引用本文
Xiao Xiaochun,Ding Xin,Xu Jun,et al.Coal rock microscopic damage evolution model and permeability increase mechanism research under ultrasound[J].Natural Gas Geoscience,2016,27(1):166-172.[肖晓春,丁鑫,徐军,等.超声作用下煤岩细观损伤演化模型及增渗机理研究[J].天然气地球科学,2016,27(1):166-172.]

doi:10.11764/j.issn.1672-1926.2016.01.0166
超声作用下煤岩细观损伤演化模型及增渗机理研究
中图分类号:TE311 文献标志码:A 文章编号:1672-1926(2016)01-0166-07
Coal rock microscopic damage evolution model and permeabilityincrease mechanism research under ultrasound
Key words: Ultrasonic incentive; Meso-scale; Phenomenological theory; Secondary damage;
引言
颗粒煤岩是一多结构层次,多尺度并存的大量初次损伤作用的复杂体系。在荷载作用下,颗粒间发生强烈的挤压和摩擦,其内部复杂的力链结构发生断裂和重组,进而耗散大量能量[1-4]。当超声作用于颗粒煤岩体系时,声波在颗粒煤岩体内衰减的同时与其内部煤岩颗粒产生了强烈的机械和温度效应,其作用过程就是煤岩颗粒间摩擦力和黏聚力的弱化过程,这一过程使得煤岩内部颗粒产生了二次损伤演化。持续的超声作用会使小尺度的微损伤在演化过程中逐渐饱和,大尺度的微损伤前沿将向更大的尺寸发展[5-8]。超声致裂煤岩的二次损伤过程将使煤岩体系的孔隙率和渗透率发生显著变化,而这2者是非固结颗粒床最重要的2个物理参数[9,10],许多重要参数均与这2个参数直接相关[11-13]。 在煤岩体渗透率模型研究和应用方面,许多学者做了大量工作,通过实验室以及现场试验研究发现:煤的渗透率与有效应力呈负指数相关,而随孔隙压力的变化存在一临界值[14,15];煤层气解吸时,煤基质会产生收缩效应[16-18];前人[19-21]从不同角度建立了考虑有效应力以及基质收缩效应的渗透率理论模型;邓泽等[22],贺玉龙等[23]分析了地应力、有效应力与渗透率之间的关系,并给出了拟合经验公式;孟召平等[24]利用实验方法和现场测试建立了高煤级煤储层渗透性与应力之间的相关关系和模型,探讨了渗透性变化的控制机理;肖晓春等[25,26]对超声激励低渗煤层甲烷增透机理进行了深入研究取得了一系列成果;前人[27-29]对煤层气储层渗透率变化规律进行了物理和数值实验研究。