0 引言
1 研究区概况
2 结果与讨论
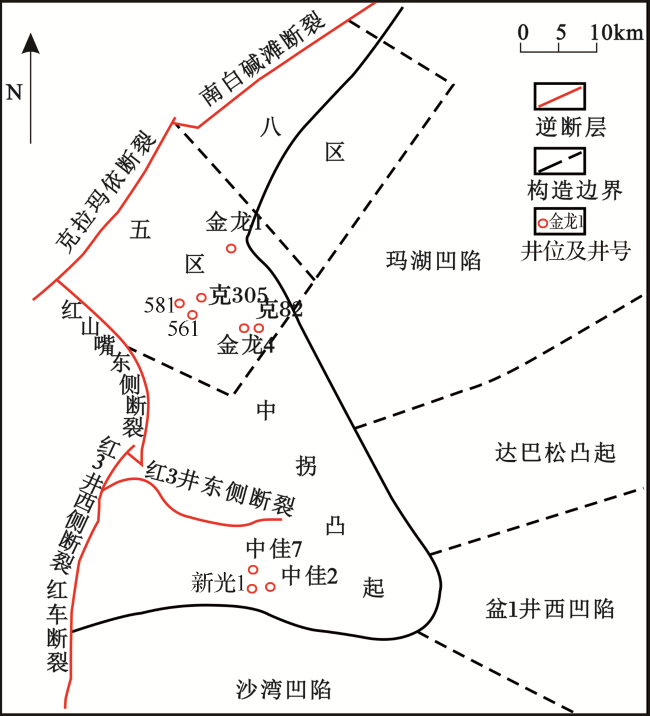
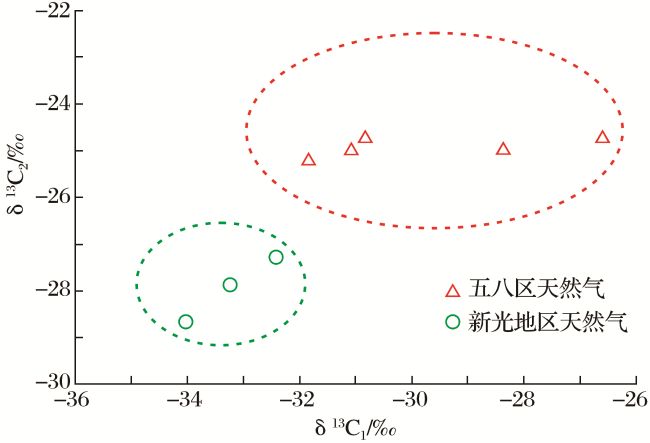
2.1 新光地区佳木河组天然气与典型佳木河组来源天然气地球化学特征对比
图2 准噶尔盆地中拐凸起新光地区佳木河组天然气与五八区天然气碳同位素特征Fig.2 Carbon isotope characteristics of natural gas in Jiamuhe Formation in Xinguang area, Wuba area of Karamay Oil Field, Junggar Basin |
表1 准噶尔盆地中拐凸起新光地区及五八区佳木河组天然气碳同位素及轻烃组成特征Table 1 Carbon isotope and light hydrocarbon composition of natural gas in Jiamuhe Formation, Xinguang area and Wuba area, Zhongguai Uplift, Junggar Basin |
| 井区 | 井号 | 层位 | 天然气碳同位素 /‰ | 干燥系数 C1/(C1-C5) | C7轻烃组成 /% | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| δ13C1 | δ13C2 | δ13C3 | 甲基环己烷 | 正庚烷 | 二甲基环戊烷 | ||||
| 新光地区 | 中佳2 | P1 j | -33.24 | -27.87 | -27.74 | 0.96 | 37.11 | 50.62 | 12.27 |
| 新光1 | P1 j | -32.51 | -27.36 | -26.56 | 0.96 | 37.89 | 50.57 | 11.54 | |
| 中佳7 | P1 j | -34.11 | -27.88 | -28.06 | 0.97 | 34.78 | 43.48 | 21.74 | |
