引用本文
Han Zhongxi,Li Jian,Gou Yanxia,et al.The application of methane and ethane carbon isotopes as an identification index for gas origin study[J].Natural Gas Geoscience,2016,27(4):665-671.[韩中喜,李剑,垢艳侠,等.甲、乙烷碳同位素用于判识天然气成因类型的讨论[J].天然气地球科学,2016,27(4):665-671.]

doi:10.11764/j.issn.1672-1926.2016.04.0665
甲、乙烷碳同位素用于判识天然气成因类型的讨论
中图分类号:TE122.1 文献标志码:A 文章编号:1672-1926(2016)04-0665-07
The application of methane and ethane carbon isotopesas an identification index for gas origin study
Key words: Methane; Ethane; Carbon isotope; Natural gas; Genetic type; Identification chart;
引言
作为判识天然气成因类型的重要指标之一,甲、乙烷碳同位素在天然气地质研究中得到了广泛的应用。但在使用过程中,也呈现出一些问题,使人们对甲、乙烷碳同位素判识天然气类型的可靠性产生了质疑。如松辽盆地深层的徐深气田,大多数气井的乙烷碳同位素δ13C2值介于-32‰~-29.2‰之间。国内学者一般将乙烷碳同位素δ13C2=-28‰或-29‰作为划分煤型气和油型气的界限[1-3],按照这一划分标准,徐深气田则会被判识成油型气,而这与徐深气田在钻井过程中发现的大量煤系地层事实是不符的。虽然按照乙烷碳同位素划分标准,塔里木盆地阿克莫木气田天然气可以很容易被判识成煤型气,但有相当一部分学者认为阿克莫木气田的天然气主要来自于腐泥型或偏腐泥型的石炭系的海相深灰色泥岩和泥灰岩[4-7]。因此,有必要对甲、乙烷碳同位素在判识天然气成因类型方面的应用作进一步讨论。
1 研究方法
一般认为甲烷碳同位素组成主要受烃源岩的热演化程度的影响,演化程度越高甲烷碳同位素值越大,而乙烷碳同位素既与母质类型有关,又受烃源岩热演化程度的影响,因此可以用甲、乙烷碳同位素来共同判断天然气类型。黄汝昌[8]建立了用甲、乙烷碳同位素判识天然气成因类型的图版,并取得了很好的应用效果。但由于该图版主要是基于成熟气、高成熟天然气甲、乙烷碳同位素规律的总结,随着天然气勘探向深层的发展,过成熟气越来越多,这就需要对该图版作进一步丰富和完善。为此,笔者采集了国内7个含气盆地的近200口井的天然气样品,分别开展了天然气组分和烷烃碳同位素分析。
2 结果及讨论
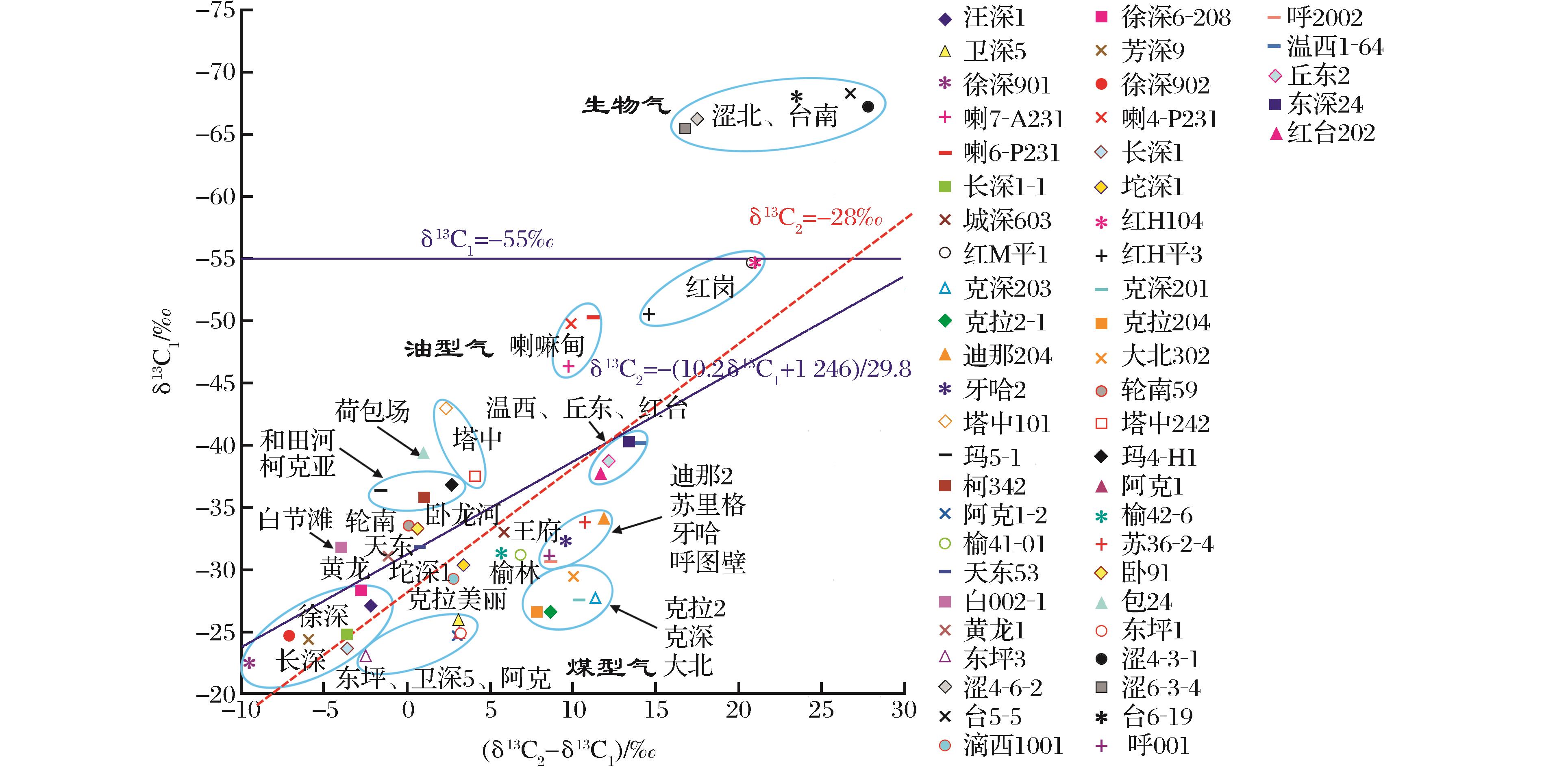
为便于表述和绘图,对于产自于同一气田、同一产层且相互邻近的一组气井,若天然气组分和烷烃碳同位素数据基本一致,笔者仅取其中一口气井的检测结果列于图1和表1中。对于世界上大多数气田和实验室模拟结果,天然气的烷烃碳同位素序列均为正碳同位素序列,即δ13C1<δ13C2<δ13C3<δ13C4,而负碳同位素序列通常被认为是无机气[3],这可能是黄汝昌[8]在绘制用甲、乙烷碳同位素判识划分天然气成因类型图版时,其δ13C2—δ13C1坐标轴没有出现负值的原因。但随着天然气勘探向深层的不断推进,开始出现一些同位素序列倒转的报道[9-14]。在这些报道当中一般是部分碳同位素倒转,即δ13C1>δ13C2或者δ13C3>δ13C4。对于烷烃碳同位素的倒转通常被归结为混合成因,即不同气源或不同成熟度天然气的混合[9-15]。但也有一部分报道是同位素序列的完全倒转,如美国Appalachian盆地北部的深层气(埋深>3 000m),其碳同位素序列呈现出δ13C1>δ13C2>δ13C3的现象。Burruss等[16]认为混合作用不足以造成该地区烷烃碳同位素的完全倒转,在高温(250~300℃)作用下,重烃发生裂解,促使甲烷不断富集13C,从而导致烷烃碳同位素序列的倒转。 