这些研究成果多是在传统的连续介质力学领域,研究煤岩类颗粒体系时,将煤岩系统视为连续的非均匀介质取得的,但利用宏观尺度简化平均的宏观唯象研究方法,难以考虑颗粒材料内在的微细观尺度层次的影响,因此,需要在连续介质力学及唯象理论的基础上,从细观尺度对颗粒煤岩在超声作用过程的二次机械和热损伤导致的渗透率变化规律进行深入研究,为颗粒煤岩体渗透率损伤演化模型建立及连续介质力学在颗粒煤岩体系中的发展及应用提供新的研究方法和思路。
1 颗粒煤岩超声二次损伤增渗机理
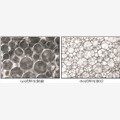
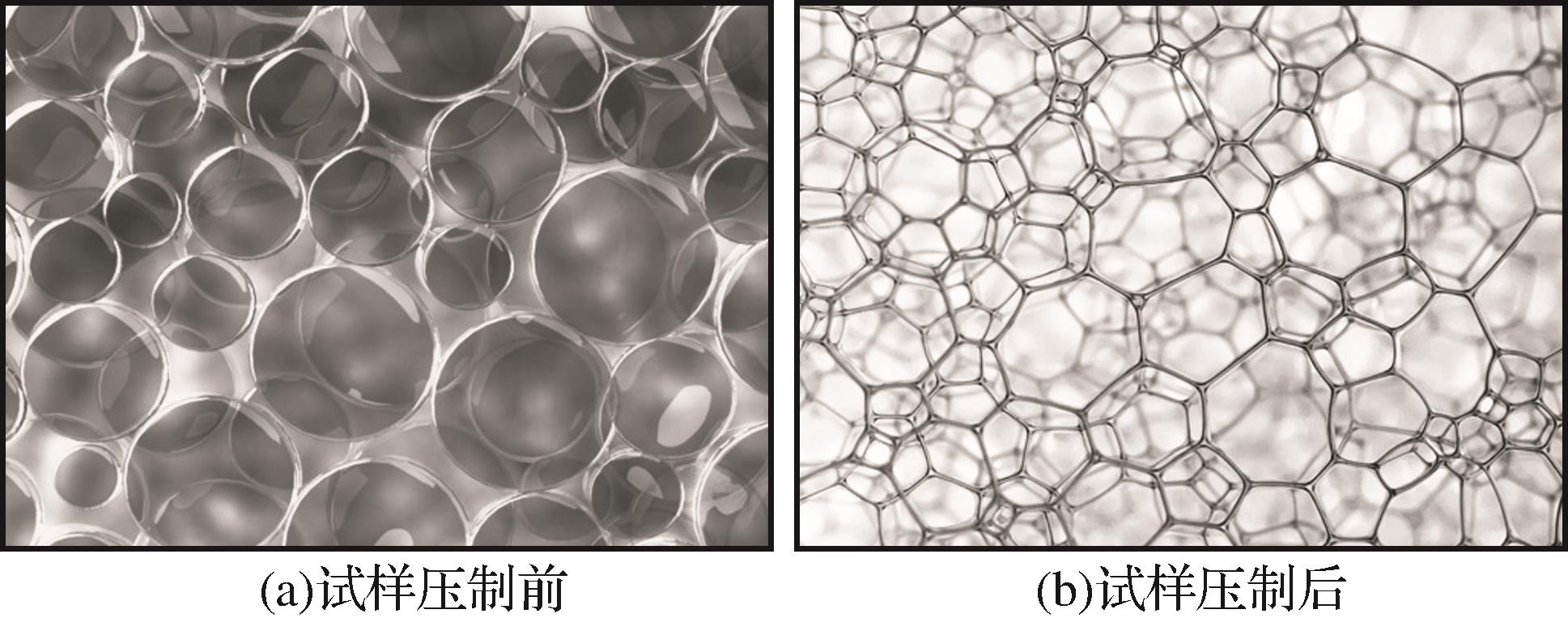
由于煤岩自身结构是由复杂的有机质和无机物组成的复合体[30-35],其颗粒粒径跨度和结构构成复杂,在荷载作用下,煤岩内部的初次损伤受节理和微裂纹等因素影响无法获知,为了探讨超声物理激励导致的煤岩体二次损伤,选用颗粒粒径(0.075~0.25mm)偏小,粒径尺寸跨度较大的型煤相似材料试件作为研究对象,选用的型煤相似材料试件具有了原煤的颗粒粒径跨度大且结构构成复杂的特点,同时弱化了节理和微裂纹的影响,且在压制过程中保留了连续非均匀性固体介质的特性,图1为颗粒型煤试样压制前、后细观“气泡状”唯象模型。
图1 颗粒煤岩试样细观唯象模型
Fig.1 Microscopic phenomenological model of granular coal sample
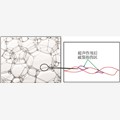
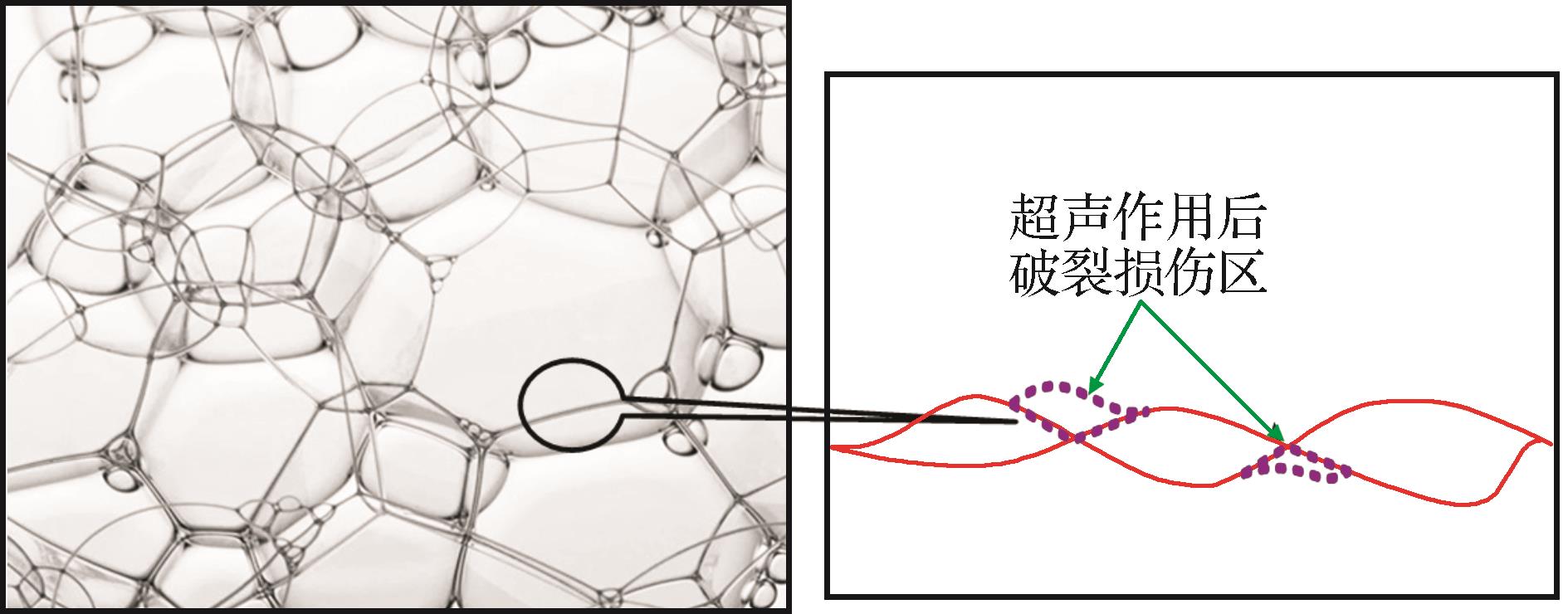
图2 超声作用后二次损伤细观唯象模型
Fig.2 The second damage microscopic phenomenological model after ultrasonic action
2 超声激励颗粒煤岩渗透率规律研究
2.1 超声作用下颗粒煤岩渗透率实验方案
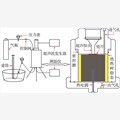
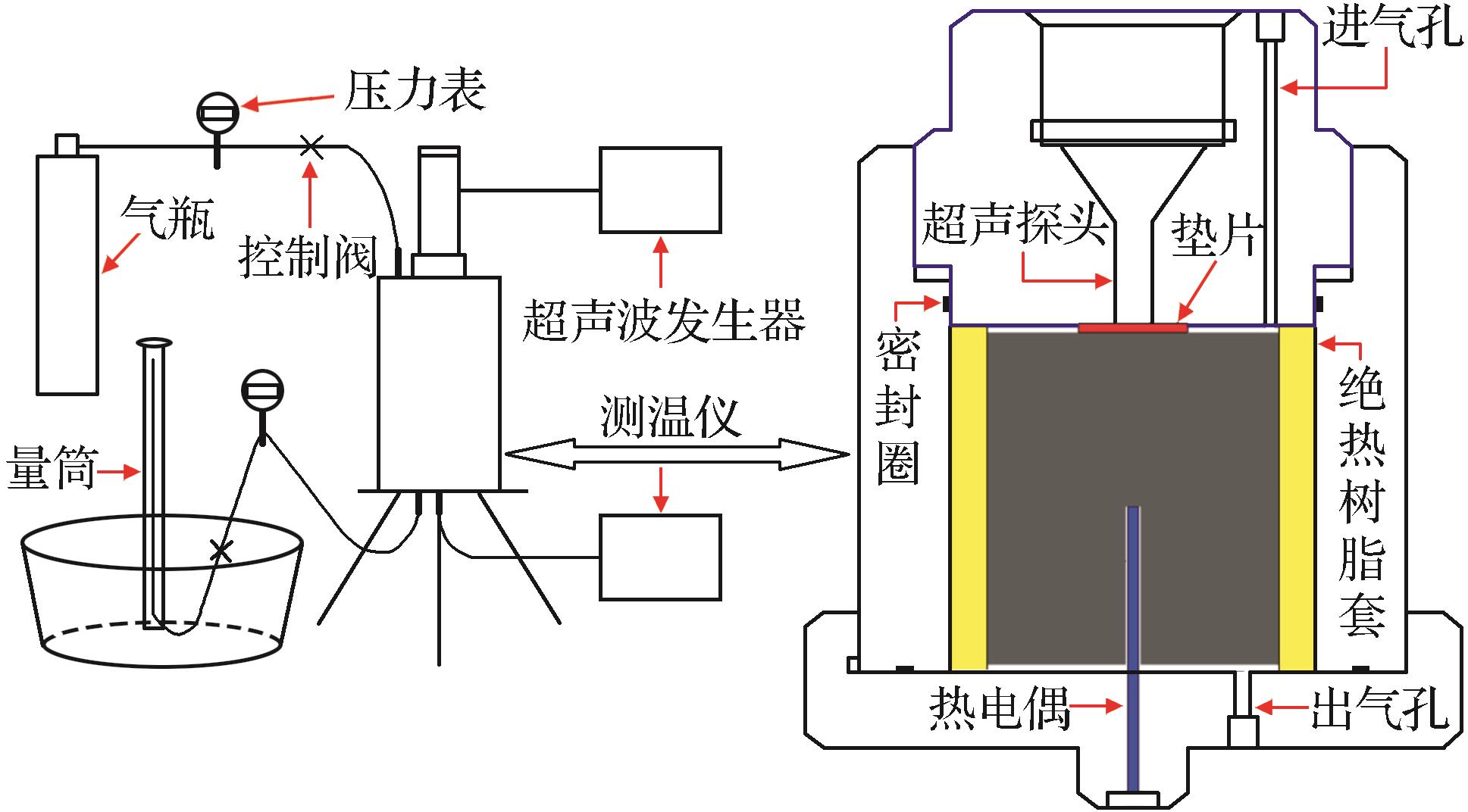
为了深入揭示超声二次损伤导致的气体增渗机理,采用宏观渗透率统计测定实验方法,对粒径在0.075~0.25mm范围内的颗粒煤岩试样进行渗透率测定实验。首先将粒径在0.075~0.25mm范围的煤粉颗粒装入绝热树脂套中,利用压制模具将其压制成Φ70mm×150mm的颗粒煤岩试样,成型压力为850kN,然后置于密封性能良好的封闭腔体内,实验装置如图4所示。