| 五八区 | 金龙4 | P1 j | -31.08 | -24.96 | -21.96 | 0.96 | 74.16 | 17.54 | 8.30 |
| 金龙4 | P1 j | -30.83 | -24.74 | -21.97 | 0.96 | 70.86 | 18.54 | 10.60 | |
| 金龙2 | P1 j | -31.84 | -25.18 | -20.80 | 0.96 | 58.24 | 21.30 | 20.46 | |
| 克305 | P1 j | -26.60 | -24.70 | -20.92 | 0.97 | 75.57 | 12.80 | 11.62 | |
| 克305 | P1 j | -28.37 | -24.95 | / | 0.97 | 73.75 | 15.86 | 10.39 | |
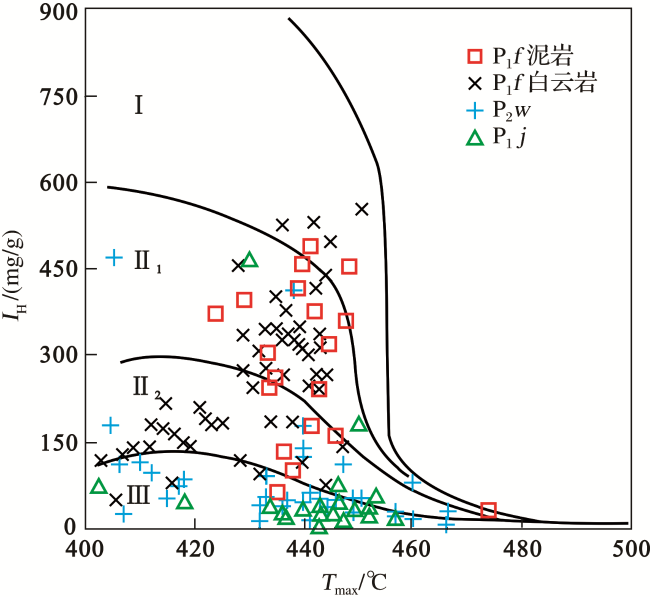
2.2 二叠系烃源岩生烃潜力分析
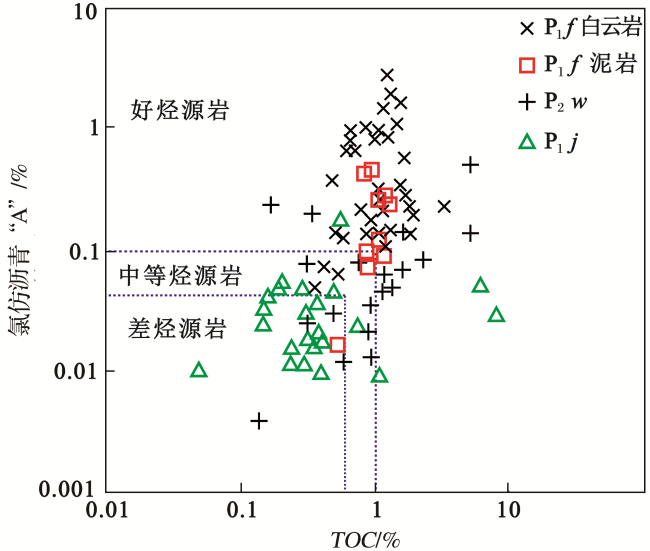
图4 准噶尔盆地西北缘二叠系烃源岩TOC与氯仿沥青“A”相关关系Fig.4 Correlation diagram of TOC andchloroform asphalt “A” of Permian source rocks in the northwestern margin, Junggar Basin |
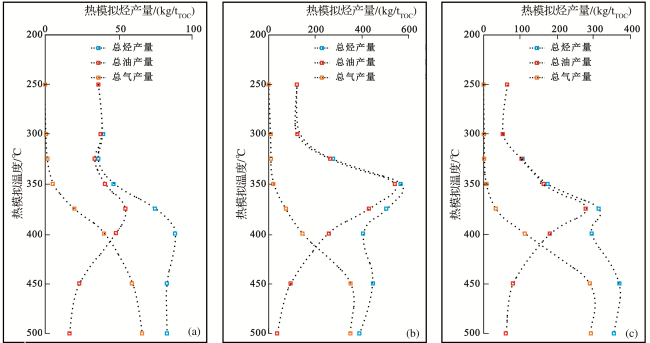
2.3 二叠系烃源岩生烃模拟实验
表2 准噶尔盆地西北缘二叠系烃源岩热模拟样品信息Table 2 Thermal simulation sample information of Permian source rocks in the northwestern margin of Junggar Basin |
| 井号 | 层位 | 岩性 | TOC/% | I H/(mg/g) | T max/℃ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 拐16 | P1 j | 凝灰质泥岩 | 2.76 | 71 | 433 |