因此,对于有机气来说,其δ13C2—δ13C1值是可以出现负值的。根据表1中的碳同位素数据,笔者将黄汝昌[8]的甲、乙烷碳同位素判识模板δ13C2—δ13C1轴由0点向左侧延伸至-10‰处(图1)。通过属于煤型气的徐深气田、双坨子气田、王府气田、迪那2气田和苏里格气田等的甲、乙烷碳同位素值以及属于油型气的黄龙、天东和红台地区的甲、乙烷碳同位素值可以确定出煤型气和油型气的划分界限为δ13C2=-(10.2δ13C1+1 246)/29.8。生物气的特点就是热演化程度很低,可通过反映热演化程度的甲烷碳同位素进行判断。即当δ13C1<-55‰时天然气类型为生物气,当δ13C2<-(10.2δ13C1+1 246)/29.8且δ13C1>-55‰时,天然气类型为油型气,当δ13C2>-(10.2δ13C1+1 246)/29.8时,天然气类型为煤型气。
图1 用甲、乙烷碳同位素判识天然气类型图版
Fig.1 Chart for natural gas genetic type identification by methane and ethane carbon isotope
Table 1 Natural gas composition and carbon isotope of some wells from Chinese gas bearing basins
| 盆地 | 气田/区块 | 井号 | 天然气组成/% | 烷烃碳同位素/‰ | 烷烃气 类型 | |||||||||
| N2 | CO2 | C1 | C2 | C3 | C4+ | δ13C1 | δ13C2 | δ13C3 | δ13C4 | |||||
| 松辽 | 徐深 | 汪深1 | 5.04 | 1.78 | 91.49 | 1.37 | 0.17 | 0.14 | -27.0 | -29.2 | -33.5 | -32.9 | 煤型气[19-22] | |
| 喇嘛甸 | 徐深6-208 | 1.47 | 0.32 | 95.67 | 2.24 | 0.22 | 0.08 | -28.3 | -31.1 | -33.5 | -35.1 | 油型气[23] | ||
| 长深 | 卫深5 | 1.03 | 0.31 | 93.89 | 3.75 | 0.70 | 0.32 | -26 | -22.9 | -23 | -22.35 | 煤型气 | ||
| 双坨子 | 芳深9 | 0.60 | 88.93 | 9.75 | 0.56 | 0.10 | 0.06 | -24.4 | -30.3 | / | / | 煤型气[24] | ||
| 王府 | 徐深901 | 3.89 | 5.87 | 87.63 | 2.60 | 0 | 0 | -22.4 | -32.0 | -32.8 | / | 煤型气 | ||
| 红岗 | 徐深902 | 2.47 | 2.59 | 92.26 | 2.67 | 0 | 0 | -24.65 | -31.78 | -32.35 | -32.5 | 生物气、 过渡带气[25] | ||
| 喇7-A231 | 0.49 | 1.43 | 92.75 | 2.19 | 1.63 | 1.51 | -46.4 | -36.6 | -32.8 | -31.1 | ||||
| 喇4-P231 | 0.48 | 0.69 | 93.32 | 2.10 | 1.81 | 1.60 | -49.8 | -39.8 | -33.2 | -31.6 | ||||
| 喇6-P231 | 0.41 | 1.62 | 88.67 | 3.02 | 3.23 | 3.05 | -50.3 | -39.2 | -32.8 | -32.3 | ||||
| 长深1 | 10.19 | 21.45 | 67.22 | 1.10 | 0.04 | 0 | -23.5 | -27.1 | -26.3 | / | ||||
| 长深1-1 | 6.96 | 15.45 | 76.29 | 1.25 | 0.05 | 0 | -24.8 | -28.4 | -30.9 | -32.7 | ||||