图4 超声作用下渗透率实验装置
Fig.4 The permeability test device diagram of ultrasonic
2.2 超声激励颗粒煤岩渗透率实验结果分析
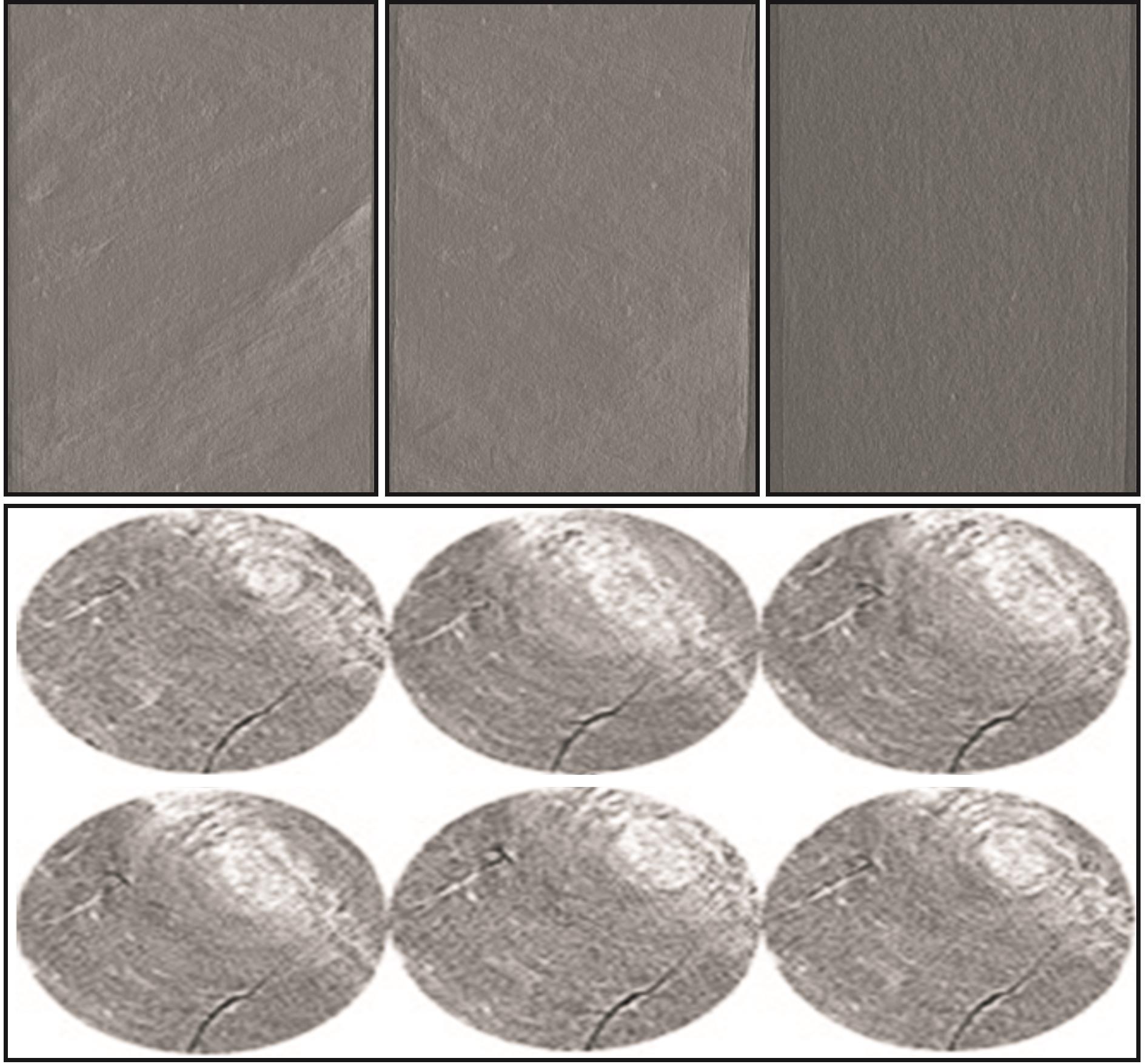
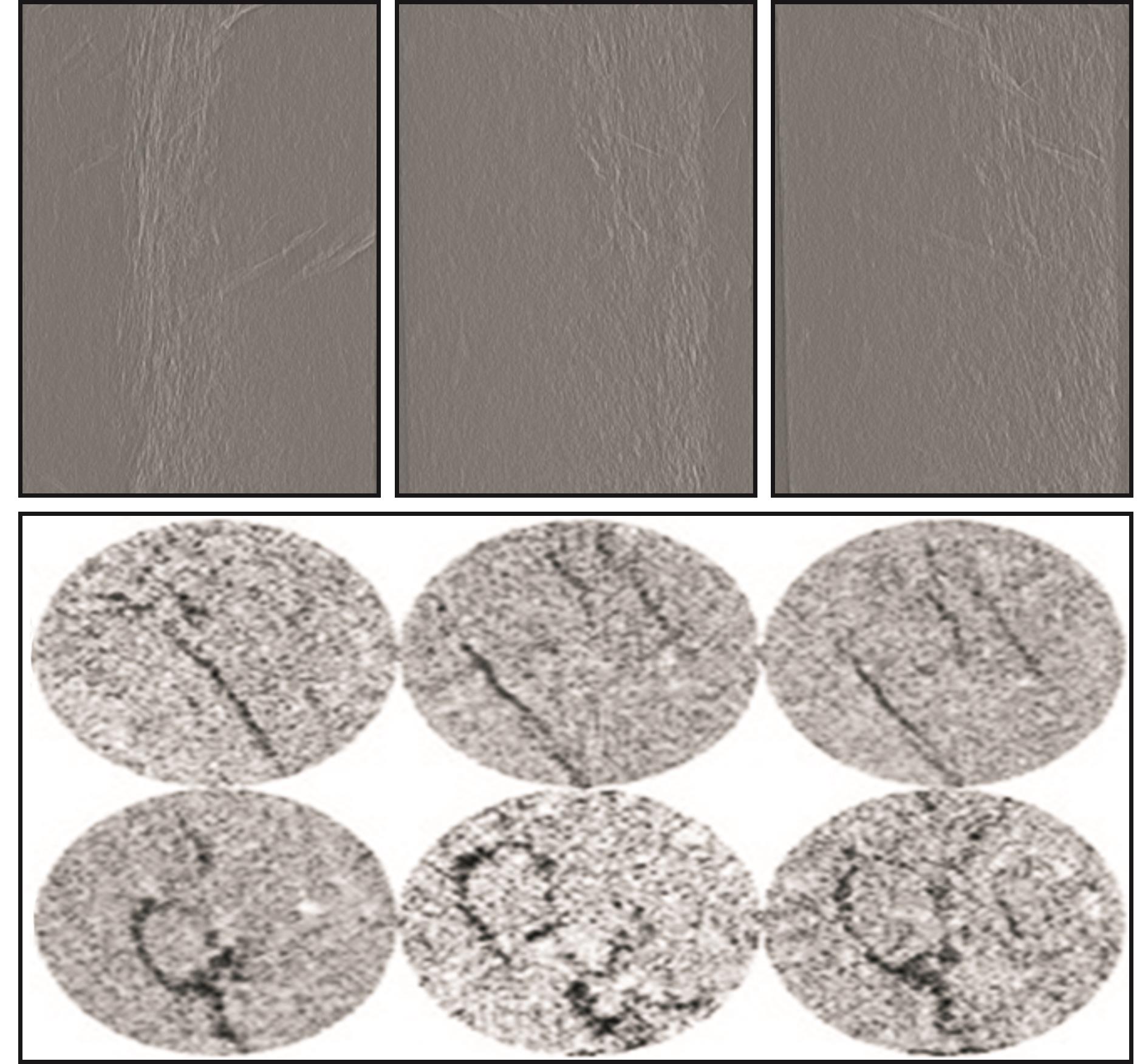
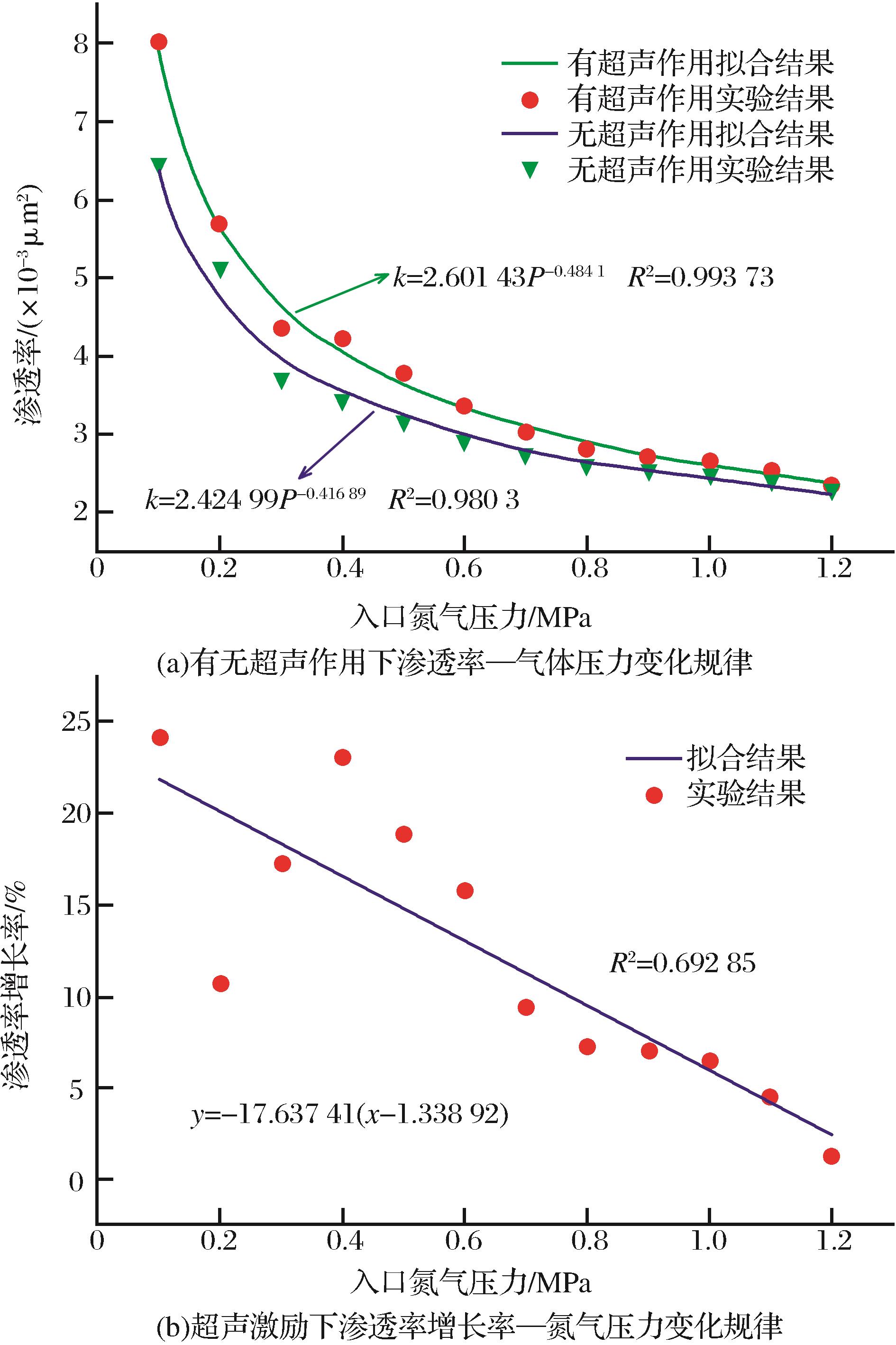
图5和图6给出了超声作用前后实验煤试样纵横剖面的CT扫描结果,由扫描结果知,超声作用后对煤岩试样内部的裂隙网格发育有显著影响,结合细观CT观测和试样宏观渗透率测试结果可以对超声激励导致的煤样损伤演化进行深入分析。表1为不同气体压力下有、无超声激励时颗粒煤岩试样的气体流速、渗透率和渗透率增长率的变化情况。
图5 煤样不同纵横剖面超声作用前CT观测结果
Fig.5 The CT observation of different longitudinal and transverse profiles of coal sample without ultrasound
图6 煤样不同纵横剖面超声作用后CT观测结果
Fig.6 The CT observation of different longitudinal and transverse profiles of coal sample with ultrasound
Table 1 The permeability test results of ultrasound and no ultrasound
| 入口压 /MPa | 出口压/MPa | 流速/(mL/s) | 渗透率/(×10-3μm2) | 渗透率 增长率 /% | |||||
| 超声作用 | 超声作用 | 超声作用 | |||||||
| 无 | 有 | 无 | 有 | 无 | 有 | ||||
| 0.10 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 4.61 | 5.72 | 6.46 | 8.02 | 24.15 | ||
| 0.20 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 14.67 | 16.23 | 5.14 | 5.69 | 10.70 | ||
| 0.30 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 23.79 | 27.93 | 3.71 | 4.35 | 17.25 | ||