| 乌351 | P1 f | 凝灰岩 | 2.37 | 608 | 436 |
| 金探1 | P2 w | 深灰色泥岩 | 2.36 | 394 | 450 |
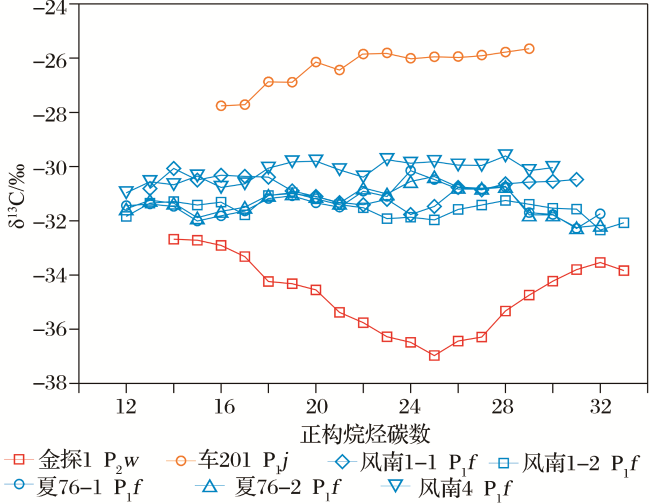
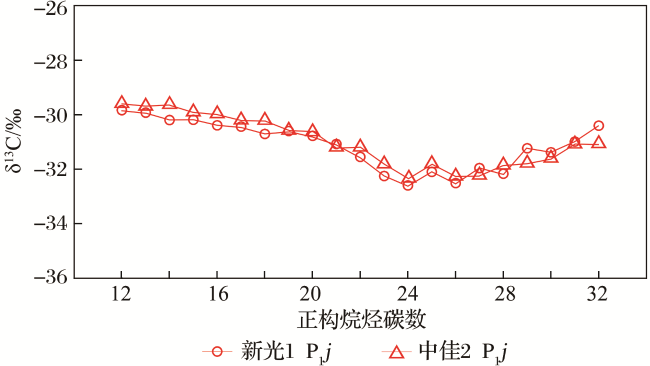
2.4 新光地区佳木河组气藏伴生凝析油正构烷烃碳同位素分布特征
表3 准噶尔盆地西北缘二叠系烃源岩地球化学特征 of the Junggar BasinTable 3 Geochemical characteristics of the Permian source rocks in the northwestern margin of the Junggar Basin |
| 烃源岩 | 层位 | 岩性 | TOC/% | I H/(mg/g) | T max/°C |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 金探1 | P2 w | 深灰色泥岩 | 3.37 | 550 | 450 |
| 风南1-1 | P1 f | 白云质泥岩 | 1.82 | 505 | 440 |
| 风南1-2 | P1 f | 白云质泥岩 | 1.22 | 447 | 437 |
| 风南4 | P1 f | 黑灰色泥岩 | 1.95 | 505 | 447 |
| 夏76-1 | P1 f | 深灰色泥岩 | 2.77 | 523 | 438 |
| 夏76-2 | P1 f | 深灰色泥岩 | 1.92 | 524 | 440 |
| 车201 | P1 j | 凝灰岩 | 1.64 | 55 | 453 |


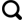
 甘公网安备 62010202000678号
甘公网安备 62010202000678号