| 坨深1 | 4.34 | 0 | 87.71 | 4.28 | 1.78 | 1.89 | -30.4 | -27.0 | -26.2 | -26.6 | ||||
| 城深603 | 0.98 | 0.12 | 81.73 | 9.97 | 4.19 | 3.01 | -33.0 | -27.1 | -26.1 | -25.8 | ||||
| 红H104 | 3.61 | 0.45 | 95.67 | 0.23 | 0.02 | 0.02 | -54.7 | -33.7 | / | / | ||||
| 红M平1 | 4.40 | 0.03 | 95.35 | 0.22 | 0 | 0 | -54.8 | -34.0 | / | / | ||||
| 红H平3 | 6.71 | 0.06 | 92.06 | 1.00 | 0.08 | 0.08 | -50.6 | -36.0 | -25.8 | -30.3 | ||||
| 塔里木 | 克深 | 克深203 | 0.72 | 0.30 | 98.33 | 0.55 | 0.04 | 0.06 | -27.7 | -16.3 | -19.9 | / | 煤型气[26] | |
| 克拉2 | 克深201 | 0.70 | 0.78 | 97.86 | 0.54 | 0.04 | 0.08 | -27.6 | -17.3 | -19.8 | / | 煤型气[27] | ||
| 迪那2 | 克拉2-1 | 0.37 | 0.60 | 97.55 | 1.34 | 0.11 | 0.03 | -26.4 | -17.8 | -19.6 | -20.7 | 煤型气[28] | ||
| 大北 | 克拉204 | 0.36 | 0.43 | 97.73 | 1.34 | 0.11 | 0.03 | -26.7 | -19.0 | -19.8 | -20.9 | 煤型气[26] | ||
| 牙哈 | 迪那204 | 0.62 | 0.36 | 88.72 | 6.76 | 2.13 | 1.41 | -34.0 | -22.1 | -19.7 | -20.1 | 煤型气[29] | ||
| 轮南 | 大北302 | 0.58 | 0.81 | 97.08 | 1.23 | 0.16 | 0.14 | -29.4 | -19.4 | -20.0 | / | 油型气[30] | ||
| 塔中 | 牙哈2 | 3.95 | 0.54 | 82.60 | 7.76 | 3.09 | 2.06 | -32.2 | -22.6 | -19.7 | -21.6 | 油型气[31] | ||
| 和田河 | 轮南59 | 3.38 | 0.42 | 93.49 | 1.80 | 0.43 | 0.48 | -33.6 | -33.5 | -30.5 | -28.7 | 煤型气[32] | ||
| 阿克莫木 | 塔中101 | 9.68 | 1.20 | 82.98 | 3.36 | 1.14 | 1.64 | -42.9 | -40.6 | -34.6 | -28.9 | |||
| 塔中242 | 4.47 | 1.50 | 88.40 | 2.72 | 1.13 | 1.78 | -37.7 | -33.7 | -30.9 | -28.8 | ||||
| 玛5-1 | 9.05 | 5.91 | 81.91 | 1.78 | 0.63 | 0.72 | -36.4 | -38.0 | -34.0 | -30.2 | ||||
| 玛4-H1 | 11.83 | 0.37 | 82.79 | 2.53 | 1.07 | 1.41 | -36.8 | -34.1 | -29.5 | -28.6 | ||||
| 阿克1 | 7.57 | 14.39 | 77.04 | 0.65 | 0.11 | 0.24 | -24.9 | -21.7 | / | / | ||||
| 阿克1-2 | 7.86 | 14.49 | 76.68 | 0.75 | 0.12 | 0.10 | -24.7 | -21.7 | -20.2 | -21.5 | ||||