| 0.40 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 39.09 | 43.67 | 3.42 | 4.21 | 23.10 | ||
| 0.50 | 0.05 | 0.06 | 56.74 | 66.79 | 3.18 | 3.78 | 18.87 | ||
| 0.60 | 0.07 | 0.09 | 74.46 | 85.47 | 2.91 | 3.37 | 15.81 | ||
| 0.70 | 0.09 | 0.12 | 95.88 | 103.52 | 2.76 | 3.02 | 9.42 | ||
| 0.80 | 0.13 | 0.14 | 117.44 | 125.79 | 2.62 | 2.81 | 7.25 | ||
| 0.90 | 0.16 | 0.18 | 143.87 | 153.93 | 2.54 | 2.72 | 7.01 | ||
| 1.00 | 0.20 | 0.22 | 171.48 | 181.82 | 2.49 | 2.65 | 6.43 | ||
| 1.10 | 0.25 | 0.27 | 200.76 | 208.33 | 2.42 | 2.54 | 4.53 | ||
| 1.20 | 0.30 | 0.32 | 225.73 | 226.24 | 2.32 | 2.35 | 1.29 | ||
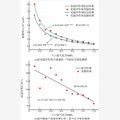
Table 2 Parameters table of permeability fitting equation with and without ultrasound
| 拟合条件 | 拟合方程参数 | ||
| A/(m2/MPa) | B | R2 | |
| 无超声 | 2.424 99 | -0.416 89 | 0.980 3 |
| 有超声 | 2.601 43 | -0.484 1 | 0.993 73 |
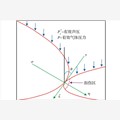
图7 渗透率、渗透率增长率与氮气压力关系
Fig.7 The diagram of granular coal permeability and permeability growth rate
3 结论
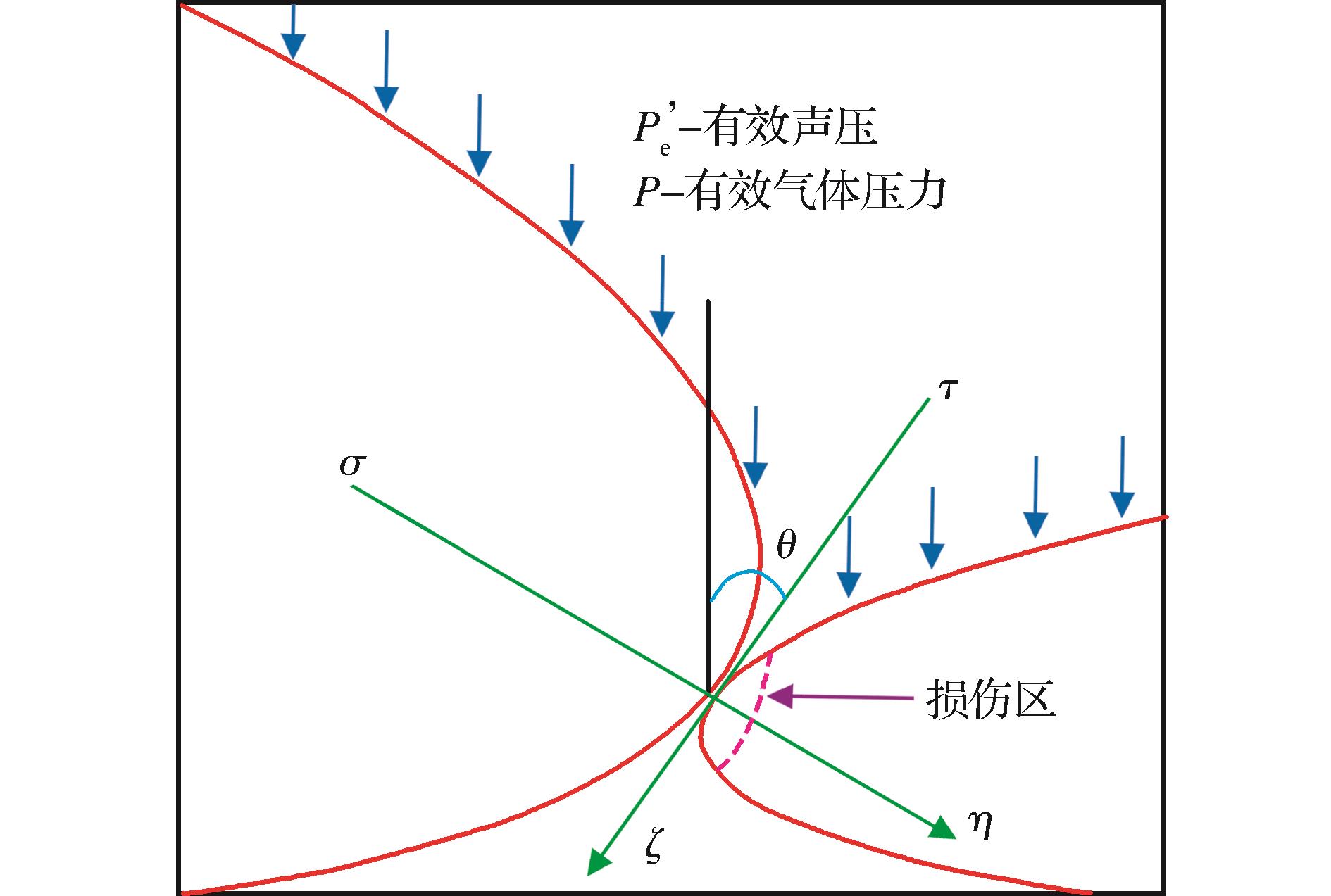
