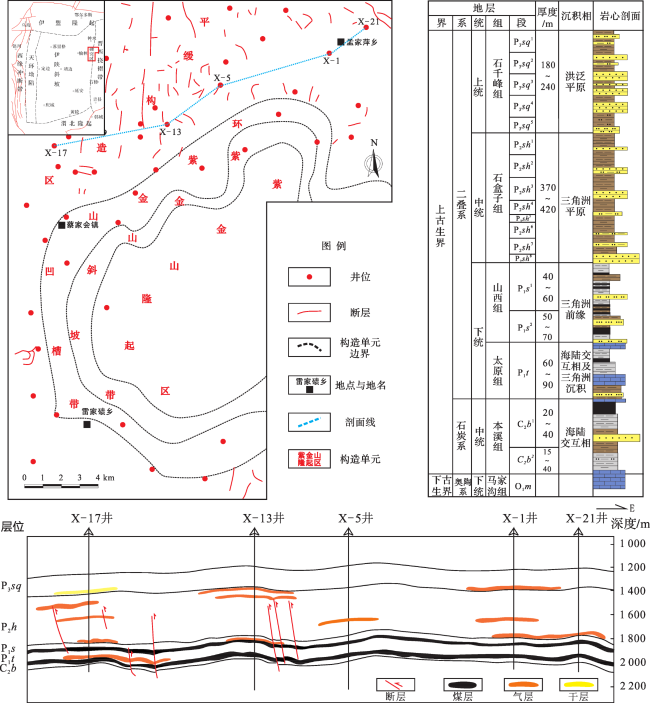
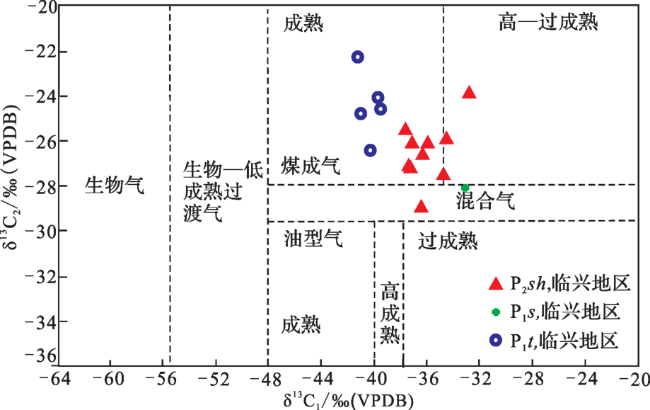
3.2 碳同位素特征
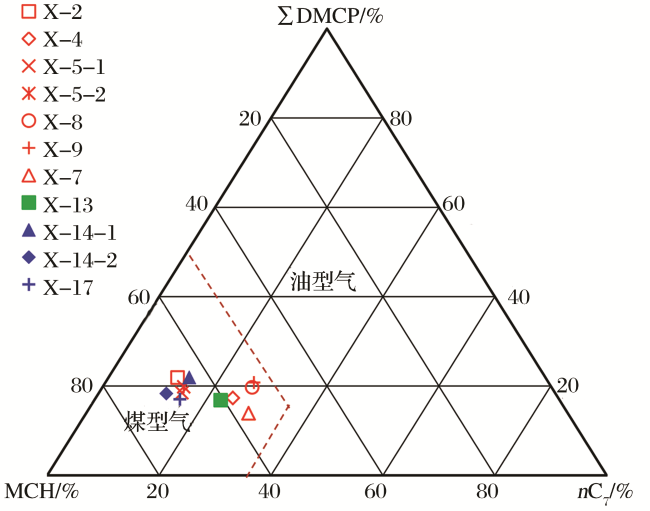
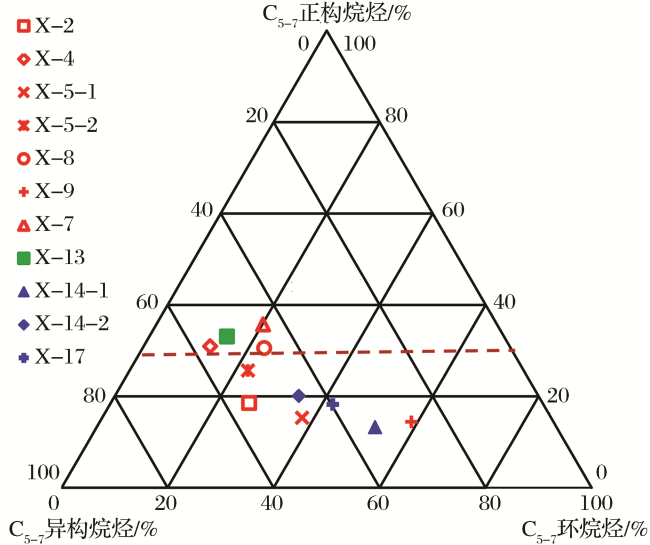
3.3 轻烃特征
4 天然气成因分析
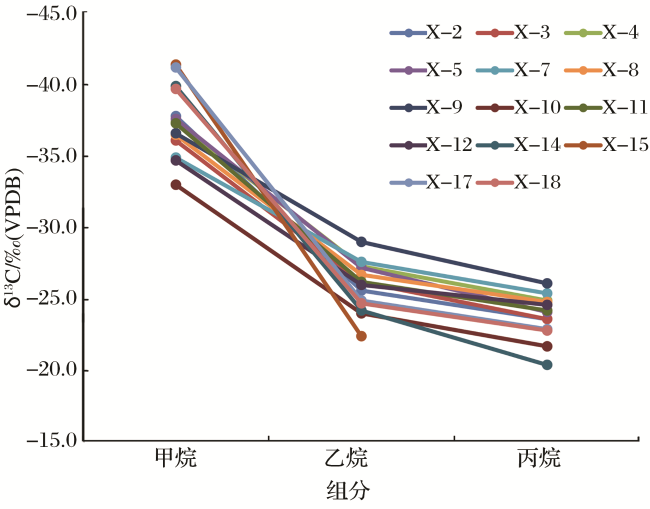
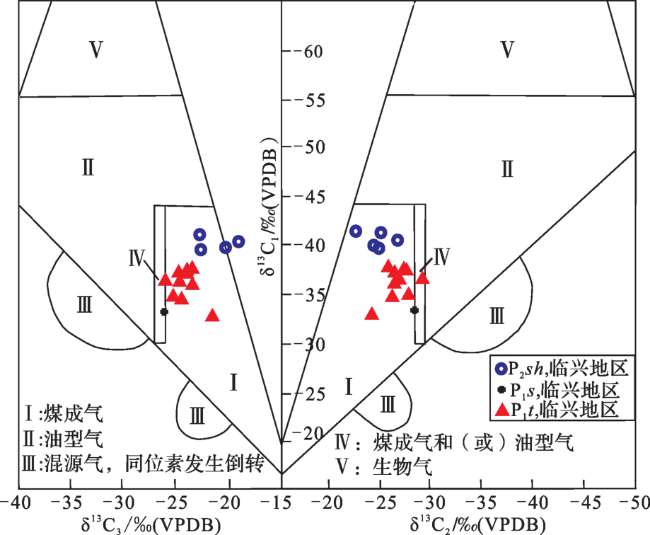
4.1 碳同位素判识成因
图4 天然气δ13C1—δ13C2成因类型鉴别图版(图版来自于文献[44])Fig.4 The identification of genetic types of natural gas δ13C2-δ13C1 (Plate from Ref.[44]) |
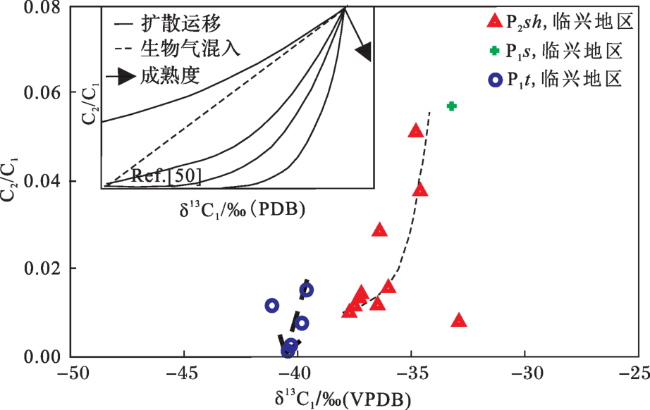
4.2 轻烃判识成因
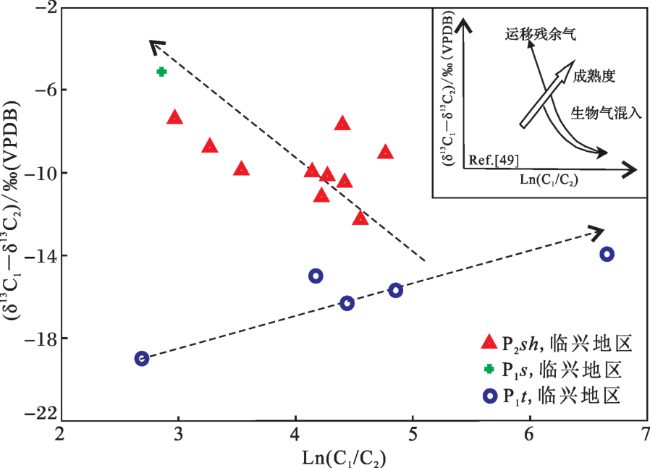
5 天然气来源分析
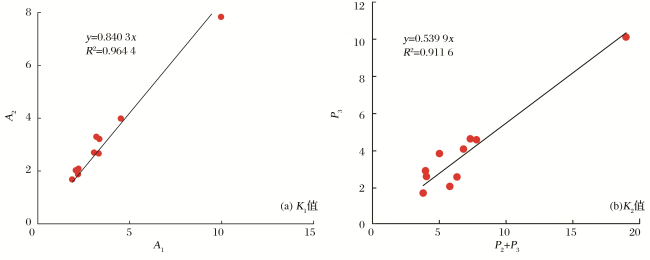