| 榆林 | 榆42-6 | 0.24 | 2.00 | 92.75 | 3.69 | 0.85 | 0.47 | -31.3 | -25.5 | -23.7 | -22.4 | 煤型气 | ||
| 苏里格 | 榆41-01 | 0.75 | 0.50 | 94.40 | 3.81 | 0.19 | 0.35 | -31.2 | -24.4 | -25.2 | -23.5 | |||
| 苏36-2-4 | 0.66 | 1.09 | 89.92 | 5.55 | 1.65 | 1.13 | -33.8 | -23.0 | -23.5 | -22.8 | ||||
| 四川 | 天东 | 天东53 | 0.25 | 8.14 | 91.35 | 0.25 | 0.01 | 0 | -31.8 | -31.1 | / | / | 油型气[33] | |
| 卧龙河 | 卧91 | 0.08 | 0.16 | 99.10 | 0.63 | 0.03 | 0 | -33.2 | -32.6 | -27.0 | / | |||
| 白节滩 | 白002-1 | 0.41 | 0.93 | 97.09 | 1.38 | 0.17 | 0.02 | -31.8 | -35.8 | -31.2 | / | |||
| 黄龙场 | 黄龙1 | 0.60 | 3.07 | 95.26 | 0.15 | 0.92 | 0 | -31.0 | -32.1 | / | / | |||
| 柴达木 | 东坪 | 东坪1 | 4.55 | 0.02 | 92.67 | 1.93 | 0.32 | 0.50 | -25.0 | -21.8 | -23.3 | -26.1 | 煤型气[34] | |
| 涩北 | 东坪3 | 21.14 | 0.68 | 76.69 | 1.05 | 0.20 | 0.23 | -23.1 | -25.6 | -24.7 | -24.8 | 生物气 | ||
| 台南 | 涩4-3-1 | 0.03 | 0 | 99.59 | 0.31 | 0.06 | 0.01 | -67.2 | -39.4 | -29.2 | -27.2 | |||
| 涩4-6-2 | 0.06 | 0 | 99.38 | 0.41 | 0.12 | 0.03 | -66.1 | -48.7 | -33.9 | -32.2 | ||||
| 涩6-3-4 | 0.06 | 0 | 99.38 | 0.41 | 0.12 | 0.03 | -65.6 | -48.8 | -34.0 | -33.3 | ||||
| 台5-5 | 0.16 | 0 | 99.41 | 0.33 | 0.09 | 0.01 | -68.3 | -41.5 | -28.6 | -31.3 | ||||
| 台6-19 | 0.11 | 0 | 99.41 | 0.35 | 0.12 | 0.01 | -68.0 | -44.6 | -32.6 | -32.3 | ||||
Table 1 Natural gas composition and carbon isotope of some wells from Chinese gas bearing basins(continued)
| 盆地 | 气田/区块 | 井号 | 天然气组成/% | 烷烃碳同位素/‰ | 烷烃气 类型 | |||||||||
| N2 | CO2 | C1 | C2 | C3 | C4+ | δ13C1 | δ13C2 | δ13C3 | δ13C4 | |||||
| 准噶 尔 | 克拉美丽 | 滴西1001 | 4.56 | 0 | 89.94 | 3.88 | 1.37 | 0.25 | -29.3 | -26.5 | -24.1 | -23.4 | 煤型气 | |
| 呼图壁 | 呼001 | 1.12 | 0 | 92.18 | 4.66 | 1.05 | 0.99 | -31.0 | -22.4 | -21.4 | -22.5 | 煤型气 | ||