本文基于连续介质力学与唯象理论,在细观尺度上考虑了超声二次损伤对颗粒煤岩渗透率的重要影响,针对超声作用下机械和热效应对颗粒煤增渗机理及损伤演化规律做了深入研究,得到以下结论: (1)建立了超声机械和热效应影响的有效应力和损伤量理论模型,由理论分析知,有效应力随着超声热效应引起的颗粒接触面元上摩擦系数和损伤量的增加而增大。 (2)建立了颗粒煤岩体气测渗透率和有效应力与二次损伤量间的渗透率损伤演化控制模型。 (3)超声作用下,损伤空间中的二次损伤量逐渐增大,由此引发了煤岩基质有效应力的增大,而有效应力的增大是超声增渗的主要原因;持续超声作用导致了接触颗粒面元间损伤量的增加,由此产生的显著热效应使得的煤岩颗粒发生膨胀,损伤裂纹因膨胀挤压作用重新闭合,宏观表现为超声增渗效果下降。 (4)煤岩体具有多结构层次和多尺度的复杂特性,文中所做的各向同性损伤假设较理想化,仍需深入开展受节理、微裂隙影响的各向异性材料损伤特性和渗透率演化规律研究。
参考文献(References)
[1] Song Shixiong,Sun Qicheng,Fei Minglong,et al.Thermodynamic analysis of simple shear granular flows[J].Scientia Sinica Phys Mech & Astron,2013,43(7):881-889.[宋世雄,孙其诚,费明龙,等.颗粒材料热力学理论在简单剪切流中的应用[J].中国科学:物理学,力学,天文学,2013,43(7):881-889.]
[2] Sun Qicheng,Wang Guangqian.Force distribution in static granular matter in two dimensions[J].Acta Physica Sinica,2008,57(8):4667-4674.[孙其诚,王光谦.静态堆积颗粒中的力链分布[J].物理学报,2008,57(8):4667-4674.]
[3] Ji S Y,Shen H H.Effect of contact force models on granular flow dynamics[J].Journal of Engineering Mechanics-asce,2006,132(11):1252-1259.
[4] Lu Kunquan,Liu Jixing.Static and dynamic properties of granular matter(I)[J].Physics,2004,33(9):629-635.[陆坤权,刘寄星.颗粒物质(上)[J].物理,2004,33(9):629-635.]