表4 临兴地区上古生界天然气K 1值和K 2值分布Table 4 The distribution of K 1 and K 2 values of natural gas in Upper Paleozoic in Linxing area |
| 井号 | 层位 | A 1/% | A 2/% | P 2/% | P 3/% | N 2/% | K 1/% | K 2/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X-4 | P2 h | 2.22 | 2.08 | 2.99 | 2.53 | 1.06 | 1.06 | 0.63 |
| X-5-1 | P2 h | 4.52 | 3.99 | 5.02 | 4.50 | 2.78 | 1.13 | 0.58 |
| X-5-2 | P2 h | 2.19 | 1.87 | 2.42 | 2.84 | 1.55 | 1.17 | 0.71 |
| X-8 | P2 h | 3.06 | 2.70 | 4.32 | 2.00 | 1.48 | 1.13 | 0.34 |
| X-9 | P2 h | 9.97 | 7.83 | 14.04 | 10.02 | 4.95 | 1.27 | 0.53 |
| X-7 | P2 h | 3.32 | 2.66 | 4.69 | 2.08 | 1.63 | 1.25 | 0.33 |
| X-13 | P1 s | 1.88 | 1.68 | 2.64 | 1.64 | 1.15 | 1.12 | 0.43 |
| X-14-1 | P1 t | 3.35 | 3.21 | 4.01 | 4.56 | 3.32 | 1.04 | 0.62 |
| X-14-2 | P1 t | 2.07 | 2.03 | 2.72 | 3.04 | 2.30 | 1.02 | 0.61 |
| X-17 | P1 t | 3.19 | 3.29 | 4.41 | 4.00 | 2.42 | 0.97 | 0.59 |
图9 临兴地区上古生界天然气Ln(C1/C2)—(δ13C1-δ13C2)关系Fig.9 The relationship diagram of natural gas Ln(C1/C2)vs.(δ13C1⁃δ13C2)in Upper Paleozoic in Linxing area |


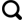
 甘公网安备 62010202000678号
甘公网安备 62010202000678号