| 呼2002 | 1.14 | 0 | 92.31 | 4.61 | 1.02 | 0.92 | -30.6 | -22.0 | -21.2 | -22.4 | ||||
| 吐 哈 | 温西 | 温西1-64 | 4.41 | 0.13 | 80.16 | 7.45 | 4.34 | 3.51 | -40.2 | -26.3 | -24.7 | -24.7 | 煤型气[35] | |
| 丘东24 | 2.24 | 0 | 81.17 | 8.98 | 4.51 | 3.10 | -38.7 | -26.5 | -25.5 | -25.3 | ||||
| 东深2 | 1.59 | 0 | 82.76 | 8.54 | 4.10 | 3.01 | -40.2 | -26.9 | -26.1 | -26.0 | ||||
| 红台202 | 3.17 | 0.16 | 82.09 | 7.71 | 3.98 | 2.89 | -37.6 | -25.9 | -24.8 | -24.9 | ||||
Table 2 Natural gas mercury content of some wells from Chinese gas bearing basins
| 盆地名称 | 气田 | 井号 | 层位 | 层段/m | 汞含量/(ng/m3) |
| 鄂尔多斯 | 苏里格 | 苏47-17-61 | P2h8 | 3 597~3 626 | 46 100 |
| 榆林 | 苏48-15-68 | P2h8 | 3 577~3 595 | 47 500 | |
| 苏48-17-74 | P2s1 | 3 627.9~3 631 | 48 700 | ||
| 榆42-0 | P2s2 | 2 925.2~2 928.3 | 30 600 | ||
| 榆42-1 | P2s2 | 2 993.7~2 998.6 | 31 900 | ||
| 塔里木 | 牙哈 | 牙哈23-1-22 | E | 5 142.5~5 163 | 34 500 |
| 克拉2 | 牙哈23-1-18 | E+K | 5 128.1~5 165.4 | 32 300 | |
| 克拉2-4 | E+K | 3 577.1~3 715.3 | 62 600 | ||
| 克拉2-9 | K | 3 780.6~3 883.3 | 68 300 | ||
| 松辽 | 徐深 | 徐深1 | K1yc | 3 520~3 705 | 64 800 |
| 长深 | 徐深6-208 | K1yc | 3 550~3 542 | 146 000 | |
| 徐深901 | K1yc | 3 892~3 899 | 168 000 | ||
| 长深1 | K1yc | 3 566~3 651 | 187 000 | ||
| 长深1-1 | K1yc | 3 701~3 753 | 227 000 |
3 结论
(1)对于大多数天然气来说用乙烷碳同位素δ13C2=-28‰或-29‰作为划分煤型气和油型气的界限是合理的,但对于部分演化程度较高的天然气来说还需要结合甲烷碳同位素进行综合判断。 (2)在用甲、乙烷碳同位素判断天然气类型时,煤型气和油型气的划分界限为δ13C2=-(10.2δ13C1+1 246)/29.8,当δ13C2>-(10.2δ13C1+1 246)/29.8时,天然气类型为煤型气,当δ13C2<-(10.2δ13C1+1 246)/29.8且δ13C1>-55‰时,天然气类型为油型气,当δ13C1<-55‰时为生物气。
参考文献(References)
[1] Zhang Shiya,Hao Jianjun,Jiang Tairan.A New Method Distinguishing Natural Gas Type with Carbon Isotopes from Methane and Ethane[M].Beijing:Geological Publishing House,1998:48-58.[张士亚,郜建军,蒋泰然.利用甲、乙烷碳同位素判识天然气类型的一种新方法[M].北京:地质出版社,1988:48-58.]