[5] Han W S,Xia M F,Shen L T,et al.Statistical formulation and experimental determination of growth rate of micrometre cracks under impact loading[J].International Journal of Solids and Structs,1990,34(22):2905-2925.
[6] Han W S,Bai Y L.Embryo-damage induced nucleation of micro-cracks in an aluminium alloy under impact loading[J].Acta Metall Mater,1995,43(6):2157-2162.
[7] Ke F J,Bai Y L,Xia M F.Evolution of ideal micro-crack system[J].Science in China:Series A,1990,33(12):1447-1459.
[8] Bai Yilong,Wang Haiying,Xia Mengfen,et al.Statistical mesomechanics of solid,linking coupled multiple space and time scales[J].Advances in Mechanics,2006,36(2):286-305.[白以龙,汪海英,夏蒙棼,等.固体的统计细观力学-连接多个耦合的时空尺度[J].力学进展,2006,36(2):286-305.]
[9] Lei Shuye,Wang Liqun,Jia Lanqing,et al.Relationship between porosity and permeability of the particles packed bed[J].Journal of Tsinghua University:Science & Technology,1998,38(5):76-79.[雷树业,王利群,贾兰庆,等.颗粒床孔隙率与渗透率的关系[J].清华大学学报:自然科学版,1998,38(5):76-79.]
[10] Zhao Lijuan,Qin Yong.Experiment on improving the permeability of coal reservoir under ultrasound[J].Natural Gas Geoscience,2014,25(5):747-752.[赵丽娟,秦勇.超声波作用对改善煤储层渗透性的实验分析[J].天然气地球科学,2014,25(5):747-752.]