[2] Huang Jizhong.Natural gas genetic classification and its application in Sichuan Basin[J].Natural Gas Geoscience,1991,2(1):1-15.[黄籍中.油气区天然气成因分类及其在四川盆地的应用[J].天然气地球科学,1991,2(1):1-15.]
[3] Dai Jinxing.Significance of the study on carbon isotopes alkane gases[J].Natural Gas Industry,2011,31(12):1-5.[戴金星.天然气中烷烃气碳同位素研究的意义[J].天然气工业,2011,31(12):1-5.]
[4] Zhao Mengjun,Xia Xinyu,Qin Shengfei,et al.Gas source of Well Ake 1 resource in Tarim Basin[J].Natural Gas Industry,2003,23(2):31-33.[赵孟军,夏新宇,秦胜飞,等.塔里木盆地阿克1井气藏气源研究[J].天然气工业,2003,23(2):31-33.]
[5] Zhang Qiucha,Wang Fuhuan,Xiao Zhongyao,et al.The discussion of natural gas source in well Ake 1[J].Natural Gas Geoscience,2003,14(6):484-487.[张秋茶,王福焕,肖中尧,等.阿克1井天然气气源讨论[J].天然气地球科学,2003,14(6):484-487.]
[6] Wang Zhaoming,Zhao Mengjun,Zhang Shuichang,et al.A preliminary study on formation of Akemomu Gasfield in the Kashi Sag,Tarim Basin[J].Chinese Journal of Geology,2005,40(2):237-247.[王招明,赵孟军,张水昌,等.塔里木盆地西部阿克莫木气田形成初探[J].地质科学,2005,40(2):237-247.]
[7] Li Xianqing,Xiao Xianming,Tang Yongchun,et al.Origin of natural gas from Ake1 gas pool using the method of carbon isotope kinetics[J].Geochimica,2005,34(5):525-531.[李贤庆,肖贤明,唐永春,等.应用碳同位素动力学方法探讨阿克1气藏天然气的来源[J].地球化学,2005,34(5):525-531.]
[8] Huang Ruchang.Formation and distribution regularity of low maturity and condensed gas pools in China[M].Beijing:Petroleum Industry Press,1997:27-28.[黄汝昌.中国低熟油及凝析气藏形成与分布规律[M].北京:石油工业出版社,1997:27-28.]
[9] Jenden P D,Drazan D J,Kaplan I R.Mixing of thermogenic natural gases in northern Appalachian basin[J].AAPG Bulletin,1993,77(6):980-998.
[10] Laughrey C D,Baldassare F J.Geochemistry and origin of some natural gases in the Plateau province of the central Appalachian basin,Pennsylvania and Ohio[J].AAPG Bulletin,1998,82(2):317-335.
[11] Burruss R C,Ryder R T.Composition of crude oil and natural gas produced from 14 wells in the Lower Silurian “Clinton” sandstone and Medina Group,northeastern Ohio and northwestern Pennsylvania[J].US Geological Survey Professional Paper 1708,2003:64.
[12] Huang Shipeng,Gong Deyu,Yu Cong,et al.Geochemical characteristics of the gases sourced from the Carboniferous-Permian coal measures:A case study of Ordos and Bohai Bay Basin,China[J].Natural Gas Geoscience,2014,25(1):98-108.[黄士鹏,龚德瑜,于聪,等.石炭系—二叠系煤成气地球化学特征——以鄂尔多斯盆地和渤海湾盆地为例[J].天然气地球科学,2014,25(1):98-108.]
[13] Yu Cong,Gong Deyu,Huang Shipeng,et al.Geochemical characteristics of carbon and hydrogen isotopes for the Xujiahe Formation natural gas in Sichuan Basin[J].Natural Gas Geoscience,2014,25(1):87-97.[于聪,龚德瑜,黄士鹏,等.四川盆地须家河组天然气碳、氢同位素特征及其指示意义[J].天然气地球科学,2014,25(1):87-97.]
[14] Song Zhenxiang,Gao Jianjun,Zhou Zhuoming.Preliminary study on genetic tyeps of natural gas in Shiwu fault depress[J].Natural Gas Geoscience,2012,23(1):167-174.[宋振响,郜建军,周卓明.十屋断陷天然气成因类型初探[J].天然气地球科学,2012,23(1):167-174.]
[15] Dai Jinxing,Xia Xinyu,Qin Shengfei,et al.Origins of partially reversed alkane δ13C values for biogenic gases in China[J].Organic Geochemistry,2004,35(4):405-411.
[16] Burruss R C,Laughrey C D.Carbon and hydrogen isotopic reversals in deep basin gas:Evidence for limits to the stability of hydrocarbons[J].Organic Geochemistry,2010,41(12):1285-1296.
[17] Dai Jinxing,Qi Houfa,Hao Shisheng.Natural Gas Geology Introduction[M].Beijing:Petroleum Industry Press,1989:68-70.[戴金星,戚厚发,郝石生.天然气地质学概论[M].北京:石油工业出版社,1989:68-70.]
[18] Han Zhongxi,Li Jian,Yan Qituan,et al.Discussion of natural gas mercury content as an identification index of coal type gas and oil type gas[J].Natural Gas Geoscience,2013,24(1):129-133.[韩中喜,李剑,严启团,等.天然气汞含量作为煤型气和油型气判识指标的探讨[J].天然气地球科学,2013,24(1):129-133.]
[19] Meng Fanchao.Reverse sequence of natural gas carbon isotope and formation mechanism in the deep zone in Songliao Basin[J].Special Oil and Gas Reservoirs,2013,20(2):25-28.[孟凡超.松辽盆地深层天然气碳同位素反序及形成机理探讨[J].特种油气藏,2013,20(2):25-28.]
[20] Feng Zihui,Liu Wei.A study of genetic type of deep gas in Xujiaweizi fault depression[J].Natural Gas Industry,2006,26(6):18-20.[冯子辉,刘伟.徐家围子断陷深层天然气的成因类型研究[J].天然气工业,2006,26(6):18-20.]
[21] Zhang Shuichang,Zhu Guangyou.Large and medium gas fields distribution and natural gas genesis in Chinese sedimentary basins[J].Science in China Press,2007,37(supplement Ⅱ):1-11.[张水昌,朱光有.中国沉积盆地大中型气田分布与天然气成因[J].中国科学:D辑,2007,37(增刊Ⅱ):1-11.]
[22] Liu Ting,Mi Jingkui,Zhang Min.Carbon isotopic reversal numerical simulation of deep-seated gases,Songliao Basin[J].Natural Gas Geoscience,2008,19(5):722-726.[刘婷,米敬奎,张敏.松辽盆地深层天然气碳同位素倒转数值模拟[J].天然气地球科学,2008,19(5):722-726.]
[23] Wang Jianxin,Ji Bingyu,Song Jishui,et al.The development Process of Daqing Oilfield[M].Beijing:Petroleum Industry Press,2003:64-68.[王建新,计秉玉,宋吉水,等.大庆油田开发历程[M].北京:石油工业出版社,2003:64-68.]
[24] Li Hongjian,Li Shengye,Zhang Yan,et al.Deep zone geology characteristics of Shuangtuozi region in the south of Songliao Basin[J].Mud Logging Engineering,2005,16(1):56-59.[李宏建,李生业,张妍,等.浅谈松辽盆地南部双坨子地区深层地质特征[J].录井工程,2005,16(1):56-59.]
[25] Jing Chengjie,Niu Shizhong,Huang Yuxin.Geochemical characteristics of shallow gas in Honggang region,Songliao Basin[J].Petroleum Geology & Experiment,2012,34(1):53-56.[景成杰,牛世忠,黄玉欣.松辽盆地红岗地区浅层气地球化学特征研究[J].石油实验地质,2012,34(1):53-56.]
[26] Feng Songbao,Zhang Zhijun.Accumulation process and characteristics of overpressured large gasfield in Keshen belt of Kelasu tectonic zone[J].Journal of Hefei University of Technology:Natural Science,2013,36(10):1242-1248.[冯松宝,张志军.克拉苏构造带克深区带超高压大气田成藏过程与特征[J].合肥工业大学学报:自然科学版,2013,36(10):1242-1248.]