[11] Nield D A.Estimation of the stagnant thermal condu-ctivity of saturated porous media[J].International Journal of Heat Mass Transfer,1991,34(9):1793-1796.
[12] Nimick F B,Leith J R.A model for thermal conductivity of granular porous media[J].Journal of Heat Transfer,1992,114:2(2):506-508.
[13] Lei Shuye,Zheng Guanyu.Numerical simulation of heat andmass transfer in wet unsaturated porous media[J].Journal of Tsinghua University:Science & Technology,1997,37(2):86-90.[雷树业,郑贯宇.含湿多孔介质传热传质三参数渗流模型研究方法[J].清华大学学报:自然科学版,1997,37(2):86-90.]
[14] Sun Peide.Testing study on coal specimen permeability during solid deformation process[J].Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2001,20(supplement 1):1801-1804.[孙培德.变形过程中煤样渗透率变化规律的实验研究[J].岩石力学与工程学报,2001,20(增刊1):1801-1804.]
[15] Tang Jupeng,Pan Yishan,Li Chengquan,et al.Experimental study on effect of effective stress on desorption and seepage of coal bed methane[J].Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2006,25(8):1563-1568.[唐巨鹏,潘一山,李成全,等.有效应力对煤层气解吸渗流影响试验研究[J].岩石力学与工程学报,2006,25(8):1563-1568.]
[16] Gray I.Reservoir engineering in coal seams:Part 1-the physical process of gas storage and movement in coal seams[J].SPE Reservoir Engineering,1987,2(1):28-34.
[17] Harpalani S,Chen G.Effect of gas production on porosity and permeability of coal[C]//Symposium on Coalbed Methane Reserch and Development in Australia,Australia:James Cook University of North Queensland 1992:67.
[18] Harpalani S,Chen G.Estimation o f changes in fracture porosity of coal with gas emission[J].Fuel,1995,74(10):1491-1498.
[19] Seidle J P,JeansonneM W,Erickson D J.Application of Matchstick Geometry to Stress Dependent Permeability in Coals[C].SPE24361,1992.
[20] Palmer I,M ansoori J.How permeability depends on stress and pore pressure in coal beds:A new model[J].Society of Petroleum Engineers,1998,1(6):539-544.
[21] Shi J Q,Durucan S.Changes in permeability of coal beds during primary recovery:Part 1-model formation and analy sis [C]//Proceeding of the 2003 Coal bed Methane Symposium.Tuscaloosa A labama:University of A labama,2003.
[22] Deng Ze,Kang Yongshang,Liu Honglin,et al.Dynamic variation character of coal bed methane reservoir permeability during depletion[J].Journal of China Coal Society,2009,34(7):947-951.[邓泽,康永尚,刘洪林,等.开发过程中煤储层渗透率动态变化特征[J].煤炭学报,2009,34(7):947-951.]
[23] He Yulong,Yang Lizhong.Testing study on variational characteristics of rock mass permeability under loading unloading of confining pressure[J].Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2004,23(3):415-419.[贺玉龙,杨立中.围压升降过程中岩体渗透率变化特性的试验研究[J].岩石力学与工程学报,2004,23(3):415-419.]
[24] Meng Zhaoping,Hou Quanlin.Coupling model of stress-dependent permeability in high-rank coal reservoir and its control mechanism[J].Chinese Journal of Geophysics,2013,56(2):667-675.[孟召平,侯泉林.高煤级煤储层渗透性与应力耦合模型及控制机理[J].地球物理学报,2013,56(2):667-675.]
[25] Xiao Xiaochun,Pan Yishan,Lü Xiangfeng,et al.Mechanism of methane permeability enhance through ultrasonic irradiating on low permeable coal seam[J].Chinese Journal of Geophysics,2013,56(5):1726-1733.[肖晓春,潘一山,吕祥锋,等.超声激励低渗煤层甲烷增透机理[J].地球物理学报,2013,56(5):1726-1733.]
[26] Xiao Xiaochun,Xu Jun,Pan Yishan,et al.Experimental study of promoting methane desorption law in coal considering power ultrasound effect[J].Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2013,32(1):65-71.[肖晓春,徐军,潘一山,等.功率超声影响的煤中甲烷气促解规律实验研究[J].岩石力学与工程学报,2013,32(1):65-71.]
[27] Wang Bo,Jiang Bo,Wang Hongyan,et al.The coalbed methane reservoir physical simulation study of coal seam physical variation rule[J].Natural Gas Geoscience,2005,16(5):684-686.[王勃,江波,王红岩,等.煤层气储层渗透率变化规律的物理模拟实验研究[J].天然气地球科学,2005,16(5):684-686.]
[28] Wang Xiaomei,Zhang Qun,Zhang Peihe,et al.Aplication of coalbed methane reservoir simulation[J].Natural Gas Geoscience,2004,15(6):664-668.[王晓梅,张群,张培河,等.煤层气储层数值模拟研究的应用[J].天然气地球科学,2004,15(6):664-668.]
[29] Ma Feiying,Wang Yongqing,Wang Lin,et al.The permeability dynamic variation features of coals with the consideration of moisture content[J].Nature Gas Geoscience,2014,25(9):1477-1482.[马飞英,王永清,王林,等.考虑水分含量的煤岩渗透率动态变化特征[J].天然气地球科学,2014,25(9):1477-1482.]
[30] Shui H F,Lin C H,Zhang M,et al.Comparison of the associative structure of two different types of rich coals and their coking properties[J].Fuel,2010,89(7):1647-1653.
[31] Gulyaev V M,Barskiy V D,Rudnitskiy A G,et al.Group chemical composition of coal batch and reactivity of coke 3 Phase composition of the primary products of coal pyrolysis[J].Coke and Chemistry,2013,56(10):361-363.
[32] Fomenko E V,Anshits N N,Solov’ev L A,et al.Composition and structure of the shells of fly ash cenospheres from the combustion of coal of the Kuznetsk Basin[J].Solid Fuel Chemistry,2014,48(2):129-139.
[33] Jonathan P M,Vijayaragavan K,Enette L,et al.A review of the correlations of coal properties with elemental composition[J].Fuel Processing Technology,2014,121(5):104-113.
[34] Wang Zutong.Effect of composition,structure and property of coal on its conversion and preparation[J].Coal Conversion,1992,15(1):12-18.[王祖侗.煤的组成、结构和性质对煤转化和制备的影响[J].煤炭转化,1992,15(1):12-18.]
[35] Matthias W H.Recent progress in coal structure research[J].Fuel,1992,71(11):1211-1223.
[36] Li Hao.Damage Mechanics Fundamentals[M].Ji’nan:Shandong Science & Technology Press,1992.[李灏.损伤力学基础[M].济南:山东科学技术出版社,1992.]
[37] Du Gonghuan,Zhu Zhemin,Gong Xiufen.Acoustics Foundation[M].3rd edition.Nanjing:Nanjing University Press,2012.[杜功焕,朱哲民,龚秀芬.声学基础[M].第三版.南京:南京大学出版社,2012.]
[38] Bhushan B.Introduction to Tribology[M].Ge Shirong translated.Beijing:China Machine Press,2007.[(美)布尚B.摩擦学导论 [M].葛世荣译.北京:机械工业出版社,2007.]