[27] Li Xinqing,Xiao Xianming,Mi Jingkui,et al.Natural gas genesis of Kela2 big gasfield in Tarim Basin[J].Natural Gas Industry,2004,24(11):8-10.[李贤庆,肖贤明,米敬奎,等.塔里木盆地克拉2大气田天然气的成因探讨[J].天然气工业,2004,24(11):8-10.]
[28] Zhu Guangyou,Yang Haijun,Zhang Bin,et al.The geological feature and origin of Dina 2 large gasfield in Kuqa Depression,Tarim Basin[J].Acta Petrologica Sinica,2012,28(8):2479-2492.[朱光有,杨海军,张斌,等.塔里木盆地迪那2大型凝析气田的地质特征及其成藏机制[J].岩石学报,2012,28(8):2479-2492.]
[29] Wang Feiyu,Du Zhili,Zhang Shuichang,et al.Source kitchen and natural gas accumulation in Kuqa Depression,Tarim Basin[J].Xinjiang Petroleum Geology,2009,30(4):431-439.[王飞宇,杜治利,张水昌,等.塔里木盆地库车坳陷烃源灶特征和天然气成藏过程[J].新疆石油地质,2009,30(4):431-439.]
[30] Wan Haojie,Chen Chao,Yi Yuchuan.Distribution feature and significance of natural gas carbon isotope in platform region,Tarim Basin[J].Inner Mongolia Petrochemical,2011,(17):98-99.[万豪杰,陈超,尹玉川.塔里木盆地台盆区天然气碳同位素分布特征及其意义[J].内蒙古石油化工,2011,(17):98-99.]
[31] Tang Xiaoqiang,Yin Yuchuan,Li Xiaohui,et al.Natural gas geochemical study of the Hetianhe Gasfield in Tarim Basin[J].Geology in China,2011,38(4):1025-1030.[唐小强,尹玉川,李晓辉.等.塔里木盆地和田河气田研究[J].中国地质,2011,38(4):1025-1030.]
[32] Liu Wei,Yang Fei,Wu Jincai,et al.The discussion on natural gas source in Akmomu Gasfield,northern margin of Kashi Sag[J].Natural Gas Geoscience,2015,26(3):486-494.[刘伟,杨飞,吴金才,等.喀什凹陷北缘阿克莫木气田气源探讨[J].天然气地球科学,2015,26(3):486-494.]
[33] Zhu Guangyou,Zhang Shuichang,Liang Yingbo,et al.The characteristics of natural gas in Sichuan Basin and its sources[J].Earth Science Frontiers,2006,13(2):234-248.[朱光有,张水昌,梁英波,等.四川盆地天然气特征及气源[J].地学前缘,2006,13(2):234-248.]
[34] Cao Zhenglin,Wei Zhifu,Zhang Xiaojun,et al.Oil-gas source correlation in Dongping area,Qaidam Basin[J].Lithologic Reservoirs,2013,25(3):17-42.[曹正林,魏志福,张小军,等.柴达木盆地东坪地区油气源对比分析[J].岩性油气藏,2013,25(3):17-42.]
[35] Feng Qiao,Zhang Xiaoli,Yuan Mingsheng,et al.Petroleum-entrapped system and accumulation in the Wenjiasan-Qiudong area,Tuha Basin[J].Acta Sedimentologica Sinica,1997,15(4):121-125.[冯乔,张小莉,袁明生,等.吐哈盆地温吉桑—丘东地区油气成藏体系与聚集[J].沉积学报,1997,15(4):121-125.]
[36] Li Chunguang.Discussion on the distribution and formation of the deep seated oil gas reservoir in Songliao Basin[J].Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency,2004,11(3):31-34.[李春光.试论松辽盆地深层油气藏分布与形成[J].油气地质与采收率,2004,11(3):31-34.]
[37] Li Jingqiu,Miao Hongwei,Li Lili,et al.Characteristics and main controlling factors of gas accumulation in deep clastic rocks of Changling fault depression in southern Songliao Basin[J].China Petroleum Exploration,2009,14(4):34-39.[李晶秋,苗宏伟,李立立,等.松辽盆地南部长岭断陷深层碎屑岩天然气成藏特征及主控因素[J].中国石油勘探,2009,14(4):34-39.]